* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Stars - Department of Physics and Astronomy
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Hayashi track wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
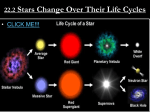
The Stars HNRT 227 Chapter 14 22 October 2015 Great Idea: The Sun and other stars use nuclear fusion reactions to convert mass into energy. Eventually, when a star’s nuclear fuel is depleted, the star must burn out. 1 Chapter Outline • • • • The Nature of Stars The Anatomy of Stars The Variety of Stars The Life Cycles of Stars 2 The Nature of Stars 3 The Nature of Stars • Astronomy – Oldest science (?) • Star – Ball of gas – Fusion reactor • All stars have a beginning and an ending 4 Measuring the Stars with Telescopes and Satellites • Electromagnetic radiation • Measurement of photons – – – – Wavelength Intensity Direction Variation 5 Telescopes 6 Orbiting Observatories • Great Observatories Program – Hubble Space Telescope – Spitzer Infrared Telescope – Chandra X-Ray Observatory 7 The Anatomy of Stars 8 The Structure of the Sun • Structure – – – – – – Stellar core Radiative zone Convection zone Photosphere Chromosphere Corona • Solar Wind – Stream of particles 9 Our Sun 10 More On Solar Structure • Hydrogen fusion takes place in a core extending from the Sun’s center to about 0.25 solar radius • The core is surrounded by a radiative zone extending to about 0.71 solar radius – In this zone, energy travels outward through radiative diffusion • The radiative zone is surrounded by a rather opaque convective zone of gas at relatively low temperature and pressure – In this zone, energy travels outward primarily through convection 11 How do we know the Sun’s interior? • Helioseismology is the study of how the Sun vibrates • These vibrations have been used to infer pressures, densities, chemical compositions, and rotation rates within the Sun 12 Magnetic Fields 13 Northern Lights (Aurora Borealis) 14 The Sun’s Energy Source: Fusion • • • Sun’s Energy Source – – Historical Current • hydrogen Fusion – 3-steps-hydrogen burning 1) P + P D + e+ + neutrino + energy 2) D + P 3He + photon + energy 3) 3He + 3He 4He + 2protons + photon + energy Life expectancy – 11-12 billion years 15 The Variety of Stars • Differences – Color – Brightness • Distance • Absolute brightness – Energy output – luminosity • Apparent brightness • Behavior – Total mass – age 16 The Cosmic Distance Ladder • Distance – Light-years • Measurement – Triangulation (parallax) – Spectroscopic parallax – Cepheid variable – Tully-Fisher – Supernovae Type Ia – Hubble’s Law 17 The Hertzsprung-Russel Diagram • Star Groupings – Main-sequence stars – Red giants – White dwarfs 18 Step 1 to an H-R Diagram 20 15 10 Absolute Magnitude • Plot for the 20 nearest and brightest stars to Earth Not an H-R Diagram 5 0 0 5000 10000 15000 20000 25000 30000 -5 -10 Temperature 19 Step 2 to an H-R Diagram • Reversing the y-axis Getting Closer to an H-R Diagram Temperature (K) -10 -5 Absolute Magnitude 0 5 10 15 20 0 5000 10000 15000 20000 25000 2030000 Step 3 to an H-R Diagram • Reversing the x-axis – Lowest temperature to the right Now it's looking Like an H-R Diagram Temperature (K) -10 -5 5 10 15 20 30000 25000 20000 15000 10000 5000 0 21 Absolute Magnitude 0 A Standard H-R Diagram 22 The Life Cycles of Stars 23 The Birth of Stars • Nebular Hypothesis – Laplace 24 The Main Sequence and the Death of Stars • Stars much less massive than the Sun – Glows 100 billion years • No change in size, temperature, energy output – Brown dwarfs • Some don’t consider these stars 25 The Main Sequence and the Death of Stars • Stars about the mass of the sun – Hydrogen burning at faster rate – – – – • Move off main sequence Helium burning Red giant Begin collapse White dwarf 26 The Life Cycle of a Star Like the Sun • • • • • • • • Gas cloud Fragmentation Protostar Kelvin-Helmholz contraction Hayashi Track Ignition Adjustment to Main Sequence Hydrogen Core Depletion • • • • • • • • Hydrogen shell burning Helium flash Helium core burning Helium core depletion Helium shell burning Helium shell flashes Planetary nebula White Dwarf 27 Sun’s Life Cycle on H-R Diagram H-R Diagram with annotations for Stellar Stages Temperature (log) 100000 10000 1000 -10 Planetary Nebula Asymptotic Branch Horizontal Branch Helium Flash -5 Kelvin-Helmholtz Contraction Adjust to Main Sequence 5 Absolute Magnitude 0 Sub Giant Hayashi Core Track Contraction 10 White Dwarf 15 28 20 The Main Sequence and the Death of Stars • Very Large Stars – Successive collapses and burnings – Iron core – Catastrophic collapse • supernova 29 Layers of Massive Star H -> He Layers of He -> C C -> O O -> Ne Ne -> Mg Nuclear Fusion Mg -> in High Mass Stars Si Si -> Fe Fe 30 Neutron Stars and Pulsars • Neutron Star – Dense and small – High rotation rate – Little light • Pulsar – Special neutron star – Electromagnetic radiation – End state of supernova 31 Black Holes • Black Hole – Result of collapsed large star – Nothing escapes from surface – Cannot “see” them • See impact on other stars, dust, etc. • Detect x-rays, gamma rays 32