How Far To That Star?
... the amount of red-shift in the star’s or galaxy’s light. • It is based on the assumption that due to the Big Bang the farther away an object is the greater its red-shift must be. • It is only usable for extremely distant objects (millions of LY away!). Astronomers use this method as a last resort du ...
... the amount of red-shift in the star’s or galaxy’s light. • It is based on the assumption that due to the Big Bang the farther away an object is the greater its red-shift must be. • It is only usable for extremely distant objects (millions of LY away!). Astronomers use this method as a last resort du ...
Lesson 3 Power Notes Outline
... White dwarfs shine for billions of years, becoming fainter as they cool. This is the final stage in the life cycle of low-mass stars. ...
... White dwarfs shine for billions of years, becoming fainter as they cool. This is the final stage in the life cycle of low-mass stars. ...
Exercise 9
... Introduction: By looking at an apparently flat background of stars at night or at a star chart printed on a page, we often forget about the three-dimensional nature of the universe. In this exercise, you will construct (with welding rods and Styrofoam balls) a model of nearby space including many of ...
... Introduction: By looking at an apparently flat background of stars at night or at a star chart printed on a page, we often forget about the three-dimensional nature of the universe. In this exercise, you will construct (with welding rods and Styrofoam balls) a model of nearby space including many of ...
VISIT TO NORMAN LOCKYER OBSERVATORY IN SIDMOUTH
... Ursa Major contains many interesting "deep sky" objects. The brightest, listed in Messier's Catalogue, are shown on the chart, but there are many fainter galaxies in the region too. In the upper right of the constellation are a pair of interacting galaxies M81 and M82 shown in the image below. M82 i ...
... Ursa Major contains many interesting "deep sky" objects. The brightest, listed in Messier's Catalogue, are shown on the chart, but there are many fainter galaxies in the region too. In the upper right of the constellation are a pair of interacting galaxies M81 and M82 shown in the image below. M82 i ...
Document
... Spectroscopy is a tool of astronomy in which the light produced by a star or other object (called its spectrum) is analyzed. ...
... Spectroscopy is a tool of astronomy in which the light produced by a star or other object (called its spectrum) is analyzed. ...
Issue 118 - Apr 2014
... for starting observing programs, h. However one of the most exciting stars in the sky is SS Cygni going from ~mag 12 to ~mag 8 in a few days. Eclipsing Binaries - These are not true variable stars like the ones listed above. They are binary star systems with the stars rotating in the same plane as o ...
... for starting observing programs, h. However one of the most exciting stars in the sky is SS Cygni going from ~mag 12 to ~mag 8 in a few days. Eclipsing Binaries - These are not true variable stars like the ones listed above. They are binary star systems with the stars rotating in the same plane as o ...
What is your wager?
... the actual luminosity (brightness) of the star; Apparent magnitude is how bright it appears to us on earth. ...
... the actual luminosity (brightness) of the star; Apparent magnitude is how bright it appears to us on earth. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Different clusters have different age • Observe stellar evolution by looking at stars of same age but different mass ...
... • Different clusters have different age • Observe stellar evolution by looking at stars of same age but different mass ...
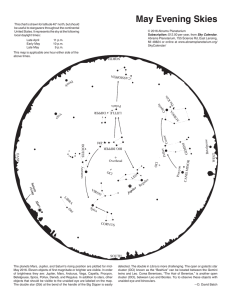
May Evening Skies
... The planets Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn's rising position are plotted for midMay 2016. Eleven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Mars, Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Procyon, Betelgeuse, Spica, Pollux, Deneb, and Regulus. In addition to stars, other ...
... The planets Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn's rising position are plotted for midMay 2016. Eleven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Mars, Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Procyon, Betelgeuse, Spica, Pollux, Deneb, and Regulus. In addition to stars, other ...
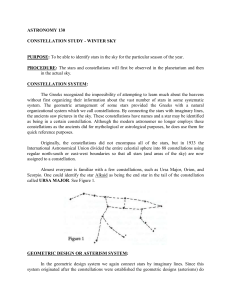
ASTRONOMY 130
... Major). These three constellations make good reference points for the winter sky. Look below and to the left of Betelgeuse you will see a line of three stars of almost equal brightness, this is the belt of Orion. Below this there is a dimmer line of stars "hanging" from the belt and this is the swor ...
... Major). These three constellations make good reference points for the winter sky. Look below and to the left of Betelgeuse you will see a line of three stars of almost equal brightness, this is the belt of Orion. Below this there is a dimmer line of stars "hanging" from the belt and this is the swor ...
Lab 5 Takehome
... twice as big in radius has four times higher luminosity (because the surface area of a sphere is 4πr2 ...
... twice as big in radius has four times higher luminosity (because the surface area of a sphere is 4πr2 ...
Events - Temecula Valley Astronomers
... numbers, and why are there negative (or minus) magnitudes? The answer to the first question begins with the origin of the magnitude system. Claudius Ptolemaeus of Alexandria, usually just called Ptolemy (but Ptolemy was a clan; Cleopatra was a Ptolemy), published a book of everything he knew about t ...
... numbers, and why are there negative (or minus) magnitudes? The answer to the first question begins with the origin of the magnitude system. Claudius Ptolemaeus of Alexandria, usually just called Ptolemy (but Ptolemy was a clan; Cleopatra was a Ptolemy), published a book of everything he knew about t ...
Grand Tour Worksheet - School District of La Crosse
... 1. WHEN WAS THE LAST VISIT FOR HALLEY’S COMET? 2. Comets mat very well be what? 3. Are new comets predictable? 4. How often does Halley’s Comet return? 5. Where does Halley’s spend most of its time? 6. How long has Halley’s been observed? ...
... 1. WHEN WAS THE LAST VISIT FOR HALLEY’S COMET? 2. Comets mat very well be what? 3. Are new comets predictable? 4. How often does Halley’s Comet return? 5. Where does Halley’s spend most of its time? 6. How long has Halley’s been observed? ...
doc - EU-HOU
... In this exercise, we explain how an invisible companion orbiting its parent star can be detected using precise measurement of the star’s velocity. The radial-velocity method uses the fact that a star with a companion will be in orbit around the center of mass of the system. The goal is thus to measu ...
... In this exercise, we explain how an invisible companion orbiting its parent star can be detected using precise measurement of the star’s velocity. The radial-velocity method uses the fact that a star with a companion will be in orbit around the center of mass of the system. The goal is thus to measu ...
COM 2014 January
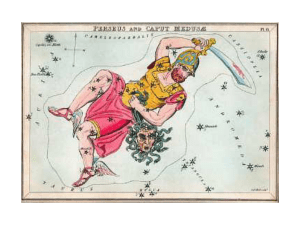
... with his fondness for mortal women. He entered her prison and Perseus (per Zeus, sired by Zeus) was the result. Dismayed, Acrisius put his daughter and her child into a wooden chest and set them adrift on the high seas. But luck smiled upon them and they eventually reached the island of Seriphos, wh ...
... with his fondness for mortal women. He entered her prison and Perseus (per Zeus, sired by Zeus) was the result. Dismayed, Acrisius put his daughter and her child into a wooden chest and set them adrift on the high seas. But luck smiled upon them and they eventually reached the island of Seriphos, wh ...
TAP 702- 6: Binary stars - Teaching Advanced Physics
... shifts are due to stars moving away from Earth, blue shifts are due to stars ...
... shifts are due to stars moving away from Earth, blue shifts are due to stars ...
luminosity1
... • To figure out the total luminosity being emitted by the box, we would need to multiply the luminosity of one side by 6. This is because there are six sides of the cube for the energy to escape from. ...
... • To figure out the total luminosity being emitted by the box, we would need to multiply the luminosity of one side by 6. This is because there are six sides of the cube for the energy to escape from. ...
Volume 20 Number 10 September 2012
... In 2010, observers reported the most massive stars ever seen, - it exceeded what many astronomers thought was a maximum about 150 times the mass of the Sun. The heavyweight champs resided 160,000 light-years from Earth in Radcliffe 136, a dense star cluster within the Large Magellanic Cloud, the bri ...
... In 2010, observers reported the most massive stars ever seen, - it exceeded what many astronomers thought was a maximum about 150 times the mass of the Sun. The heavyweight champs resided 160,000 light-years from Earth in Radcliffe 136, a dense star cluster within the Large Magellanic Cloud, the bri ...
Stages of stars - University of Dayton
... The color of a star is determined by its temperature Hottest stars are blue and the coolest are red Nuclear fusion in the stars core produces the star’s energy Brightness is measured in magnitude (the brighter the star, the lower the magnitude) ...
... The color of a star is determined by its temperature Hottest stars are blue and the coolest are red Nuclear fusion in the stars core produces the star’s energy Brightness is measured in magnitude (the brighter the star, the lower the magnitude) ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.