Winter Stargazing - Trimble County Schools
... Distance-11.4 LY Diameter-2.8 Million km Luminosity-7 Suns It is the eighth brightest star in the sky, only four LY away from Sirius. • It is also a double star, revolved by a white dwarf, Procyon B. • The name means “before the dog” because it rises in the east well before Sirius. ...
... Distance-11.4 LY Diameter-2.8 Million km Luminosity-7 Suns It is the eighth brightest star in the sky, only four LY away from Sirius. • It is also a double star, revolved by a white dwarf, Procyon B. • The name means “before the dog” because it rises in the east well before Sirius. ...
1 - Stellar Life Cycle
... center of the new star, this heats stops the rest of the star from collapsing. The balance between gravity trying to make the star shrink and heat holding it up is called Thermodynamic Equilibrium. The star then stays almost exactly the same for a long time (about 10 billion years for a star lik ...
... center of the new star, this heats stops the rest of the star from collapsing. The balance between gravity trying to make the star shrink and heat holding it up is called Thermodynamic Equilibrium. The star then stays almost exactly the same for a long time (about 10 billion years for a star lik ...
Star Formation
... and spend most of their lives • Once on the main sequence, a star stays in the same location on the H-R diagram until it runs out of fuel and begins to die ...
... and spend most of their lives • Once on the main sequence, a star stays in the same location on the H-R diagram until it runs out of fuel and begins to die ...
THE LIFE CYCLES OF STARS (3)
... into classes of brightness. The brightest stars were called first magnitude, the somewhat dimmer stars were second magnitude, even dimmer were third magnitude, down to sixth magnitude which were the faintest stars visible. ( We have to remember these early astronomers suffered the same eye defects a ...
... into classes of brightness. The brightest stars were called first magnitude, the somewhat dimmer stars were second magnitude, even dimmer were third magnitude, down to sixth magnitude which were the faintest stars visible. ( We have to remember these early astronomers suffered the same eye defects a ...
Searching for planets around evolved stars with COROT
... possibility of using COROT also to search planets around evolved stars. The main goal of this project is the search for planetary systems orbiting solar-type evolved stars, namely stars with solar metallicity and masses around 1-3 solar mass, at different evolutionary stages, from the turn-off to th ...
... possibility of using COROT also to search planets around evolved stars. The main goal of this project is the search for planetary systems orbiting solar-type evolved stars, namely stars with solar metallicity and masses around 1-3 solar mass, at different evolutionary stages, from the turn-off to th ...
bbColors
... account the size of and distance to the star. So in truth, we are missing a term of R2 /r2 , where R is the radius of the star, and r is the distance to the star (the 4π’s cancel out, obviously). Since we are only measuring magnitude differences in each filter, this term can be separated (by logarit ...
... account the size of and distance to the star. So in truth, we are missing a term of R2 /r2 , where R is the radius of the star, and r is the distance to the star (the 4π’s cancel out, obviously). Since we are only measuring magnitude differences in each filter, this term can be separated (by logarit ...
Protostars and planets
... known were those in the Solar System: the most massive of them is only MJupiter ≈ 10−3 M⊙ , and there are many of them follow approximately circular orbits about the Sun (indeed “planet” comes from Greek “wanderer” because planets appear to move through the fixed stars). Classifications based on mas ...
... known were those in the Solar System: the most massive of them is only MJupiter ≈ 10−3 M⊙ , and there are many of them follow approximately circular orbits about the Sun (indeed “planet” comes from Greek “wanderer” because planets appear to move through the fixed stars). Classifications based on mas ...
constellations - Otterbein University
... - constellation shapes and names - star names and position in constellation - deep sky objects’ names and position • Quiz: You will be asked to find these objects on a star map. ...
... - constellation shapes and names - star names and position in constellation - deep sky objects’ names and position • Quiz: You will be asked to find these objects on a star map. ...
Astronomy of the Northern Sky—
... from its own gravity, and starts to spin, it contracts and forms a disk with a thicker center where the star itself forms. The disk likely forms smaller, non-energy producing, non-glowing bodies—planets—with moons, comets and other small bodies around them. What kind of star? All depends on the mass ...
... from its own gravity, and starts to spin, it contracts and forms a disk with a thicker center where the star itself forms. The disk likely forms smaller, non-energy producing, non-glowing bodies—planets—with moons, comets and other small bodies around them. What kind of star? All depends on the mass ...
Wednesday, April 17 - Otterbein University
... intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
... intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
There are 88 constellations in the sky around the Earth. 12 are the
... Hercules and Leo took place. After killing the lion, Hercules wore its skin as his symbol. : an early Arab constellation called Asad, the lion, actually stretched over a much larger portion of the sky then present day Leo. It included stars from Gemini through Libra and as far north as Ursa Major an ...
... Hercules and Leo took place. After killing the lion, Hercules wore its skin as his symbol. : an early Arab constellation called Asad, the lion, actually stretched over a much larger portion of the sky then present day Leo. It included stars from Gemini through Libra and as far north as Ursa Major an ...
The Magnitude Scale
... The scale below is given as an instructive tool, to give a general idea of how the magnitude scale works. The scale below is intended to be roughly visual; the human eye's (dark-adapted) detection efficiency peaks around 495 nanometers, while the formal photoelectric V peak (a filtered band intended ...
... The scale below is given as an instructive tool, to give a general idea of how the magnitude scale works. The scale below is intended to be roughly visual; the human eye's (dark-adapted) detection efficiency peaks around 495 nanometers, while the formal photoelectric V peak (a filtered band intended ...
Solutions3
... Problem 1: The star Mizar in the Big Dipper was the first binary system to be observed (Benedetto Castelli asked Galileo to observe it in 1617, presumably to confirm his observations of this double star)–though not the first where orbital motion was observed. The parallax angle to Mizar is 4.2 × 10− ...
... Problem 1: The star Mizar in the Big Dipper was the first binary system to be observed (Benedetto Castelli asked Galileo to observe it in 1617, presumably to confirm his observations of this double star)–though not the first where orbital motion was observed. The parallax angle to Mizar is 4.2 × 10− ...
your star chart here - Australasian Science Magazine
... the 15th the Moon is next to Jupiter. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 8th. The two brightest stars in the night sky can also be seen; Sirius in the constellation Canis Major is the brightest star followed ...
... the 15th the Moon is next to Jupiter. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 8th. The two brightest stars in the night sky can also be seen; Sirius in the constellation Canis Major is the brightest star followed ...
Stars - RSM Home
... • When a neutron star is rapidly spinning, it is called PULSAR. It emits rapid pulses of radio waves and optical energy. • This is Pulsar B1509. It is spinning so rapidly(7 rotations/sec), 12 miles wide, it creates a hand-shaped nebula ...
... • When a neutron star is rapidly spinning, it is called PULSAR. It emits rapid pulses of radio waves and optical energy. • This is Pulsar B1509. It is spinning so rapidly(7 rotations/sec), 12 miles wide, it creates a hand-shaped nebula ...
chapter 7
... Note: These are apparent magnitudes because they are an attempt to measure brightness as seen from Earth. Furthermore, they are apparent visual magnitudes, since the human eye only detects or is sensitive to a limited portion of all the radiations emitted by an object. This portion is called the vi ...
... Note: These are apparent magnitudes because they are an attempt to measure brightness as seen from Earth. Furthermore, they are apparent visual magnitudes, since the human eye only detects or is sensitive to a limited portion of all the radiations emitted by an object. This portion is called the vi ...
AST 207 Test 2 26 October 2011
... a. (1 pt.) The sun and solar system are 4.5 Byr old. Approximately how much longer will the sun be small enough so as not to engulf Earth? The sun will be a main-sequence star for 10 Byr, and then it becomes a giant, which engulfs Earth. Therefore the sun will stay small for another 5 Byr. b. (2 pts ...
... a. (1 pt.) The sun and solar system are 4.5 Byr old. Approximately how much longer will the sun be small enough so as not to engulf Earth? The sun will be a main-sequence star for 10 Byr, and then it becomes a giant, which engulfs Earth. Therefore the sun will stay small for another 5 Byr. b. (2 pts ...
October 2013
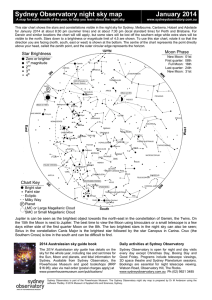
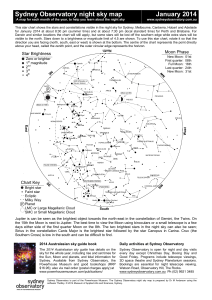
... and is typical of areas where new stars can form. Between the Scorpion and the Centaur are the Altar, the Level and the Wolf, while to the east of the Milky Way stretches a great expanse of sky with relatively few bright stars, dominated by birds and 'water constellations'. In the south these includ ...
... and is typical of areas where new stars can form. Between the Scorpion and the Centaur are the Altar, the Level and the Wolf, while to the east of the Milky Way stretches a great expanse of sky with relatively few bright stars, dominated by birds and 'water constellations'. In the south these includ ...
Superwind - The University of Sydney
... headlights on a car in Australia. This extreme resolution made it possible to resolve the red giant stars, and to see the shells ejected by their winds. Stars like the Sun end their lives with a ‘superwind’, 100 million times stronger than the solar wind. This wind lasts over a period of 10,000 year ...
... headlights on a car in Australia. This extreme resolution made it possible to resolve the red giant stars, and to see the shells ejected by their winds. Stars like the Sun end their lives with a ‘superwind’, 100 million times stronger than the solar wind. This wind lasts over a period of 10,000 year ...
star
... brightness. Other important properties of stars include their chemical composition and mass. ...
... brightness. Other important properties of stars include their chemical composition and mass. ...
PDF version (two pages, including the full text)
... Alphard, heart of the serpent, high in the northwest. Above and to the left of the Crow, for an observer facing east, is the Cup. Alphard is an Arabic name meaning the ‘solitary one’, as there are no other bright stars near it. At about 40 times the diameter of the sun and 400 times as bright, Alpha ...
... Alphard, heart of the serpent, high in the northwest. Above and to the left of the Crow, for an observer facing east, is the Cup. Alphard is an Arabic name meaning the ‘solitary one’, as there are no other bright stars near it. At about 40 times the diameter of the sun and 400 times as bright, Alpha ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.