formation of stars
... In a stable state a star’s diameter and radiation remain constant for billions of years. When so many of the core’s light nuclei are used up that the energy of fusion no longer balances the force of gravity the star loses its stability. When the star loses its stability the centre of the star contra ...
... In a stable state a star’s diameter and radiation remain constant for billions of years. When so many of the core’s light nuclei are used up that the energy of fusion no longer balances the force of gravity the star loses its stability. When the star loses its stability the centre of the star contra ...
Lars Bildsten - nnpss
... The luminosity of the star is determined by heat transport, since the core is hot, and the surface is cold (VACUUM!). Unlike in your house, the heat is transported by diffusion of photons, which have a mean free path l, giving: ...
... The luminosity of the star is determined by heat transport, since the core is hot, and the surface is cold (VACUUM!). Unlike in your house, the heat is transported by diffusion of photons, which have a mean free path l, giving: ...
Astronomy and Space Science
... But by definition this M is also the absolute magnitude. More: In the real world, it is necessary to specify what type of EM radiation is being measured, for example a star may have very different UV, visible, IR, etc. magnitudes. Color index B-V is the difference in magnitudes of a star by blue and ...
... But by definition this M is also the absolute magnitude. More: In the real world, it is necessary to specify what type of EM radiation is being measured, for example a star may have very different UV, visible, IR, etc. magnitudes. Color index B-V is the difference in magnitudes of a star by blue and ...
Sample final exam
... • the position of the Sun currently (should line up with marks on both axes) • the path of the Sun’s evolution from protostar to main sequence star • the path of the Sun’s evolution from main sequence star to its helium flash Calculation section Choose one of the following problems; select the appro ...
... • the position of the Sun currently (should line up with marks on both axes) • the path of the Sun’s evolution from protostar to main sequence star • the path of the Sun’s evolution from main sequence star to its helium flash Calculation section Choose one of the following problems; select the appro ...
White Dwarf Stars Near The Earth
... the “ages” of the white dwarfs on this page, I mean how long they have been white dwarfs, not how long they were main-sequence stars before that.) 40 Eridani B is a member of a triple star system and was once the brightest and most massive of the three, since the other two are relatively cool K-clas ...
... the “ages” of the white dwarfs on this page, I mean how long they have been white dwarfs, not how long they were main-sequence stars before that.) 40 Eridani B is a member of a triple star system and was once the brightest and most massive of the three, since the other two are relatively cool K-clas ...
27.1: Characteristics of Stars
... About 3 billion can be seen through ground-based telescopes Over 1 trillion can be observed from the Hubble Space Telescope The visibility of a star depends on its brightness and its distance from the Earth. Astronomers use two scales to describe the brightness of a star: apparent magnitude and abso ...
... About 3 billion can be seen through ground-based telescopes Over 1 trillion can be observed from the Hubble Space Telescope The visibility of a star depends on its brightness and its distance from the Earth. Astronomers use two scales to describe the brightness of a star: apparent magnitude and abso ...
AST 1010 Quiz questions
... across the sky and set in the west on a daily basis. Quiz 2. 1. The orbital period of an object in the Kuiper belt is 845 years. Calculate the average distance of this object from the Sun. 2. The orbital period of the planet Neptune is 164.8 years. Calculate the average distance of Neptune from the ...
... across the sky and set in the west on a daily basis. Quiz 2. 1. The orbital period of an object in the Kuiper belt is 845 years. Calculate the average distance of this object from the Sun. 2. The orbital period of the planet Neptune is 164.8 years. Calculate the average distance of Neptune from the ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... If you measure a star's apparent magnitude and know its absolute magnitude, you can find the star's distance (using the inverse square law of light brightness). If you know a star's apparent magnitude and distance, you can find the star's luminosity A star can be luminous because it is hot or it is ...
... If you measure a star's apparent magnitude and know its absolute magnitude, you can find the star's distance (using the inverse square law of light brightness). If you know a star's apparent magnitude and distance, you can find the star's luminosity A star can be luminous because it is hot or it is ...
Stars Chapter 21
... that astronomers use • Uses of H-R Diagram – Classify Stars – Understand how stars change over time ...
... that astronomers use • Uses of H-R Diagram – Classify Stars – Understand how stars change over time ...
Stars - PAMS-Doyle
... Motion of Stars • They rotate on an axis • They may revolve around another star • They move toward or away from our solar system. • The Doppler Effect can determine their direction…works just like sound in the apparent shift because of motion! ...
... Motion of Stars • They rotate on an axis • They may revolve around another star • They move toward or away from our solar system. • The Doppler Effect can determine their direction…works just like sound in the apparent shift because of motion! ...
Stellar Evolution
... layers of the star are now pushed outward. The star expands to larger than it ever was during its lifetime a few to about a hundred times bigger. ...
... layers of the star are now pushed outward. The star expands to larger than it ever was during its lifetime a few to about a hundred times bigger. ...
Lecture 13
... • These stars have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • They may be fusing He to Carbon in their core or fusing H to He in shell outside the core … but there is no H to He fusion in the core. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hyd ...
... • These stars have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • They may be fusing He to Carbon in their core or fusing H to He in shell outside the core … but there is no H to He fusion in the core. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hyd ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 •
... • Measuring the masses of stars • Measuring the sizes (radii) of stars ...
... • Measuring the masses of stars • Measuring the sizes (radii) of stars ...
BV Color Index and Temperature - The University of Texas at Dallas
... • B-V color index way of quantifying this - determining spectral class using two different filters Ø one a blue (B) filter that only lets a narrow range of colors or wavelengths through centered on the blue colors, Ø and a “visual” (V) filter that only lets the wavelengths close to the ...
... • B-V color index way of quantifying this - determining spectral class using two different filters Ø one a blue (B) filter that only lets a narrow range of colors or wavelengths through centered on the blue colors, Ø and a “visual” (V) filter that only lets the wavelengths close to the ...
Galaxies - C. Levesque
... sequence where it is stable and consistent. • A cooler smaller star like our sun can last for about 8 billion years • Fast burning blue stars only last for a million years ...
... sequence where it is stable and consistent. • A cooler smaller star like our sun can last for about 8 billion years • Fast burning blue stars only last for a million years ...
Milky Way - Wayne Hu`s Tutorials
... • Combined with the angular position on the sky, the 3d position of the star can be measured - mapping the galaxy • Use the star counts to determine statistical properities: number density of stars in each patch of sky • A fall off in the number density in radial distance would determine the edge of ...
... • Combined with the angular position on the sky, the 3d position of the star can be measured - mapping the galaxy • Use the star counts to determine statistical properities: number density of stars in each patch of sky • A fall off in the number density in radial distance would determine the edge of ...
Star Life Cycle
... Gravity is so strong, light cannot escape. Makes it look like a dark hole in space. If the star's remaining mass is greater than three times the mass of the Sun, the star contracts tremendously and becomes a black hole ...
... Gravity is so strong, light cannot escape. Makes it look like a dark hole in space. If the star's remaining mass is greater than three times the mass of the Sun, the star contracts tremendously and becomes a black hole ...
Stellar Distances - Red Hook Central School District
... Beyond 10 Mpc, it’s hard to distinguish a bright far star from a dimmer closer star. A “standard candle” is a star of known L in a cluster. We can then compare it with other stars in the same galaxy or cluster to determine the luminosity of other stars. ...
... Beyond 10 Mpc, it’s hard to distinguish a bright far star from a dimmer closer star. A “standard candle” is a star of known L in a cluster. We can then compare it with other stars in the same galaxy or cluster to determine the luminosity of other stars. ...
Sun, Stars, HR Diagram
... white dwarf B) to shrink to a white dwarf then eventually expand to a red giant C) become hotter and expand into a blue supergiant D) to become a black hole 17. By using a spectroscope an astronomer can A) B) C) D) ...
... white dwarf B) to shrink to a white dwarf then eventually expand to a red giant C) become hotter and expand into a blue supergiant D) to become a black hole 17. By using a spectroscope an astronomer can A) B) C) D) ...
The Sun and Stars The Sun is a typical star with a mass of about 2
... away appears 100 time less bright. The brightness is sometimes expressed not in Watt/m2 but in magnitudes. The magnitude of Sirius (the brightest star in our sky) is -1.46, of Canopus -0.72, of Vega 0.04, of Deneb 1.26,. . . more or less according to an ancient scale developed by Hipparchus. Each st ...
... away appears 100 time less bright. The brightness is sometimes expressed not in Watt/m2 but in magnitudes. The magnitude of Sirius (the brightest star in our sky) is -1.46, of Canopus -0.72, of Vega 0.04, of Deneb 1.26,. . . more or less according to an ancient scale developed by Hipparchus. Each st ...
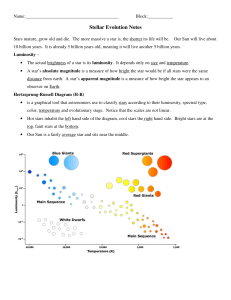
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
Hubble`s Law is the relation between the recession velocity of a
... Stars on the main sequence are lined up according to luminosity. But the more luminous a star is, the more massive it is. And the more massive a star is, the quicker it burns its hydrogen, and therefore the shorter its lifetime. The stars in a cluster are all formed at the same time. Since the more ...
... Stars on the main sequence are lined up according to luminosity. But the more luminous a star is, the more massive it is. And the more massive a star is, the quicker it burns its hydrogen, and therefore the shorter its lifetime. The stars in a cluster are all formed at the same time. Since the more ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.