Redshift - Old Age and Red Giants
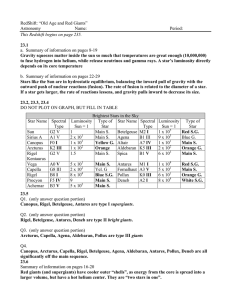
... cooler. But the core is highly compressed where helium is made. Q11. Aldebaran (K5 III) and Pollux (K0 III) are orange giants that will cool into red giants like the sun. 23.8 (OMIT THIS SECTION) Q12. Q13. Q14. Q15. Q16. Conclusion Describe what you learned about the path a star takes after it moves ...
... cooler. But the core is highly compressed where helium is made. Q11. Aldebaran (K5 III) and Pollux (K0 III) are orange giants that will cool into red giants like the sun. 23.8 (OMIT THIS SECTION) Q12. Q13. Q14. Q15. Q16. Conclusion Describe what you learned about the path a star takes after it moves ...
File - Awakening in Grade 6
... called the plane of the ecliptic (or just the ecliptic). The zodiac is the group (or “belt”) of constellations that fall along the plane of the ecliptic. It is through these constellations that our Sun appears to “pass” during the year. While there are 12 astrological constellations of the zodiac, t ...
... called the plane of the ecliptic (or just the ecliptic). The zodiac is the group (or “belt”) of constellations that fall along the plane of the ecliptic. It is through these constellations that our Sun appears to “pass” during the year. While there are 12 astrological constellations of the zodiac, t ...
Stellar Evolution – Test Review Answers
... Nearly in the middle of both the temperature and luminosity scales relative to other stars. This puts it around the middle of the main sequence. 17. Where are giant stars, supergiant stars and white dwarfs found on the H-R diagram, relative to the main sequence? Giant and supergiant stars lie above ...
... Nearly in the middle of both the temperature and luminosity scales relative to other stars. This puts it around the middle of the main sequence. 17. Where are giant stars, supergiant stars and white dwarfs found on the H-R diagram, relative to the main sequence? Giant and supergiant stars lie above ...
Back to basics: naked-eye astronomical observation
... a scale (logarithmic to match the nonlinear response of the eye) for their ‘magnitude’ as apparent to us on the Earth’s surface. The smaller the number the brighter the object. Most well known constellations will have 0 or 1st magnitude stars. A few objects will be seen even earlier as the Sun sets— ...
... a scale (logarithmic to match the nonlinear response of the eye) for their ‘magnitude’ as apparent to us on the Earth’s surface. The smaller the number the brighter the object. Most well known constellations will have 0 or 1st magnitude stars. A few objects will be seen even earlier as the Sun sets— ...
3. Stellar Formation and Evolution
... the star's core starts to collapse and heat up. This causes the outer layers of the star to expand and cool, similar to the process that occurred after the star ran out of hydrogen fuel and left the main sequence. As the star becomes larger and larger, it eventually becomes a red supergiant. • Extre ...
... the star's core starts to collapse and heat up. This causes the outer layers of the star to expand and cool, similar to the process that occurred after the star ran out of hydrogen fuel and left the main sequence. As the star becomes larger and larger, it eventually becomes a red supergiant. • Extre ...
Orion - Starry Starry Night!
... Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the northern hemisphere's winter sky. It is one of the oldest constellations, dating back to at least the Early Bronze Age when it marked the location of the Sun during the spring equinox. Taurus hosts two of the nearest open clusters to Earth, the Pl ...
... Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the northern hemisphere's winter sky. It is one of the oldest constellations, dating back to at least the Early Bronze Age when it marked the location of the Sun during the spring equinox. Taurus hosts two of the nearest open clusters to Earth, the Pl ...
Small Wonders: Ursa Minor
... from the showing true north. Not only that, but the relationship between North and the North Star is constantly changing. Because of a phenomenon known as precession, (basically a wobble of earth along it's axis - much like a top) the northern pole carves out a 47 degree diameter circle on the nigh ...
... from the showing true north. Not only that, but the relationship between North and the North Star is constantly changing. Because of a phenomenon known as precession, (basically a wobble of earth along it's axis - much like a top) the northern pole carves out a 47 degree diameter circle on the nigh ...
Chapter 26 Book Questions
... Hubble’s Law (pages 852–853) 22. True or false? The apparent change in frequency and wavelength of a wave as it moves towards or away from an observer is known as the Doppler effect. __________________ 23. How can astronomers use the Doppler effect? ______________________________________________ ___ ...
... Hubble’s Law (pages 852–853) 22. True or false? The apparent change in frequency and wavelength of a wave as it moves towards or away from an observer is known as the Doppler effect. __________________ 23. How can astronomers use the Doppler effect? ______________________________________________ ___ ...
Characteristics of Stars (Ph)
... Imagine you could travel to the stars at the speed of light. To travel from Earth to the sun would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet the next nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is much farther away—a trip to Proxima Centauri would take 4.2 years! Most stars are much fart ...
... Imagine you could travel to the stars at the speed of light. To travel from Earth to the sun would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet the next nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is much farther away—a trip to Proxima Centauri would take 4.2 years! Most stars are much fart ...
Study Guide: Unit 1, The Universe and its Stars, HS
... 13) HS-ESS1-1 As _____________ shrinks, gravitational energy is converted into energy of motion, or heat energy, and the mass of contracting gases slowly heats up. A) interstellar clouds B) quasars C) solar winds D) milky way galaxies E) plages 14) HS-ESS1-2 One of the most common units used to expr ...
... 13) HS-ESS1-1 As _____________ shrinks, gravitational energy is converted into energy of motion, or heat energy, and the mass of contracting gases slowly heats up. A) interstellar clouds B) quasars C) solar winds D) milky way galaxies E) plages 14) HS-ESS1-2 One of the most common units used to expr ...
A Star is “Born,” and then How Will it Move
... Young (Embedded) Clusters: Very young (<10 Myr-old) groups of young stars that form together. Future binding depends on cluster mass & velocity, seems that 90% dissolve before ~10 Myr (Lada & Lada 2003). When they unbind but are still seen to move together, they’re known as a “stellar association.” ...
... Young (Embedded) Clusters: Very young (<10 Myr-old) groups of young stars that form together. Future binding depends on cluster mass & velocity, seems that 90% dissolve before ~10 Myr (Lada & Lada 2003). When they unbind but are still seen to move together, they’re known as a “stellar association.” ...
Basic properties of stars
... This is data for NGC 2482. It is about 400 million years old. Stars considerably right of the main sequence are more distant giants. ...
... This is data for NGC 2482. It is about 400 million years old. Stars considerably right of the main sequence are more distant giants. ...
Pretest
... inner solar system, most gases escaped the gravity of planets forming in this region, causing the inner planets to be rocky. The outer solar system, being farther from the sun, was cooler. As a result, planets forming in this region were able to capture gases and so became gas giants. ...
... inner solar system, most gases escaped the gravity of planets forming in this region, causing the inner planets to be rocky. The outer solar system, being farther from the sun, was cooler. As a result, planets forming in this region were able to capture gases and so became gas giants. ...
Star Classification Lab
... In bold letters, label the following regions of your Hertzsprung-Russell diagram: White Dwarfs, Red Dwarfs, Red Giants, Main Sequence Stars, and Blue Supergiants. ...
... In bold letters, label the following regions of your Hertzsprung-Russell diagram: White Dwarfs, Red Dwarfs, Red Giants, Main Sequence Stars, and Blue Supergiants. ...
Brichler-powerpoint
... HertzsprungWhat’s an H-R Russell diagram, and it is Diagram? used to show the relationship between the surface temperature and the absolute brightness of stars. • (see page 114) ...
... HertzsprungWhat’s an H-R Russell diagram, and it is Diagram? used to show the relationship between the surface temperature and the absolute brightness of stars. • (see page 114) ...
Learning Objectives Weeks 9-11 . 1. Know that star birth can begin
... Novae and thermonuclear supernovae both occur in close binary systems with a white dwarf, but a while a nova can recur a supernova is a one-shot event. 17. Like a white dwarf, a neutron star has an upper limit on its mass. For a neutron star to collapse, gravity must overwhelm both degeneracy pressu ...
... Novae and thermonuclear supernovae both occur in close binary systems with a white dwarf, but a while a nova can recur a supernova is a one-shot event. 17. Like a white dwarf, a neutron star has an upper limit on its mass. For a neutron star to collapse, gravity must overwhelm both degeneracy pressu ...
Starlight & Stars - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... The Doppler effect doesn’t affect the overall color of an object, unless it is moving at a significant fraction of the speed of light (VERY fast!) For an object moving toward us, the red colors will be shifted to the orange and the near-infrared will be shifted to the red, etc. All of the colors shi ...
... The Doppler effect doesn’t affect the overall color of an object, unless it is moving at a significant fraction of the speed of light (VERY fast!) For an object moving toward us, the red colors will be shifted to the orange and the near-infrared will be shifted to the red, etc. All of the colors shi ...
Stars and Temperature and Color
... The star’s distance from Earth The density of the star’s core The luminosity of the star ...
... The star’s distance from Earth The density of the star’s core The luminosity of the star ...
File - greenscapes4you
... Most stars fall along the main sequence – upper left to lower right. These stars fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores and have a wide range of life spans, which depend on their mass. Higher mass stars on main sequence have shorter life spans. A star has a limited supply of core hydrogen and ther ...
... Most stars fall along the main sequence – upper left to lower right. These stars fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores and have a wide range of life spans, which depend on their mass. Higher mass stars on main sequence have shorter life spans. A star has a limited supply of core hydrogen and ther ...
Slide 1
... 2. Birth: A star is born when its cores temperature reaches 10 million K. This happens for masses > 0.08 M(Sun). --the star blasts away its womb of dust and shines. --T Tauri Stars: variable brightness (like contractions). Low mass stars just about to move to the main sequence. ...
... 2. Birth: A star is born when its cores temperature reaches 10 million K. This happens for masses > 0.08 M(Sun). --the star blasts away its womb of dust and shines. --T Tauri Stars: variable brightness (like contractions). Low mass stars just about to move to the main sequence. ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... • Star expels outermost layers as Planetary Nebulae • Inert core left as white dwarf • Dwarf has such tiny surface area it takes billions of years to cool • Coolest (oldest?) known: 3900 K ...
... • Star expels outermost layers as Planetary Nebulae • Inert core left as white dwarf • Dwarf has such tiny surface area it takes billions of years to cool • Coolest (oldest?) known: 3900 K ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.