Due April 2 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... 3. Why do sunspots appear darker than their surroundings? (a) They are cooler than their surroundings. (b) They block some sunlight. (c) They do not emit any light. 4. If the star Alpha Centauri were moved to a distance 10 times greater than its actual distance, its parallax angle would (a) get larg ...
... 3. Why do sunspots appear darker than their surroundings? (a) They are cooler than their surroundings. (b) They block some sunlight. (c) They do not emit any light. 4. If the star Alpha Centauri were moved to a distance 10 times greater than its actual distance, its parallax angle would (a) get larg ...
65008_StarFinderPart2
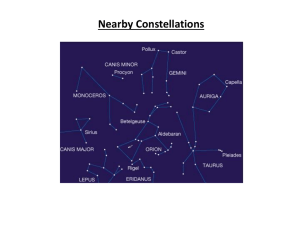
... What unique feature can be easily found in the Big Dipper, aka Ursa Major? In what other constellation might you find a double star? ...
... What unique feature can be easily found in the Big Dipper, aka Ursa Major? In what other constellation might you find a double star? ...
Document
... predictable curve. – Initial brightness increase followed by a slowly decaying “tail” ...
... predictable curve. – Initial brightness increase followed by a slowly decaying “tail” ...
Chapter20
... This effect, called framedragging, is most prominent near massive, fast spinning objects. Matter in this system gets caught up and spun around the black hole. Such discoveries help scientists better understand gravity itself. ...
... This effect, called framedragging, is most prominent near massive, fast spinning objects. Matter in this system gets caught up and spun around the black hole. Such discoveries help scientists better understand gravity itself. ...
binary stars - El Camino College
... Two-thirds of all stars are part of multiple star systems, where two or more stars are born at the same time from the same gas cloud. Only about 30% of all stars are single, like the Sun. The distances between companion stars ranges from less than 10 million miles (0.1 AU), to over 10,000 AU. Simila ...
... Two-thirds of all stars are part of multiple star systems, where two or more stars are born at the same time from the same gas cloud. Only about 30% of all stars are single, like the Sun. The distances between companion stars ranges from less than 10 million miles (0.1 AU), to over 10,000 AU. Simila ...
–1– Order of Magnitude Astrophysics
... The H-R Diagram Once reactions occur at the hot central region of the star, its structure changes significantly. If the transport of this energy to the outer regions is through photon diffusion, then the opacity matter will play a vital role in determining the stellar structure. In particular, opaci ...
... The H-R Diagram Once reactions occur at the hot central region of the star, its structure changes significantly. If the transport of this energy to the outer regions is through photon diffusion, then the opacity matter will play a vital role in determining the stellar structure. In particular, opaci ...
MT 2 Answers Version D
... It is converted into light energy, giving o↵ a flash of light upon impact. ...
... It is converted into light energy, giving o↵ a flash of light upon impact. ...
MT 2 Answers Version C
... Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification during the exam. Mark your answers on the scantron sheet and on your copy of the exam. Keep your copy of the exam and chec ...
... Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification during the exam. Mark your answers on the scantron sheet and on your copy of the exam. Keep your copy of the exam and chec ...
April - Bristol Astronomical Society
... Alpha (α) Corvi marks the beak of the crow, it is a F-class (F0) yellow dwarf star. Despite its alpha designation it only 5th in brightness at magnitude +4.00. The star’s proper name, Alchiba means ‘tent’ in Arabic and is thought to refer to the four stars that make up the main body of the crow. Bet ...
... Alpha (α) Corvi marks the beak of the crow, it is a F-class (F0) yellow dwarf star. Despite its alpha designation it only 5th in brightness at magnitude +4.00. The star’s proper name, Alchiba means ‘tent’ in Arabic and is thought to refer to the four stars that make up the main body of the crow. Bet ...
Slide 1 - Physics @ IUPUI
... period of pulsation and their absolute brightness. • The longer the period, the bigger the star is, and the brighter it is (sort of like a bigger bell has a larger period of vibration). • This allows us to measure distances (especially since these are very bright stars which can be seen a LONG dista ...
... period of pulsation and their absolute brightness. • The longer the period, the bigger the star is, and the brighter it is (sort of like a bigger bell has a larger period of vibration). • This allows us to measure distances (especially since these are very bright stars which can be seen a LONG dista ...
Homework Problem #1: (pdf file)
... brightness at Mauna Kea is listed at the CFHT WWW site as 20.9 mag/arcsec2 . The LRIS pixel scale is 0.22 arcseconds/pixel, the readout noise is 8e- and the inverse gain of the system is 2.0 e-/DN. (a) What is the rate of detected e-/pixel from the sky in the R band? (b) What is the rate of detected ...
... brightness at Mauna Kea is listed at the CFHT WWW site as 20.9 mag/arcsec2 . The LRIS pixel scale is 0.22 arcseconds/pixel, the readout noise is 8e- and the inverse gain of the system is 2.0 e-/DN. (a) What is the rate of detected e-/pixel from the sky in the R band? (b) What is the rate of detected ...
October 2013
... and is typical of areas where new stars can form. Between the Scorpion and the Centaur are the Altar, the Level and the Wolf, while to the east of the Milky Way stretches a great expanse of sky with relatively few bright stars, dominated by birds and 'water constellations'. In the south these includ ...
... and is typical of areas where new stars can form. Between the Scorpion and the Centaur are the Altar, the Level and the Wolf, while to the east of the Milky Way stretches a great expanse of sky with relatively few bright stars, dominated by birds and 'water constellations'. In the south these includ ...
TYPES OF STARS
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
HW #4 (due March 27)
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
AnwerkeyChaper1516
... C. Longest: Venus; Shortest: Jupiter D. Longest: Pluto; Shortest: Mercury E. Most: Earth; Least: Saturn ...
... C. Longest: Venus; Shortest: Jupiter D. Longest: Pluto; Shortest: Mercury E. Most: Earth; Least: Saturn ...
Stars - Science
... – The color of a star indicates the temperature of the star (Think of a candle, the hottest colors at the bottom.) The coolest stars are red. Medium temperature stars are orange and yellow. The hottest stars are blue. ...
... – The color of a star indicates the temperature of the star (Think of a candle, the hottest colors at the bottom.) The coolest stars are red. Medium temperature stars are orange and yellow. The hottest stars are blue. ...
SECTION 30.2 Measuring the Stars 1. Constellations are a. the
... 5. When estimating the distance of stars from Earth, astronomers use the fact that nearby stars shift in position as observed from Earth, which is called a. parsec. b. parallax. c. precision. d. shafting. 6. Ancient Greek classification system based on how bright a star appears to be is ___________. ...
... 5. When estimating the distance of stars from Earth, astronomers use the fact that nearby stars shift in position as observed from Earth, which is called a. parsec. b. parallax. c. precision. d. shafting. 6. Ancient Greek classification system based on how bright a star appears to be is ___________. ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... • Can’t Build Beyond Fe by Adding Protons – Repulsion of nuclei = Charge1 x Charge2 – He + C = O: Repulsion = 2 x 6 = 12 – Fe + p = Co: Repulsion = 26 x 1 = 26 ...
... • Can’t Build Beyond Fe by Adding Protons – Repulsion of nuclei = Charge1 x Charge2 – He + C = O: Repulsion = 2 x 6 = 12 – Fe + p = Co: Repulsion = 26 x 1 = 26 ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.