Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Smaller masses – lower surface temperatures – lower luminosities – take longer to form – have longer main sequence lifetimes ...
... • Smaller masses – lower surface temperatures – lower luminosities – take longer to form – have longer main sequence lifetimes ...
Stars and Galaxies
... can get a glimpse of it. Every time we look at the Moon, for example, we see it as it was a little more than a second ago. That’s because sunlight reflected from the Moon’s surface takes a little more than a second to reach Earth. We see the Sun as it looked about eight minutes ago, and the other st ...
... can get a glimpse of it. Every time we look at the Moon, for example, we see it as it was a little more than a second ago. That’s because sunlight reflected from the Moon’s surface takes a little more than a second to reach Earth. We see the Sun as it looked about eight minutes ago, and the other st ...
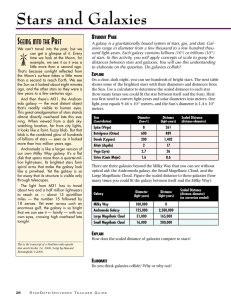
Assessment Star Characteristics and Life Cycle
... Assessment Star Characteristics and Life Cycle 1. Below is a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram that scientists use to compare stars based on their properties. ...
... Assessment Star Characteristics and Life Cycle 1. Below is a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram that scientists use to compare stars based on their properties. ...
Unit 1
... electrons merge into neutrons, taking energy away from the core • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the core material and “bounce” • The “bounced material collides with the remaining infalling gas, raising temperatures high enough to set ...
... electrons merge into neutrons, taking energy away from the core • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the core material and “bounce” • The “bounced material collides with the remaining infalling gas, raising temperatures high enough to set ...
read in advance to speed your work
... seen when we look in the direction of the constellation of Orion. Begin making an H-R diagram for the stars in Orion (Table II). Plot the MV values (MV again is simply absolute magnitude, M, with the subscript indicating that the magnitude is measured in the visual part of the spectrum) against the ...
... seen when we look in the direction of the constellation of Orion. Begin making an H-R diagram for the stars in Orion (Table II). Plot the MV values (MV again is simply absolute magnitude, M, with the subscript indicating that the magnitude is measured in the visual part of the spectrum) against the ...
Prep/Review Questions - Faculty Web Sites at the University
... the ostensible time of night. At what times of night can this happen in real life? In a new Tom Hanks "Castaway" sequel, the hero finds the latitude of his lonely island by determining the maximum altitude of the full Moon at the time of the Vernal Equinox. Is this possible without having profession ...
... the ostensible time of night. At what times of night can this happen in real life? In a new Tom Hanks "Castaway" sequel, the hero finds the latitude of his lonely island by determining the maximum altitude of the full Moon at the time of the Vernal Equinox. Is this possible without having profession ...
The Assembly of M31`s Halo from Dwarf Galaxy Building Blocks
... Studies of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation allow us to probe the properties of the Universe all the way back to Big Bang ...
... Studies of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation allow us to probe the properties of the Universe all the way back to Big Bang ...
worksheet
... A. The Sun’s Evolution during its lifetime. ☆ Click the play button below the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to show the Sun’s evolution. 1. Name the three stages of the Sun’s life shown on the Hertzsprung –Russell diagram. ...
... A. The Sun’s Evolution during its lifetime. ☆ Click the play button below the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to show the Sun’s evolution. 1. Name the three stages of the Sun’s life shown on the Hertzsprung –Russell diagram. ...
Astro 210 Lecture 4 Sept. 4, 2013 Announcements: • PS 1 available
... most stars (∼ 90%) fall on curve: “main sequence” (including the Sun!); “dwarfs” most of the rest: cooler but more luminous: “giants” Q: how do we know they are giant? a rare few: hot but luminous: “supergiants” not rare but dim and hard to find: very hot but very low-L objects: “white dwarfs” Q: ho ...
... most stars (∼ 90%) fall on curve: “main sequence” (including the Sun!); “dwarfs” most of the rest: cooler but more luminous: “giants” Q: how do we know they are giant? a rare few: hot but luminous: “supergiants” not rare but dim and hard to find: very hot but very low-L objects: “white dwarfs” Q: ho ...
1 Chapter 1 1-1. How long does it take the Earth to orbit the Sun? a
... 1-13. What type of motion leads to the Sun rising and setting? a.) Earth’s rotation X b.) Earth’s revolution c.) The Sun’s revolution d.) The Sun’s rotation 1-14. What type of motion leads to stars rising approximately 4 minutes earlier each day than it did the day before? a.) Earth’s rotation b.) E ...
... 1-13. What type of motion leads to the Sun rising and setting? a.) Earth’s rotation X b.) Earth’s revolution c.) The Sun’s revolution d.) The Sun’s rotation 1-14. What type of motion leads to stars rising approximately 4 minutes earlier each day than it did the day before? a.) Earth’s rotation b.) E ...
astronomy - Scioly.org
... A. as the radius decreases, the temperature decreases and the opacity increases. B. as the radius decreases, the temperature and opacity increase. C. as the radius decreases, the temperature increases and the opacity decreases. D. as the radius decreases, the temperature and opacity decrease. 26. In ...
... A. as the radius decreases, the temperature decreases and the opacity increases. B. as the radius decreases, the temperature and opacity increase. C. as the radius decreases, the temperature increases and the opacity decreases. D. as the radius decreases, the temperature and opacity decrease. 26. In ...
The Family of Stars
... more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 100 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. Both stars are equally luminous, but the flux received from star A is 5 times less than from star B, so star A ...
... more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 100 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. Both stars are equally luminous, but the flux received from star A is 5 times less than from star B, so star A ...
Spectrum Analysis Activity File
... Cut out the “Pull Tab Out” card along dashed lines. Cut out the “spectroscope fingerprints” card along dashed lines. Cut out Star B, Star C, Star C1, Star C2, and Star C3 along dashed lines. Make 5 cuts along the dashed lines A, B, C, D, E on the “spectroscope fingerprints”, making sure to stop at t ...
... Cut out the “Pull Tab Out” card along dashed lines. Cut out the “spectroscope fingerprints” card along dashed lines. Cut out Star B, Star C, Star C1, Star C2, and Star C3 along dashed lines. Make 5 cuts along the dashed lines A, B, C, D, E on the “spectroscope fingerprints”, making sure to stop at t ...
The Daily Telegraph – London… 14th February 2008… New Solar
... # Time travellers from the future 'could be here in weeks' Astronomers have identified two new planets orbiting a star about half the size of our sun some 5,000 light-years away. The system, called OGLE-2006-BLG-109L, resembles a slightly scaled down version of our Solar system because the two gas g ...
... # Time travellers from the future 'could be here in weeks' Astronomers have identified two new planets orbiting a star about half the size of our sun some 5,000 light-years away. The system, called OGLE-2006-BLG-109L, resembles a slightly scaled down version of our Solar system because the two gas g ...
Sep 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... An Open Cluster is a group of several to hundreds of stars The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great ex ...
... An Open Cluster is a group of several to hundreds of stars The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great ex ...
Stars and Galaxies part 3
... with respect to more distant objects behind it. This is because your eyes are separated from each other by a few inches - so each eye sees the finger in front of you from a slightly different angle. The amount your finger seems to shift is called its "parallax". ...
... with respect to more distant objects behind it. This is because your eyes are separated from each other by a few inches - so each eye sees the finger in front of you from a slightly different angle. The amount your finger seems to shift is called its "parallax". ...
Apparent Magnitude - RanelaghALevelPhysics
... emitted per second (units of Watts). • The Sun’s luminosity is about 4 x 1026 W. • The most luminous stars have a luminosity of about million times that of the Sun! ...
... emitted per second (units of Watts). • The Sun’s luminosity is about 4 x 1026 W. • The most luminous stars have a luminosity of about million times that of the Sun! ...
astronomy final exam - Physics and Astronomy
... A star spends most of its lifetime undergoing what process? A pulsar is believed to be what kind of object? Where were the heavy elements in our bodies formed? The turn-off point on the H-R diagram of a star cluster will tell us what property about the cluster? A 21-centimeter photon comes from what ...
... A star spends most of its lifetime undergoing what process? A pulsar is believed to be what kind of object? Where were the heavy elements in our bodies formed? The turn-off point on the H-R diagram of a star cluster will tell us what property about the cluster? A 21-centimeter photon comes from what ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.