1 7.3 Heat capacities: extensive state variables (Hiroshi Matsuoka
... diameter D and kB T is analogous to its radius r as ...
... diameter D and kB T is analogous to its radius r as ...
Energy, Work and Heat - abuad lms
... Open System permit the flow of both mass and energy across its boundaries, example is the turbine, the flow of water through a pipe. An open system is also called a control volume and its boundary is called control surface. Isolated system is a system that neither energy nor mass flows out of the bo ...
... Open System permit the flow of both mass and energy across its boundaries, example is the turbine, the flow of water through a pipe. An open system is also called a control volume and its boundary is called control surface. Isolated system is a system that neither energy nor mass flows out of the bo ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... H = E + PV A change in Enthalpy would imply: ∆H = ∆E + ∆(PV) = ∆E + P∆V + V∆P Since: ∆E = q + w; and W = - P∆V; we find: ∆H = q - P∆V + P∆V + V∆P From this it follows that at constant P (process open to the atmosphere): ∆H = qp (equals heat at constant P) Why Define Enthalpy? 1. We can measure or re ...
... H = E + PV A change in Enthalpy would imply: ∆H = ∆E + ∆(PV) = ∆E + P∆V + V∆P Since: ∆E = q + w; and W = - P∆V; we find: ∆H = q - P∆V + P∆V + V∆P From this it follows that at constant P (process open to the atmosphere): ∆H = qp (equals heat at constant P) Why Define Enthalpy? 1. We can measure or re ...
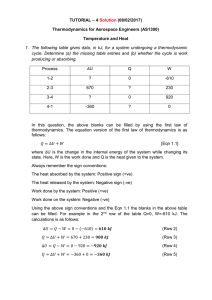
Solution Tutorial 4 - Aerospace Engineering, IIT Madras
... Thermodynamics for Aerospace Engineers (AS1300) Temperature and Heat 1. The following table gives data, in kJ, for a system undergoing a thermodynamic cycle. Determine (a) the missing table entries and (b) whether the cycle is work producing or absorbing. Process ...
... Thermodynamics for Aerospace Engineers (AS1300) Temperature and Heat 1. The following table gives data, in kJ, for a system undergoing a thermodynamic cycle. Determine (a) the missing table entries and (b) whether the cycle is work producing or absorbing. Process ...
Key - GCC
... Conservation of energy means that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. For example, in a chemical reaction, potential energy stored in chemical bonds may be converted to heat, light, or sound energy as a result of a chemical reaction. 4) Draw a picture show ...
... Conservation of energy means that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. For example, in a chemical reaction, potential energy stored in chemical bonds may be converted to heat, light, or sound energy as a result of a chemical reaction. 4) Draw a picture show ...
Thermodynamic system
... • In isochoric process, no mechanical work performed • In adiabatic process, no heat is exchanged with environment • Reversible process: by reversing the process, one can bring both the system and its environment back into the intial state • Whenever energy is dissipated (mechanical into heat, e.g. ...
... • In isochoric process, no mechanical work performed • In adiabatic process, no heat is exchanged with environment • Reversible process: by reversing the process, one can bring both the system and its environment back into the intial state • Whenever energy is dissipated (mechanical into heat, e.g. ...
Erik`s Chemistry: Thermochemistry - ECHS Chemistry
... (James Joule, 1818-1889, Joule also developed the First Law of Thermodynamics): energy is neither created nor destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes. b. Quantitative H H = qreaction mixture (at constant temperature only) q = (m)( t)(Cp) q = heat absorbed by the water in joules (J) m = ma ...
... (James Joule, 1818-1889, Joule also developed the First Law of Thermodynamics): energy is neither created nor destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes. b. Quantitative H H = qreaction mixture (at constant temperature only) q = (m)( t)(Cp) q = heat absorbed by the water in joules (J) m = ma ...
Chapter 6 ()
... the temperature is about 20O C (nearly 300O on the absolute Kelvin scale), with U =10cm/sec, and L =1,000 km, and if the overall temperature variation is about 10 degrees C, the ratio in (6.3.1 ) is of the order of 10-5, e.g. very small indeed. Our thermodynamic equation then becomes, upon ignoring ...
... the temperature is about 20O C (nearly 300O on the absolute Kelvin scale), with U =10cm/sec, and L =1,000 km, and if the overall temperature variation is about 10 degrees C, the ratio in (6.3.1 ) is of the order of 10-5, e.g. very small indeed. Our thermodynamic equation then becomes, upon ignoring ...
Heat transfer

Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems, depending on the temperature and pressure, by dissipating heat. The fundamental modes of heat transfer are conduction or diffusion, convection and radiation.Heat transfer always occurs from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat transfer changes the internal energy of both systems involved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines the concept of thermodynamic entropy, by measurable heat transfer.Thermal equilibrium is reached when all involved bodies and the surroundings reach the same temperature. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.