First Law, Enthalpy, Calorimetry, and Hess`s Law Why?
... The amount of heat transferred in a chemical or physical process depends upon (1) physical conditions, (2) amounts of substances, and (3) direction of change. The physical conditions on which enthalpy depends are temperature (T), pressure (P), and physical state (i.e., solid, liquid, gas, aqueous so ...
... The amount of heat transferred in a chemical or physical process depends upon (1) physical conditions, (2) amounts of substances, and (3) direction of change. The physical conditions on which enthalpy depends are temperature (T), pressure (P), and physical state (i.e., solid, liquid, gas, aqueous so ...
Physics 240: Worksheet 28 Name: (1) An ideal gas has the equation
... W=P∆V. The change in volume here is ∆V = Vgas − Vliquid approximately. I’m assuming that the ice and the water are about the same volume. What is the volume of the steam? We’ll assume the ideal gas equation of state here, but we’ve got to find N. How? 1 kg of water has how many molecules is the ques ...
... W=P∆V. The change in volume here is ∆V = Vgas − Vliquid approximately. I’m assuming that the ice and the water are about the same volume. What is the volume of the steam? We’ll assume the ideal gas equation of state here, but we’ve got to find N. How? 1 kg of water has how many molecules is the ques ...
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Thermal Sciences
... • consider an experiment in which a substance starts as a solid and is heated up at constant pressure until it all becomes as gas • depending on the prevailing pressure, the matter will pass through various phase transformations. At P0 : 1. solid 2. mixed phase of liquid and solid 3. sub-cooled or c ...
... • consider an experiment in which a substance starts as a solid and is heated up at constant pressure until it all becomes as gas • depending on the prevailing pressure, the matter will pass through various phase transformations. At P0 : 1. solid 2. mixed phase of liquid and solid 3. sub-cooled or c ...
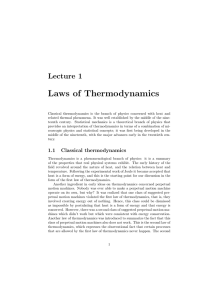
Laws of Thermodynamics
... After the first and second laws of thermodynamics had been recognized and thermodynamics was becoming a more formal subject, it was realized that there was no consistent definition of temperature. A zeroth law of thermodynamics was added to rectify this. Later still, a third law of thermodynamics wa ...
... After the first and second laws of thermodynamics had been recognized and thermodynamics was becoming a more formal subject, it was realized that there was no consistent definition of temperature. A zeroth law of thermodynamics was added to rectify this. Later still, a third law of thermodynamics wa ...
Enthalpy and Internal Energy
... • H or ΔH is used to symbolize enthalpy. • The mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics is: ΔE = q + w , where ΔE is the change in internal energy, q is heat and w is work. • Work can be defined in terms of an expanding gas and has the formula: w = -PΔV , where P is pressure in ...
... • H or ΔH is used to symbolize enthalpy. • The mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics is: ΔE = q + w , where ΔE is the change in internal energy, q is heat and w is work. • Work can be defined in terms of an expanding gas and has the formula: w = -PΔV , where P is pressure in ...
Unsteady coupling of Navier-Stokes and Radiative Heat
... from 307 824 grid points (44 × 159 × 44, in x, y and z). Grid spacing in viscous wall units is setup to be at least half the step size of the minimal channel flow DNS of Jiménez & Moin [4], namely ∆x+ ≈ 32 in the x direction and ∆z + ≈ 12 in the z direction. In the wall-normal direction grid spacin ...
... from 307 824 grid points (44 × 159 × 44, in x, y and z). Grid spacing in viscous wall units is setup to be at least half the step size of the minimal channel flow DNS of Jiménez & Moin [4], namely ∆x+ ≈ 32 in the x direction and ∆z + ≈ 12 in the z direction. In the wall-normal direction grid spacin ...
Application , First, Law of Thermodynamics
... b. Suppose that the gas expands at the expense of its energy, however, a heat bath is in contact with the system compensating for the loss in energy. What happens to the density of the gas? c. Density therefore depends on the state variables. In oceanography, a term called isopycnalis isopycnalis us ...
... b. Suppose that the gas expands at the expense of its energy, however, a heat bath is in contact with the system compensating for the loss in energy. What happens to the density of the gas? c. Density therefore depends on the state variables. In oceanography, a term called isopycnalis isopycnalis us ...
Determination of Heat of Combustion of Liquid
... The constant volume constraint means that pressure is not constant and neither is temperature making this an adiabatic process. The other type of heat of combustion is net heat of combustion. This is similar to gross heat of combustion but occurs at constant pressure rather than constant volume. The ...
... The constant volume constraint means that pressure is not constant and neither is temperature making this an adiabatic process. The other type of heat of combustion is net heat of combustion. This is similar to gross heat of combustion but occurs at constant pressure rather than constant volume. The ...
Chapter 2. The First Law
... 1. Enthalpy (H) is defined as H = U + pV 2. H is a state function because U, p, and V are state functions 3. The change in enthalpy is equal to the energy supplied as heat at constant p ...
... 1. Enthalpy (H) is defined as H = U + pV 2. H is a state function because U, p, and V are state functions 3. The change in enthalpy is equal to the energy supplied as heat at constant p ...
Ch 17--Thermochemistry(first class)
... 17.2: Enthalpy (measuring heat flow) Two types of calorimeters: a) Constant-Pressure calorimeter (eg. foam cups) • As most reactions occur at constant pressure we can say that: A change in enthalpy (ΔH) = heat supplied (q) • So, a release of heat (exothermic) corresponds to a decrease in enthalpy ( ...
... 17.2: Enthalpy (measuring heat flow) Two types of calorimeters: a) Constant-Pressure calorimeter (eg. foam cups) • As most reactions occur at constant pressure we can say that: A change in enthalpy (ΔH) = heat supplied (q) • So, a release of heat (exothermic) corresponds to a decrease in enthalpy ( ...
Thermodynamics
... For any given substance, its thermal energy depends not only on its composition but also on the amount of substance ...
... For any given substance, its thermal energy depends not only on its composition but also on the amount of substance ...
0 Quarter Three Assessment Review - SRHSchem
... the solid is completely dissolve, the water temperature drops to 15.2°C. a. Is this process endothermic or exothermic? Explain. – The temperature of the water decreases, so the dissolving process must have absorbed that heat, ...
... the solid is completely dissolve, the water temperature drops to 15.2°C. a. Is this process endothermic or exothermic? Explain. – The temperature of the water decreases, so the dissolving process must have absorbed that heat, ...
Lecture 1 1 Overview
... (a) Extensive: e.g. V , U , N , or V (Tester & Modell) (Walas), V t (Van Ness & Abbott). (b) Molar: e.g. V /N , U/N sometimes denoted V (Sandler), v (Denbigh), V (Van Ness & Abbott, Walas; note that this is the same as other author’s extensive) and Ṽ . (c) Specific: e.g. V /M where M is the total m ...
... (a) Extensive: e.g. V , U , N , or V (Tester & Modell) (Walas), V t (Van Ness & Abbott). (b) Molar: e.g. V /N , U/N sometimes denoted V (Sandler), v (Denbigh), V (Van Ness & Abbott, Walas; note that this is the same as other author’s extensive) and Ṽ . (c) Specific: e.g. V /M where M is the total m ...
Week 1 - University of Guelph
... To change the temperature of a gas, the internal energy must be changed by doing work on it or transferring energy to it, i.e., ΔU = q + w. When a gas expands, the forces due to pressure push the container walls back, so the gas is doing work. Change in w is negative. For an isothermal (i.e., ΔT = 0 ...
... To change the temperature of a gas, the internal energy must be changed by doing work on it or transferring energy to it, i.e., ΔU = q + w. When a gas expands, the forces due to pressure push the container walls back, so the gas is doing work. Change in w is negative. For an isothermal (i.e., ΔT = 0 ...
Chapter 18: Chemical Thermodynamics
... Hf is the heat of _________________. Formation reactions have - _____________ product - produce a __________ mole of that product - use only ____________ as reactants in their standard states. Sign of H (__) Rxn is exothermic, gives off heat, heat is a product. (__) Rxn is endothermic, abso ...
... Hf is the heat of _________________. Formation reactions have - _____________ product - produce a __________ mole of that product - use only ____________ as reactants in their standard states. Sign of H (__) Rxn is exothermic, gives off heat, heat is a product. (__) Rxn is endothermic, abso ...
C3 3.1-3.4 part 2 Alcohols, carboxlic acids and esters progress ticket
... Complete the balanced symbol equation for this reaction. C2H5OH + ............................................................................................ ...
... Complete the balanced symbol equation for this reaction. C2H5OH + ............................................................................................ ...
Chem161 Chapter 6
... created or destroyed but can be transformed from one form of energy to another • Also known as the first law of thermodynamics • How does water falling over a waterfall demonstrate this law? ...
... created or destroyed but can be transformed from one form of energy to another • Also known as the first law of thermodynamics • How does water falling over a waterfall demonstrate this law? ...
Heat transfer

Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems, depending on the temperature and pressure, by dissipating heat. The fundamental modes of heat transfer are conduction or diffusion, convection and radiation.Heat transfer always occurs from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat transfer changes the internal energy of both systems involved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines the concept of thermodynamic entropy, by measurable heat transfer.Thermal equilibrium is reached when all involved bodies and the surroundings reach the same temperature. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.