thermochemistry -1 - Dr. Gupta`s Professional Page
... • INTERNAL ENERGY (U): Sum of kinetic and potential energies of all particles. Etotal = Ek + Ep + U • Energy cannot be created nor destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. ...
... • INTERNAL ENERGY (U): Sum of kinetic and potential energies of all particles. Etotal = Ek + Ep + U • Energy cannot be created nor destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. ...
The Laws of Thermodinamics
... An isolated system does not interact with its surroundings No energy transfer takes place and no work is done Therefore, the internal energy of the isolated system remains constant ...
... An isolated system does not interact with its surroundings No energy transfer takes place and no work is done Therefore, the internal energy of the isolated system remains constant ...
Chapter 15: Thermal Properties of Matter
... above which material does not separate into two phases. It goes smoothly without a phase transition. ...
... above which material does not separate into two phases. It goes smoothly without a phase transition. ...
Unit 2 Thermodynamic parameters Ex.1. Read and learn new words
... Thermodynamic parameters The central concept of thermodynamics is that of energy, the ability to do work. As stipulated by the first law, the total energy of the system and its surroundings is conserved. It may be transferred into a body by heating, compression, or addition of matter, and extracted ...
... Thermodynamic parameters The central concept of thermodynamics is that of energy, the ability to do work. As stipulated by the first law, the total energy of the system and its surroundings is conserved. It may be transferred into a body by heating, compression, or addition of matter, and extracted ...
Thermo Powerpoint
... mole from liquid to gas ΔHcond : enthalpy change for to change one mole from gas to liquid ΔHmelt : enthalpy change for to change one mole from solid to liquid (aka. fusion, ...
... mole from liquid to gas ΔHcond : enthalpy change for to change one mole from gas to liquid ΔHmelt : enthalpy change for to change one mole from solid to liquid (aka. fusion, ...
Chapter One
... • The amount of heat transferred is usually expressed in calories (cal) or in the SI unit of joules (J). 1 cal = 4.184 J • Specific heat is defined as the amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of 1 g of substance by 1o C. • Each substance has a specific heat, which is a physical intensiv ...
... • The amount of heat transferred is usually expressed in calories (cal) or in the SI unit of joules (J). 1 cal = 4.184 J • Specific heat is defined as the amount of heat necessary to raise the temperature of 1 g of substance by 1o C. • Each substance has a specific heat, which is a physical intensiv ...
Carnot Cycle. Heat Engines. Refrigerators.
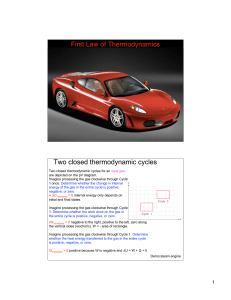
... be less than its theoretical maximum. The idea of the Carnot cycle is that as you let the engine temperatures approach those of the hot and cold reservoirs the efficiency approaches its maximum. Of course, this means that the engine will work very slowly (during steps (a) and (c)) when it is near it ...
... be less than its theoretical maximum. The idea of the Carnot cycle is that as you let the engine temperatures approach those of the hot and cold reservoirs the efficiency approaches its maximum. Of course, this means that the engine will work very slowly (during steps (a) and (c)) when it is near it ...
EXAM REVIEW !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! The examination is scheduled
... What are the best (natural) thermodynamic variables for U? Be able to show how more Thermodynamic information comes from the definition of the exact differential and the exactness criterion. What are Maxwell’s relations? How are they derived from the equation for dU? What about dG? What are the natu ...
... What are the best (natural) thermodynamic variables for U? Be able to show how more Thermodynamic information comes from the definition of the exact differential and the exactness criterion. What are Maxwell’s relations? How are they derived from the equation for dU? What about dG? What are the natu ...
Answers to Homework Problem Sheet 8
... same density as pure water, this corresponds to a mass of: mass (g) = density (g mL-1) × volume (mL) = (0.997 g mL-1) × (200 mL) = 199 g The temperature change, ΔT = (31.1 °C – 24.6 °C) = 6.7 K. The heat capacity of water is 4.184 J K-1 g-1. The heat change is therefore: q = c × m × ΔT = (4.184 J K- ...
... same density as pure water, this corresponds to a mass of: mass (g) = density (g mL-1) × volume (mL) = (0.997 g mL-1) × (200 mL) = 199 g The temperature change, ΔT = (31.1 °C – 24.6 °C) = 6.7 K. The heat capacity of water is 4.184 J K-1 g-1. The heat change is therefore: q = c × m × ΔT = (4.184 J K- ...
12. THE LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS Key Words
... From (12-9), we can clearly understand the basic idea behind any heat engine: mechanical work can be obtained from thermal energy only when heat is allowed to flow from a high temperature TH to a low temperature TC. In this process, some of the heat can be transformed into mechanical work. Equation ...
... From (12-9), we can clearly understand the basic idea behind any heat engine: mechanical work can be obtained from thermal energy only when heat is allowed to flow from a high temperature TH to a low temperature TC. In this process, some of the heat can be transformed into mechanical work. Equation ...
Some ideas from thermodynamics
... inter-molecular interaction energy, and V0 is proportional to the volume of a molecule (that is, if there are N molecules the available volume is V − N V0 rather than V). Also kB = R ⁄ NA is Boltzmann’s constant. The Van der Waals equation of state represents an attempt to take into account two phys ...
... inter-molecular interaction energy, and V0 is proportional to the volume of a molecule (that is, if there are N molecules the available volume is V − N V0 rather than V). Also kB = R ⁄ NA is Boltzmann’s constant. The Van der Waals equation of state represents an attempt to take into account two phys ...
Practice Exam #2 with Answers
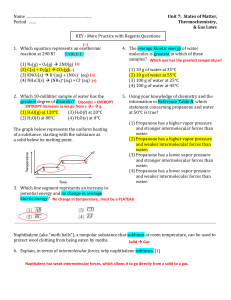
... _____17. Which of the following substances (with specific heat capacity provided) would show the greatest temperature change upon absorbing 100.0 J of heat? A) 10.0 g Fe, CFe = 0.449 J/g°C B) 10.0 g H2O, CH2O = 4.18 J/g°C C) 10.0 g ethanol, Cethanol = 2.42 J/g°C D) 10.0 g Au, CAu = 0.128 J/g°C ____ ...
... _____17. Which of the following substances (with specific heat capacity provided) would show the greatest temperature change upon absorbing 100.0 J of heat? A) 10.0 g Fe, CFe = 0.449 J/g°C B) 10.0 g H2O, CH2O = 4.18 J/g°C C) 10.0 g ethanol, Cethanol = 2.42 J/g°C D) 10.0 g Au, CAu = 0.128 J/g°C ____ ...
Heat transfer

Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems, depending on the temperature and pressure, by dissipating heat. The fundamental modes of heat transfer are conduction or diffusion, convection and radiation.Heat transfer always occurs from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat transfer changes the internal energy of both systems involved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines the concept of thermodynamic entropy, by measurable heat transfer.Thermal equilibrium is reached when all involved bodies and the surroundings reach the same temperature. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.