Momentum Heat Mass Transfer
... determined by the heat delivery by conduction and by the mechanical work. This statement can be expressed in form of a general transport equation for =uE ...
... determined by the heat delivery by conduction and by the mechanical work. This statement can be expressed in form of a general transport equation for =uE ...
FE Review Common Pitfalls in Thermodynamics
... This result is correct only when the process is constant pressure, and P = P1 = P2. 8. Temperature—When the value of temperature is substituted into an equation such as the ideal equation of state, the temperature must be in absolute units. A temperature change in the ordinary units, celsius or fahr ...
... This result is correct only when the process is constant pressure, and P = P1 = P2. 8. Temperature—When the value of temperature is substituted into an equation such as the ideal equation of state, the temperature must be in absolute units. A temperature change in the ordinary units, celsius or fahr ...
Elastomers and aging
... (refs. 1 and 2). Most tensile testers can be upgraded at a reasonable cost to perform this calculation. Work is a product of shear modulus G times an extension ratio λ, a nonlinear function; (extension ratio λ = 1 + elongation) ...
... (refs. 1 and 2). Most tensile testers can be upgraded at a reasonable cost to perform this calculation. Work is a product of shear modulus G times an extension ratio λ, a nonlinear function; (extension ratio λ = 1 + elongation) ...
A Micro-Insulation Concept for MEMS Applications
... where cv is the constant volume specific heat and is the dynamic viscosity. Figure 4 shows the air thermal conductivity as a function of Knudsen number for a given air gap 共therefore also a function of pressure兲 at 400 K. Although the free-molecule conduction is the most efficient conduction mode, ...
... where cv is the constant volume specific heat and is the dynamic viscosity. Figure 4 shows the air thermal conductivity as a function of Knudsen number for a given air gap 共therefore also a function of pressure兲 at 400 K. Although the free-molecule conduction is the most efficient conduction mode, ...
PPT
... The second law of thermodynamics is an expression of the tendency that over time, differences in temperature, pressure, and chemical potential equilibrate in an isolated physical system. From the state of thermodynamic equilibrium, the law deduced the principle of the increase of entropy and explain ...
... The second law of thermodynamics is an expression of the tendency that over time, differences in temperature, pressure, and chemical potential equilibrate in an isolated physical system. From the state of thermodynamic equilibrium, the law deduced the principle of the increase of entropy and explain ...
t 0 - PhysicsEducation.net
... 4 liter solution rises by 8C. Suppose that during this process x joules of energy flow either into or out of the system. (Your answer to #7 should have decided whether it’s into or out of, or if instead x is really just 0 joules. Which is it?) Experiment B. Suppose that again we have 2 liters of ea ...
... 4 liter solution rises by 8C. Suppose that during this process x joules of energy flow either into or out of the system. (Your answer to #7 should have decided whether it’s into or out of, or if instead x is really just 0 joules. Which is it?) Experiment B. Suppose that again we have 2 liters of ea ...
Latent Heat of Vaporization and Speci c Heat - Physlab
... Figure 3: The experimentally observed variation of CM with temperature, showing the region where Dulong{Petit law agrees with experimental results and also the region where the law breaks down. The heat capacity of solids is important information as it allows us to understand the material in a myria ...
... Figure 3: The experimentally observed variation of CM with temperature, showing the region where Dulong{Petit law agrees with experimental results and also the region where the law breaks down. The heat capacity of solids is important information as it allows us to understand the material in a myria ...
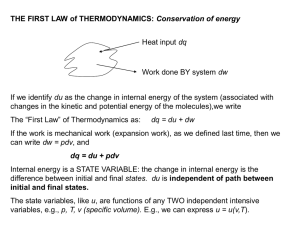
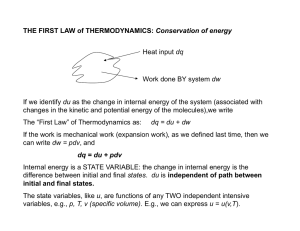
THE FIRST LAW of THERMODYNAMICS: Conservation of energy
... entropy and explains the phenomenon of irreversibility in nature. The second law declares the impossibility of machines that generate usable energy from the abundant internal energy of nature by processes called perpetual motion of the second kind. In classical thermodynamics, the second law is a ba ...
... entropy and explains the phenomenon of irreversibility in nature. The second law declares the impossibility of machines that generate usable energy from the abundant internal energy of nature by processes called perpetual motion of the second kind. In classical thermodynamics, the second law is a ba ...
first law of thermodynamics 1.introduction 2.equation form of the first
... Heat is supplied to the steam generator (boiler) where liquid is converted to steam or vapor. The vapor is then expanded adiabatically in the turbine to produce a work output. Vapor leaving the turbine then enters the condenser where heat is removed and the vapor is condensed into the liquid state. ...
... Heat is supplied to the steam generator (boiler) where liquid is converted to steam or vapor. The vapor is then expanded adiabatically in the turbine to produce a work output. Vapor leaving the turbine then enters the condenser where heat is removed and the vapor is condensed into the liquid state. ...
GCSE P1 1.1.3 Energy Transfer by Heating
... overcome the attraction forces of surface molecules and thereby escape to become vapour molecules. Some, having a medium amount of energy, escape momentarily, but are then pulled back by the attraction forces of surface molecules. ...
... overcome the attraction forces of surface molecules and thereby escape to become vapour molecules. Some, having a medium amount of energy, escape momentarily, but are then pulled back by the attraction forces of surface molecules. ...
Answer Key to Sample Questions
... positive because one molecule breaks to form two molecules b. What is the sign of H for this reaction? positive because a bond is broken, but none is formed. c. In which temperature range will this reaction be thermodynamically favored? It is entropy favored, enthalpy disfavored, so favored overall ...
... positive because one molecule breaks to form two molecules b. What is the sign of H for this reaction? positive because a bond is broken, but none is formed. c. In which temperature range will this reaction be thermodynamically favored? It is entropy favored, enthalpy disfavored, so favored overall ...
principles of reactivity: energy and chemical reactions
... Describe various forms of energy and energy transfer. Understand the terms reactant-favored, product-favored, and thermodynamics. Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy and know the SI unit used to measure thermal energy. Understand the term specific heat capacity and know how to calcu ...
... Describe various forms of energy and energy transfer. Understand the terms reactant-favored, product-favored, and thermodynamics. Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy and know the SI unit used to measure thermal energy. Understand the term specific heat capacity and know how to calcu ...
Heat transfer

Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems, depending on the temperature and pressure, by dissipating heat. The fundamental modes of heat transfer are conduction or diffusion, convection and radiation.Heat transfer always occurs from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat transfer changes the internal energy of both systems involved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines the concept of thermodynamic entropy, by measurable heat transfer.Thermal equilibrium is reached when all involved bodies and the surroundings reach the same temperature. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.