Test bank questions
... Which of the following is a true statement about chemical equilibria in general? A. At equilibrium the total concentration of products equals the total concentration of reactants, that is, [products] = [reactants]. B. Equilibrium is the result of the cessation of all chemical change. C. There is onl ...
... Which of the following is a true statement about chemical equilibria in general? A. At equilibrium the total concentration of products equals the total concentration of reactants, that is, [products] = [reactants]. B. Equilibrium is the result of the cessation of all chemical change. C. There is onl ...
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions
... Molecules move faster at higher temperatures. (Their internal motions (vibrations and rotations) also gain more energy, so vibrations and rotations are more active.) Molecules have to come together to react, so they should come together faster if they are moving faster and reactions should speed up ...
... Molecules move faster at higher temperatures. (Their internal motions (vibrations and rotations) also gain more energy, so vibrations and rotations are more active.) Molecules have to come together to react, so they should come together faster if they are moving faster and reactions should speed up ...
NMR and Parity Violation Anomalous Temperature Dependence in
... acids and L-sugars. This broken symmetry is now believed to be a feature of fundamental physics a result of symmetry-breaking induced by the weak force, which makes one enantiomer slightly more stable than the other. An amplification mechanism based on quantum mechanical tunnelling could give rise ...
... acids and L-sugars. This broken symmetry is now believed to be a feature of fundamental physics a result of symmetry-breaking induced by the weak force, which makes one enantiomer slightly more stable than the other. An amplification mechanism based on quantum mechanical tunnelling could give rise ...
Review Study Guide for the Final
... A. Solution a homogeneous mixture involving two or more pure substances. B. Solute substance dissolved in the solution. C. Solvent the substance in which the solute is dissolved ...
... A. Solution a homogeneous mixture involving two or more pure substances. B. Solute substance dissolved in the solution. C. Solvent the substance in which the solute is dissolved ...
Document
... 21.7: Preparation of Amines by Alkylation of Ammonia Ammonia and other alkylamines are good nucleophiles and react with 1° and 2° alkyl halides or tosylates via an SN2 reaction yielding alkyl amines. ...
... 21.7: Preparation of Amines by Alkylation of Ammonia Ammonia and other alkylamines are good nucleophiles and react with 1° and 2° alkyl halides or tosylates via an SN2 reaction yielding alkyl amines. ...
Document
... Refer to the “Chemical Equations and Reactions” chapter for a discussion of chemical reactions. ...
... Refer to the “Chemical Equations and Reactions” chapter for a discussion of chemical reactions. ...
Chemistry - Andhra University
... acides (c) Stability of carbonium ions. Resonance or Mesomeric effect, application to (a) acidity of phenol, and (b) acidity of carboxylic acids. Hyper conjugation and its application to stability of carbonium ions, Free radicals and alkenes, carbanions, carbenes and nitrenes. Types of Organic react ...
... acides (c) Stability of carbonium ions. Resonance or Mesomeric effect, application to (a) acidity of phenol, and (b) acidity of carboxylic acids. Hyper conjugation and its application to stability of carbonium ions, Free radicals and alkenes, carbanions, carbenes and nitrenes. Types of Organic react ...
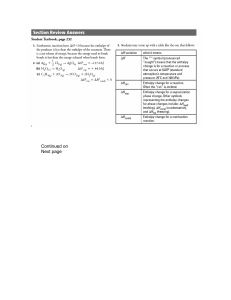
1. Define the following term: system. A) The part of the universe that
... 19. Define the following term: endothermic process. A) The study of heat change in chemical reactions B) The process of transferring thermal energy from a system to the surroundings. C) The process of transferring thermal energy from the surroundings to a system. D) The transfer of thermal energy b ...
... 19. Define the following term: endothermic process. A) The study of heat change in chemical reactions B) The process of transferring thermal energy from a system to the surroundings. C) The process of transferring thermal energy from the surroundings to a system. D) The transfer of thermal energy b ...























