Higher Chemistry Resources Guide - Glow Blogs
... The following pages show the Mandatory Course key areas table from the SQA Higher Chemistry Course and Unit Support Notes. An additional fourth column has been included which contains hyperlinks to useful resources. Please note: Practitioners are not required to use the resources listed – they are o ...
... The following pages show the Mandatory Course key areas table from the SQA Higher Chemistry Course and Unit Support Notes. An additional fourth column has been included which contains hyperlinks to useful resources. Please note: Practitioners are not required to use the resources listed – they are o ...
SQA CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the "kinetic model" of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the "kinetic model" of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
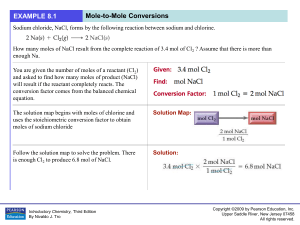
... CHAPTER 12, Stoichiometry (continued) 4. If the quantities of reactants are given in units other than moles, what is the first step for determining the amount of product? a. Determine the amount of product from the given amount of limiting reagent. b. Convert each given quantity of reactant to moles ...
03-Chemical Rxns n Stoichiometry
... When identities of reactants and products are established, we can write their formulas. Still, the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the equation to adhere to the Laws of Conservation of Matter and Mass. Thus, we must BALANCE the chemical equation! ...
... When identities of reactants and products are established, we can write their formulas. Still, the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the equation to adhere to the Laws of Conservation of Matter and Mass. Thus, we must BALANCE the chemical equation! ...
Orbitals
... 14.11 Conjugate Nucleophilic Addition to α,βUnsaturated Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophiles can add directly to carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones, called 1,2-addition Nucleophiles can also add to conjugated C=C bond adjacent to carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones, called conjugate addition ...
... 14.11 Conjugate Nucleophilic Addition to α,βUnsaturated Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophiles can add directly to carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones, called 1,2-addition Nucleophiles can also add to conjugated C=C bond adjacent to carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones, called conjugate addition ...
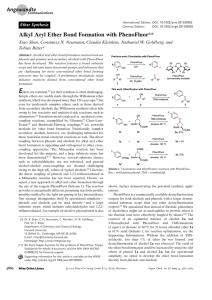
Alkyl Aryl Ether Bond Formation with PhenoFluor
... methods for ether bond formation. Functionally complex secondary alcohols, however, are challenging substrates for these transition-metal-catalyzed reactions as well. The direct coupling between phenols and alcohols for alkyl aryl ether bond formation is appealing and orthogonal to other crosscoupli ...
... methods for ether bond formation. Functionally complex secondary alcohols, however, are challenging substrates for these transition-metal-catalyzed reactions as well. The direct coupling between phenols and alcohols for alkyl aryl ether bond formation is appealing and orthogonal to other crosscoupli ...
Reactions You Should Know When You Begin Organic II
... Addition of symmetrical agents may be anti or syn depending on mechanism or catalyst. Addition of asymmetrical agents follows Markovnikov's Rule except for addition of HBr in the presence of peroxides which adds anti-Markovnikov (only works with HBr). ...
... Addition of symmetrical agents may be anti or syn depending on mechanism or catalyst. Addition of asymmetrical agents follows Markovnikov's Rule except for addition of HBr in the presence of peroxides which adds anti-Markovnikov (only works with HBr). ...
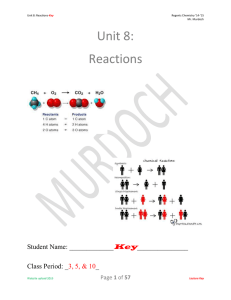
Unit 8: Reactions
... Objective: The amount of matter in reactants equals that in products! The mass on the reactants (left) side of the arrow and the mass on the products (right) side of the arrow MUST equal each other as the Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass may not be created or destroyed in any chemical re ...
... Objective: The amount of matter in reactants equals that in products! The mass on the reactants (left) side of the arrow and the mass on the products (right) side of the arrow MUST equal each other as the Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass may not be created or destroyed in any chemical re ...
First palladium- and nickel-catalyzed oxidative
... on the mechanism are currently under investigation [16]. All data points to a sequence of aminometallation followed by a second alkyl-nitrogen bond formation. No radical intermediates are involved in the overall process as selective deuteration at the terminal position of the alkene leads to diaster ...
... on the mechanism are currently under investigation [16]. All data points to a sequence of aminometallation followed by a second alkyl-nitrogen bond formation. No radical intermediates are involved in the overall process as selective deuteration at the terminal position of the alkene leads to diaster ...
Reaction of Organometallic Reagents with Aldehydes and Ketones.
... • Nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic acyl substitution involve the same first step—nucleophilic attack on the electrophilic carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate. • The difference between the two reactions is what then happens to the intermediate. • Aldehydes and ketones cannot unde ...
... • Nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic acyl substitution involve the same first step—nucleophilic attack on the electrophilic carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate. • The difference between the two reactions is what then happens to the intermediate. • Aldehydes and ketones cannot unde ...