Chemistry: Dr. Wilhelm & Ms. Greendyk
... bonds of the reactants. The energy is usually released as _________. For example, some stoves use natural gas. When natural gas burns, it releases heat. This heat is used to cook your food. Similarly, the reaction between oxygen and other fuels that produce fire, such as wood, coal, oil, or the wax ...
... bonds of the reactants. The energy is usually released as _________. For example, some stoves use natural gas. When natural gas burns, it releases heat. This heat is used to cook your food. Similarly, the reaction between oxygen and other fuels that produce fire, such as wood, coal, oil, or the wax ...
Chapter 7
... 4. Catalysts – A catalyst is a substance that alters the rate of a chemical reaction without being permanently changed in the reaction. Catalysts change the activation energy of the reaction!!! Your body has thousands of catalysts called enzymes that God created to keep your ...
... 4. Catalysts – A catalyst is a substance that alters the rate of a chemical reaction without being permanently changed in the reaction. Catalysts change the activation energy of the reaction!!! Your body has thousands of catalysts called enzymes that God created to keep your ...
Chemistry 11 - Sardis Secondary
... a) How many grams of MgCl2 would be formed if 50.0mL of 0.200M AlCl3 is reacted with excess Mg? ...
... a) How many grams of MgCl2 would be formed if 50.0mL of 0.200M AlCl3 is reacted with excess Mg? ...
- professional publication
... Preparation of Cycloalkanes, Bayer’s Strain Theory, Theory of Stainless Ring, Molecular Orbital Concept. ...
... Preparation of Cycloalkanes, Bayer’s Strain Theory, Theory of Stainless Ring, Molecular Orbital Concept. ...
N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but
... is an alkyl group then R-X is called an alkyl halide. Alkyl halides are useful reagents in synthesis as the halogen is easily replaced. If R is an aryl group (benzene) then R-X is called an aryl halide. The halogen of aryl halides is difficult to replace. ...
... is an alkyl group then R-X is called an alkyl halide. Alkyl halides are useful reagents in synthesis as the halogen is easily replaced. If R is an aryl group (benzene) then R-X is called an aryl halide. The halogen of aryl halides is difficult to replace. ...
Review Questions
... A 1.0 L reaction vessel is analyzed and found to contain 3.2 mol Cl2(g), 1.5 mol PCl3 (g) and 2.0 mol PCl5(g). Show that the reaction mixture has not yet reached equilibrium. 3. If 1.00 mol each of carbon dioxide and hydrogen is initially injected into a 10.0 L reaction chamber at 986oC, what would ...
... A 1.0 L reaction vessel is analyzed and found to contain 3.2 mol Cl2(g), 1.5 mol PCl3 (g) and 2.0 mol PCl5(g). Show that the reaction mixture has not yet reached equilibrium. 3. If 1.00 mol each of carbon dioxide and hydrogen is initially injected into a 10.0 L reaction chamber at 986oC, what would ...
In this chapter, alkanes, alkenes, alkynes
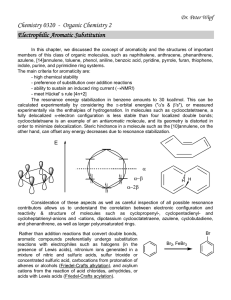
... The resonance energy stabilization in benzene amounts to 30 kcal/mol. This can be calculated experimentally by considering the -orbital energies ("'s & 's"), or measured experimentally via the enthalpies of hydrogenation. In molecules such as cyclooctatetraene, a fully delocalized -electron conf ...
... The resonance energy stabilization in benzene amounts to 30 kcal/mol. This can be calculated experimentally by considering the -orbital energies ("'s & 's"), or measured experimentally via the enthalpies of hydrogenation. In molecules such as cyclooctatetraene, a fully delocalized -electron conf ...
thermochermistry ap - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... ΔH = Hfinal – Hinitial The relationship between energy and enthalpy is that ΔE = ΔH – PΔV o ΔE is almost equal to ΔH because PΔV is typically very small 5.4 Enthalpies of Reaction The enthalpy of a reaction, or heat of a reaction, can be found by ΔH = Hproducts – Hreactants ; ΔH can also be writ ...
... ΔH = Hfinal – Hinitial The relationship between energy and enthalpy is that ΔE = ΔH – PΔV o ΔE is almost equal to ΔH because PΔV is typically very small 5.4 Enthalpies of Reaction The enthalpy of a reaction, or heat of a reaction, can be found by ΔH = Hproducts – Hreactants ; ΔH can also be writ ...
File
... • If a chemical equation is reversed, then the sign of ΔrH changes. • If the coefficients of a chemical equation are altered by multiplying or dividing by a constant factor, then the ΔrH is altered by the same factor. ...
... • If a chemical equation is reversed, then the sign of ΔrH changes. • If the coefficients of a chemical equation are altered by multiplying or dividing by a constant factor, then the ΔrH is altered by the same factor. ...
e c n i
... Chemical reactions produce new substances that can usually be detected by observing the evidence: ...
... Chemical reactions produce new substances that can usually be detected by observing the evidence: ...
Organometallic Reactions and Catalysis
... – Involved a carbene complex – The carbene reacts with an alkene to form a metallocyclobutane intermediate. The intermediate can either revert to reactants or form new products. – Schrock metathesis catalysts are most effective and the most studied (available commercially). ...
... – Involved a carbene complex – The carbene reacts with an alkene to form a metallocyclobutane intermediate. The intermediate can either revert to reactants or form new products. – Schrock metathesis catalysts are most effective and the most studied (available commercially). ...
Document
... solution containing silver-ammonia complex ions. When an aldehyde group is oxidized by this reagent, the silver ions are reduced to metallic silver, which forms a black precipitate and, if the test tube is clean, a silver mirror on the test tube. (E. Ferric Chloride Test for Phenols) When a phenol i ...
... solution containing silver-ammonia complex ions. When an aldehyde group is oxidized by this reagent, the silver ions are reduced to metallic silver, which forms a black precipitate and, if the test tube is clean, a silver mirror on the test tube. (E. Ferric Chloride Test for Phenols) When a phenol i ...
Module Description Template
... Students build on their knowledge of inorganic and physical chemistry from level 4. The module focuses on chemical and physical equilibria, chemical kinetics and their application for biological systems and transition metals; their uses, coordination chemistry, and complex formation, together with t ...
... Students build on their knowledge of inorganic and physical chemistry from level 4. The module focuses on chemical and physical equilibria, chemical kinetics and their application for biological systems and transition metals; their uses, coordination chemistry, and complex formation, together with t ...
PUC Schools - cloudfront.net
... Std 10: Organic Chemistry 44. A molecule of hexene has a) only single bonds between carbons b) a carbon-carbon double bond c) a carbon-carbon triple bond d) a hexagonally shaped ring structure 45. What functional group contains a hydrocarbon which ends in OH? a) alcohol b) ketone c) ether d) amine 4 ...
... Std 10: Organic Chemistry 44. A molecule of hexene has a) only single bonds between carbons b) a carbon-carbon double bond c) a carbon-carbon triple bond d) a hexagonally shaped ring structure 45. What functional group contains a hydrocarbon which ends in OH? a) alcohol b) ketone c) ether d) amine 4 ...
Physical Science
... Chemical reactions take place when chemical bonds are either formed or broken. Strong chemical bonds resist change: glass Weak chemical bonds breakdown easily: wood ...
... Chemical reactions take place when chemical bonds are either formed or broken. Strong chemical bonds resist change: glass Weak chemical bonds breakdown easily: wood ...