Introduction - HCC Learning Web
... The properties of any substance depend in part on the chemical bonds that hold the atoms of the substance together. The consequences of this dependence are very important in chemical reactions. Because bonds are formed or broken during a reaction, the properties of product molecules differ from thos ...
... The properties of any substance depend in part on the chemical bonds that hold the atoms of the substance together. The consequences of this dependence are very important in chemical reactions. Because bonds are formed or broken during a reaction, the properties of product molecules differ from thos ...
ChE 215, Physical Chemistry
... The objective of this course is to introduce the basic topics in Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics. In fact this course present collection of distinct topics particularly useful to chemical engineering students. The basic principles in the course are demonstrated by six experiments ...
... The objective of this course is to introduce the basic topics in Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics. In fact this course present collection of distinct topics particularly useful to chemical engineering students. The basic principles in the course are demonstrated by six experiments ...
Document
... During phase changes temperature and pressure are constant. (Heat transfer is reversible, so H = q = qrev) Calculate the entropy change when 1 mole of liquid water evaporates at 100oC (Hvap = +44 kJ/mol) ...
... During phase changes temperature and pressure are constant. (Heat transfer is reversible, so H = q = qrev) Calculate the entropy change when 1 mole of liquid water evaporates at 100oC (Hvap = +44 kJ/mol) ...
1 - contentextra
... Addition reaction A reaction in which two reactants combine to form a single product. This type of reaction is typical of unsaturated compounds. Alcohol A homologous series containing the functional group –OH. Their general formula is CnH2n + 1 OH. Aldehyde A homologous series containing a carbonyl ...
... Addition reaction A reaction in which two reactants combine to form a single product. This type of reaction is typical of unsaturated compounds. Alcohol A homologous series containing the functional group –OH. Their general formula is CnH2n + 1 OH. Aldehyde A homologous series containing a carbonyl ...
Fall.2008.Week9.Lesson.1 - reich
... (g) means the substance is a gas (l) means the substance is a liquid (s) means the substance is a solid (aq) means the substance is aqueous Aqueous means dissolved in water, which does not necessarily mean the compound was a liquid. Ethanol and sugar both become aqueous, but only one of them was a s ...
... (g) means the substance is a gas (l) means the substance is a liquid (s) means the substance is a solid (aq) means the substance is aqueous Aqueous means dissolved in water, which does not necessarily mean the compound was a liquid. Ethanol and sugar both become aqueous, but only one of them was a s ...
136KB - NZQA
... Since the monomer for this reaction, styrene, is an alkene, when polymerisation occurs, the double bond in each styrene molecule is broken, freeing up a bonding space on each of the C atoms that was part of the double bond. This allows the monomers to join together by forming covalent bonds to make ...
... Since the monomer for this reaction, styrene, is an alkene, when polymerisation occurs, the double bond in each styrene molecule is broken, freeing up a bonding space on each of the C atoms that was part of the double bond. This allows the monomers to join together by forming covalent bonds to make ...
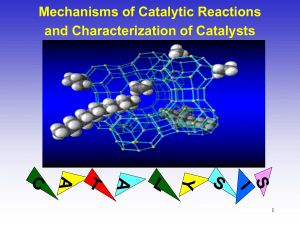
Catalysis and Catalyst
... The Activation Energy (Ea) determines how fast a reaction occurs, the higher Activation barrier, the slower the reaction rate. The lower the Activation barrier, the faster the reaction ...
... The Activation Energy (Ea) determines how fast a reaction occurs, the higher Activation barrier, the slower the reaction rate. The lower the Activation barrier, the faster the reaction ...
Ch. 21- Organic Reactions and Biochemistry
... hexamethylenediamine- in a step-growth condensation reaction Didn’t realize that he had made nylonkilled self (depressed) ...
... hexamethylenediamine- in a step-growth condensation reaction Didn’t realize that he had made nylonkilled self (depressed) ...
Big Idea 6
... Solubility constant (Ksp) • Remember, expression does not include (s) salt(s) cation (aq) + anion(aq) • Common ion effect: presence of an ion at the start of the “reaction”. Alters the solubility (think Le Chatelier) • pH and solubility: role of pH may impact the solubility of an insoluble salt bas ...
... Solubility constant (Ksp) • Remember, expression does not include (s) salt(s) cation (aq) + anion(aq) • Common ion effect: presence of an ion at the start of the “reaction”. Alters the solubility (think Le Chatelier) • pH and solubility: role of pH may impact the solubility of an insoluble salt bas ...
File
... Chemists use balanced chemical equations as a basis to calculate how much reactant is needed or product is formed in the reaction. A balanced chemical equation can be interpreted in terms of different quantities including numbers of atoms, molecules, or moles; mass; and volume. Mass and atoms ...
... Chemists use balanced chemical equations as a basis to calculate how much reactant is needed or product is formed in the reaction. A balanced chemical equation can be interpreted in terms of different quantities including numbers of atoms, molecules, or moles; mass; and volume. Mass and atoms ...
Slides
... priority on the other carbon the double bond is Z (zusammen) è If the highest priority groups are on opposite sides the alkeneis E (entgegen) ...
... priority on the other carbon the double bond is Z (zusammen) è If the highest priority groups are on opposite sides the alkeneis E (entgegen) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 7. What are the important guidelines to be followed while choosing alternate synthetic route? 8. Explain the umpolung concept of synthesis with suitable example. 9. Explain the mechanism of the following reaction. hv ...
... 7. What are the important guidelines to be followed while choosing alternate synthetic route? 8. Explain the umpolung concept of synthesis with suitable example. 9. Explain the mechanism of the following reaction. hv ...
Nucleophilic Substitution
... Let's look at how the various components of the reaction influence the reaction pathway: RReactivity order : CH3- > CH3CH2- > (CH3)2CH- > (CH3)3CIn an SN2 reaction, the transition state has 5 groups around the central C atom. As a consequence of the steric requirements at this center, less highly su ...
... Let's look at how the various components of the reaction influence the reaction pathway: RReactivity order : CH3- > CH3CH2- > (CH3)2CH- > (CH3)3CIn an SN2 reaction, the transition state has 5 groups around the central C atom. As a consequence of the steric requirements at this center, less highly su ...
Practice Test Packet
... 21. A solution is prepare by mixing 50.0mL of 0.10 M Pb(NO3)2 with 50.0 mL of 1.0 M KCl. Calculate the concentrations of Pb2+ and Cl- at equilibrium. Ksp for PbCl2 (s) is 1.6 x 10-5 22. If 100.0 mL of 0.100 M H2NNH2 ( Kb= 3.0 x 10-6) is titrated with 0.200 M HNO3. Calculate the pH in the following c ...
... 21. A solution is prepare by mixing 50.0mL of 0.10 M Pb(NO3)2 with 50.0 mL of 1.0 M KCl. Calculate the concentrations of Pb2+ and Cl- at equilibrium. Ksp for PbCl2 (s) is 1.6 x 10-5 22. If 100.0 mL of 0.100 M H2NNH2 ( Kb= 3.0 x 10-6) is titrated with 0.200 M HNO3. Calculate the pH in the following c ...
CHM 122 Chapter 8 -Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... A function or property whose value depends only on the present state, or condition, of the system, not on the path used to arrive at that state ...
... A function or property whose value depends only on the present state, or condition, of the system, not on the path used to arrive at that state ...
Enthalpy of combustion File
... • The standard enthalpy of combustion is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance completely reacts with oxygen under standard thermodynamic conditions • 1 atm and 298K ...
... • The standard enthalpy of combustion is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance completely reacts with oxygen under standard thermodynamic conditions • 1 atm and 298K ...