Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... alkene (11.1) a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon-carbon double bonds; an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n. alkyne (11.1) a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds; an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n-2. aromatic compoun ...
... alkene (11.1) a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon-carbon double bonds; an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n. alkyne (11.1) a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds; an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n-2. aromatic compoun ...
Diels-Alder Reaction
... http://www.chem.ufl.edu/~barbaro/2211L/diels-alder/da-proc.html The Diels-Alder reaction is probably the most familiar example of a reaction type known as a cycloaddition reaction, in which the conjugated p-systems of two reactants join to generate a new ring. The reactants in the Diels-Alder reacti ...
... http://www.chem.ufl.edu/~barbaro/2211L/diels-alder/da-proc.html The Diels-Alder reaction is probably the most familiar example of a reaction type known as a cycloaddition reaction, in which the conjugated p-systems of two reactants join to generate a new ring. The reactants in the Diels-Alder reacti ...
Equilibrium Constant - Faculty Server Contact
... John Dalton studied the effect of gases in a mixture. He observed that the Total Pressure of a gas mixture was the sum of the Partial Pressure of each gas. P total = P1 + P2 + P3 + .......Pn The Partial Pressure is defined as the pressure of a single gas in the mixture as if that gas alone occupied ...
... John Dalton studied the effect of gases in a mixture. He observed that the Total Pressure of a gas mixture was the sum of the Partial Pressure of each gas. P total = P1 + P2 + P3 + .......Pn The Partial Pressure is defined as the pressure of a single gas in the mixture as if that gas alone occupied ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... We will learn: a) the 5 major types. We will be able to: b) predict the products. For some, we will be able to: c) predict whether or not they will happen at all. ...
... We will learn: a) the 5 major types. We will be able to: b) predict the products. For some, we will be able to: c) predict whether or not they will happen at all. ...
020H Product Info
... identical. Isotopic coding enables univocal detection of the crosslinked products in mass spectra. Reaction products of GDHH6/D6 will manifest in mass spectra as doublets of peaks of equal intensity corresponding to light (H6) and heavy (D6) forms of the reagent separated by 6.04368 Da divided by ch ...
... identical. Isotopic coding enables univocal detection of the crosslinked products in mass spectra. Reaction products of GDHH6/D6 will manifest in mass spectra as doublets of peaks of equal intensity corresponding to light (H6) and heavy (D6) forms of the reagent separated by 6.04368 Da divided by ch ...
chemical reaction
... diatomic molecules, such as H2. Each of these elements is represented in an equation by its molecular formula. Other elements in the elemental state are usually represented simply by their atomic symbols. For Example carbon is represented as C. The symbols are not given any subscripts because the el ...
... diatomic molecules, such as H2. Each of these elements is represented in an equation by its molecular formula. Other elements in the elemental state are usually represented simply by their atomic symbols. For Example carbon is represented as C. The symbols are not given any subscripts because the el ...
Physical Organic Chemistry
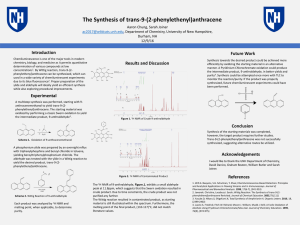
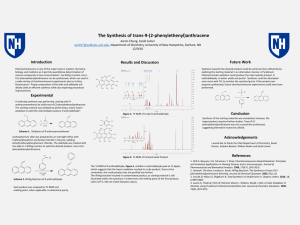
... Elimination reaction: to eliminate two atoms, two groups, or one atom and one group without substituted with another atom or group. The elimination of HX molecule from alkyl derivatives. While X is a halogen or ester… etc. the hydrogen atom on adjacent carbon with X Elimination reactions and n ...
... Elimination reaction: to eliminate two atoms, two groups, or one atom and one group without substituted with another atom or group. The elimination of HX molecule from alkyl derivatives. While X is a halogen or ester… etc. the hydrogen atom on adjacent carbon with X Elimination reactions and n ...
Hess`s law and Bond Enthalpy Practice
... Calculate Δ Ho for this reaction by combining the equations (and Δ Ho’s) for the following reactions. i) 2 C2H2 (g) + 5 O2 (g) —> 4 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (l) Δ Ho = - 2599 kJ ii) 2 C2H6 (g) + 7 O2 (g) —> 4 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (l) Δ Ho = - 3119 kJ iii) 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) —> 2 H2O (l) Δ Ho = - 572 kJ 2) When hea ...
... Calculate Δ Ho for this reaction by combining the equations (and Δ Ho’s) for the following reactions. i) 2 C2H2 (g) + 5 O2 (g) —> 4 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (l) Δ Ho = - 2599 kJ ii) 2 C2H6 (g) + 7 O2 (g) —> 4 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (l) Δ Ho = - 3119 kJ iii) 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) —> 2 H2O (l) Δ Ho = - 572 kJ 2) When hea ...
Creative Molecules Inc. ADH
... COOH-COOH crosslinking. ADH-H8/D8 is an isotopically-coded Adipic acid 1,6-DiHydrazide which can form crosslinks between carboxy-groups when used together with carboxy-group activating reagents such as EDC or DMTMM [1,2]. Light (H8) and heavy (D8) forms of the reagent differ by 8 deuterium atoms in ...
... COOH-COOH crosslinking. ADH-H8/D8 is an isotopically-coded Adipic acid 1,6-DiHydrazide which can form crosslinks between carboxy-groups when used together with carboxy-group activating reagents such as EDC or DMTMM [1,2]. Light (H8) and heavy (D8) forms of the reagent differ by 8 deuterium atoms in ...
Carbon Compounds
... releases 12. chemical reaction that releases more energy than it absorb 13. amount of energy that needs to be absorbed for a chemical reaction to start 14. substances changed during a chemical reaction 15. substances made by a chemical reaction 16. state reached when reactants and products are made ...
... releases 12. chemical reaction that releases more energy than it absorb 13. amount of energy that needs to be absorbed for a chemical reaction to start 14. substances changed during a chemical reaction 15. substances made by a chemical reaction 16. state reached when reactants and products are made ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... We will learn: a) the 5 major types. We will be able to: b) predict the products. For some, we will be able to: c) predict whether or not they will happen at all. ...
... We will learn: a) the 5 major types. We will be able to: b) predict the products. For some, we will be able to: c) predict whether or not they will happen at all. ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... We will learn: a) the 5 major types. We will be able to: b) predict the products. For some, we will be able to: c) predict whether or not they will happen at all. ...
... We will learn: a) the 5 major types. We will be able to: b) predict the products. For some, we will be able to: c) predict whether or not they will happen at all. ...
Unit 15 Electrochemistry
... Caused by a difference in potential energy between the different electrodes. Allows electrons to be pushed Denoted Ecell , measured in volts, V Also called cell potential ...
... Caused by a difference in potential energy between the different electrodes. Allows electrons to be pushed Denoted Ecell , measured in volts, V Also called cell potential ...
Topic 1: Chemical Reactions
... commonplace everyday occurrences: the burning of gas in a cooker, the rusting of cars, the hardening of glues, the digestion of food and so on. Reference should also be made to the work of chemists in developing materials which affect our way of life, although great care needs to be exercised in wid ...
... commonplace everyday occurrences: the burning of gas in a cooker, the rusting of cars, the hardening of glues, the digestion of food and so on. Reference should also be made to the work of chemists in developing materials which affect our way of life, although great care needs to be exercised in wid ...