Name / Functional Group
... 1. Put on your goggles. 2. You need a water bath of approximately 60°C. Fill a 400 mL beaker about 1/3 full of tap water and heat it to boiling by turning on the hot plate to “10”. 2. Place one spatula-tip of solid salicylic acid into the test tube (about ¼ tsp). 3. Add 20 drop of methanol (methyl a ...
... 1. Put on your goggles. 2. You need a water bath of approximately 60°C. Fill a 400 mL beaker about 1/3 full of tap water and heat it to boiling by turning on the hot plate to “10”. 2. Place one spatula-tip of solid salicylic acid into the test tube (about ¼ tsp). 3. Add 20 drop of methanol (methyl a ...
Ch. 8 Notes (Chemical Reactions) Teacher 2010
... Ch. 8 Notes -- Chemical Reactions Chemical equations give information in two major areas: Reactants products 1. _____________ and ______________ of the reaction. amount 2. Coefficients of a balanced chemical equation tell us the ______ of the substances involved. ...
... Ch. 8 Notes -- Chemical Reactions Chemical equations give information in two major areas: Reactants products 1. _____________ and ______________ of the reaction. amount 2. Coefficients of a balanced chemical equation tell us the ______ of the substances involved. ...
Document
... 65. Which of the following is true of both exothermic and endothermic reactions? A They absorb heat B They release heat C They require some energy to start D They use more energy than they produce ANSWER: C ...
... 65. Which of the following is true of both exothermic and endothermic reactions? A They absorb heat B They release heat C They require some energy to start D They use more energy than they produce ANSWER: C ...
Lecture 6 – Thermochemistry
... reactant and product 3. The phases of all reactant and product species must be stated 4. The value of ΔH applies when products and reactants are at the same temperature, usually 25 °C ...
... reactant and product 3. The phases of all reactant and product species must be stated 4. The value of ΔH applies when products and reactants are at the same temperature, usually 25 °C ...
This exam will consist of 30-35 multiple choice or short answer
... What are the starting materials? Product? What are the structures? What are some physical properties of the starting materials and product? What is petroleum ether? What is the purpose of using pet ether in this experiment? What is the mechanism of the reaction? Why must the reaction apparatus be dr ...
... What are the starting materials? Product? What are the structures? What are some physical properties of the starting materials and product? What is petroleum ether? What is the purpose of using pet ether in this experiment? What is the mechanism of the reaction? Why must the reaction apparatus be dr ...
QuickStudy - Organic Chemistry Fundamentals
... • Each step passes through an energy barrier, characterized by an unstable configuration termed the transition state (TS). • The height of the barrier is the activation energy (Ea). • The slowest step in the mechanism, the ratedetermining step, limits the overall reaction rate. • Key principle: exam ...
... • Each step passes through an energy barrier, characterized by an unstable configuration termed the transition state (TS). • The height of the barrier is the activation energy (Ea). • The slowest step in the mechanism, the ratedetermining step, limits the overall reaction rate. • Key principle: exam ...
Thermochemistry Note
... enthalpies of formation You will compare energy changes associated with a variety of chemical reactions through the analysis of data and energy diagrams This is another method to determine enthalpy for a reaction without having to perform calorimetry and a shortcut to Hess’ law depending on the in ...
... enthalpies of formation You will compare energy changes associated with a variety of chemical reactions through the analysis of data and energy diagrams This is another method to determine enthalpy for a reaction without having to perform calorimetry and a shortcut to Hess’ law depending on the in ...
Document
... Standard enthalpy of formation (DH0f) is the heat change that results when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements at a pressure of 1 atm. The standard enthalpy of formation of any element in its most stable form is zero. 0 (C, graphite) = 0 DH f DH0f (O2) = 0 0 (C, diamond) = 1.90 kJ/mol ...
... Standard enthalpy of formation (DH0f) is the heat change that results when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements at a pressure of 1 atm. The standard enthalpy of formation of any element in its most stable form is zero. 0 (C, graphite) = 0 DH f DH0f (O2) = 0 0 (C, diamond) = 1.90 kJ/mol ...
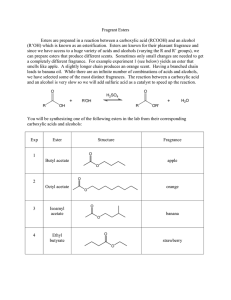
Fragrant Esters Esters are prepared in a reaction between a
... can prepare esters that produce different scents. Sometimes only small changes are needed to get a completely different fragrance. For example experiment 1 (see below) yields an ester that smells like apple. A slightly longer chain produces an orange scent. Having a branched chain leads to banana oi ...
... can prepare esters that produce different scents. Sometimes only small changes are needed to get a completely different fragrance. For example experiment 1 (see below) yields an ester that smells like apple. A slightly longer chain produces an orange scent. Having a branched chain leads to banana oi ...