Science TAKS Objective 5
... Resonance is the vibration F interference of another object struck by a G the Doppler effect wave of the correct frequency. Since the forks H resonance are identical, the second J standing waves one receives the correct frequency to begin vibrating. ...
... Resonance is the vibration F interference of another object struck by a G the Doppler effect wave of the correct frequency. Since the forks H resonance are identical, the second J standing waves one receives the correct frequency to begin vibrating. ...
Chemistry Review for End of year final honors
... reaction, is called ______________________. The reactant left over is called ________________ 5.) What is the maximum number of grams of PH3 that can be formed when 6.2 g of phosphorous reacts with 4.0 g of hydrogen to form PH3? P4 + 6H2 4PH3 6.) The first step in most stoichiometry problems that ...
... reaction, is called ______________________. The reactant left over is called ________________ 5.) What is the maximum number of grams of PH3 that can be formed when 6.2 g of phosphorous reacts with 4.0 g of hydrogen to form PH3? P4 + 6H2 4PH3 6.) The first step in most stoichiometry problems that ...
Solution - Georgetown Independent School District
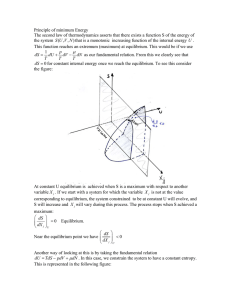
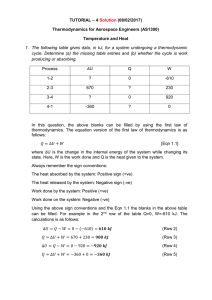
... (flows from a warmer object to a cooler one – heat transfers because of temperature difference but, remember, temperature is not a measure of energy—it just reflects the motion of particles) ...
... (flows from a warmer object to a cooler one – heat transfers because of temperature difference but, remember, temperature is not a measure of energy—it just reflects the motion of particles) ...
Spectroscopic methods for biology and medicine
... of shooting particles with well defined properties at the sample and analyzing particles which are emitted by the sample as indicated in Fig. 1.4. As a result, the measurement is due to the properties of the sample, the properties of the probing particle, and the physical laws governing the interact ...
... of shooting particles with well defined properties at the sample and analyzing particles which are emitted by the sample as indicated in Fig. 1.4. As a result, the measurement is due to the properties of the sample, the properties of the probing particle, and the physical laws governing the interact ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... Atoms tend to lose, gain, or ___________ electrons to complete their valence shells. When a chlorine atom gains an electron, it fills its valence shell forming a negative chloride________. Whenever ionic solids are formed, __________ is involved. An ionic material is composed of positive ions bonded ...
... Atoms tend to lose, gain, or ___________ electrons to complete their valence shells. When a chlorine atom gains an electron, it fills its valence shell forming a negative chloride________. Whenever ionic solids are formed, __________ is involved. An ionic material is composed of positive ions bonded ...
Kinetic Theory of Gas - emily
... the average kinetic energy of molecules in a gas is proportional to the temperature. Molecules move faster at higher temperatures. ...
... the average kinetic energy of molecules in a gas is proportional to the temperature. Molecules move faster at higher temperatures. ...
Electronic States in Solids. What will be covered? 1. Electronic
... Hence, when the atoms come close together the outer electrons begin to interact and the electronic energy levels subdivide, i.e. the 1s atomic energy level splits into two separate and distinct energy levels. Now let N identical atoms be placed on a lattice with interatomic spacing so large that th ...
... Hence, when the atoms come close together the outer electrons begin to interact and the electronic energy levels subdivide, i.e. the 1s atomic energy level splits into two separate and distinct energy levels. Now let N identical atoms be placed on a lattice with interatomic spacing so large that th ...
Heat and temperature - Home
... nature of matter and the surrounding space • Greeks - earliest written ideas on atoms • Current view – Matter comprised of microscopic particles - atoms – Atoms combine to form molecules – Many macroscopic phenomena can be traced to interactions on this level ...
... nature of matter and the surrounding space • Greeks - earliest written ideas on atoms • Current view – Matter comprised of microscopic particles - atoms – Atoms combine to form molecules – Many macroscopic phenomena can be traced to interactions on this level ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.