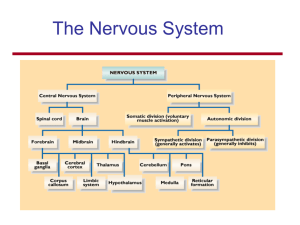
The Nervous System
... • Such drugs have two general effects:1)they impact the limbic system, and 2)they either promote or decrease the action of a particular neurotransmitter. • Drug abuse is apparent when a person takes a drug at a dose level and under circumstances that increase the potential for a harmful effect. • Ta ...
... • Such drugs have two general effects:1)they impact the limbic system, and 2)they either promote or decrease the action of a particular neurotransmitter. • Drug abuse is apparent when a person takes a drug at a dose level and under circumstances that increase the potential for a harmful effect. • Ta ...
chpt. 1 ppt
... This branch explains why humans do what they do in terms of adaptive value (survival of the species. Why do women usually prefer the guy on the right for long-term relationships? ...
... This branch explains why humans do what they do in terms of adaptive value (survival of the species. Why do women usually prefer the guy on the right for long-term relationships? ...
Behaviorism
... This branch explains why humans do what they do in terms of adaptive value (survival of the species. Why do women usually prefer the guy on the right for long-term relationships? ...
... This branch explains why humans do what they do in terms of adaptive value (survival of the species. Why do women usually prefer the guy on the right for long-term relationships? ...
Lesson 1: Attributes of Learning and Classical Conditioning
... a cognitive map, even when there is neither reward nor motivation for learning. Later, when reward is available, rats that have had the opportunity to explore will perform better than those that have not had that opportunity C. Observational learning, described by Albert Bandura, is defined as learn ...
... a cognitive map, even when there is neither reward nor motivation for learning. Later, when reward is available, rats that have had the opportunity to explore will perform better than those that have not had that opportunity C. Observational learning, described by Albert Bandura, is defined as learn ...
Chapter 2: Brain and Behavior
... acts like the brain’s alarm clock Activates and arouses cerebral cortex ...
... acts like the brain’s alarm clock Activates and arouses cerebral cortex ...
6. Brain Lateralization
... Next, with the aid of a computer, this energy is converted into three-dimensional pictures. A physician can then look at cross-sectional images of the body organ from any angle in order to detect any functional problems. In case of brain study, we follow the same procedure and study the function of ...
... Next, with the aid of a computer, this energy is converted into three-dimensional pictures. A physician can then look at cross-sectional images of the body organ from any angle in order to detect any functional problems. In case of brain study, we follow the same procedure and study the function of ...
The Biological Perspective
... 2 Adrenal glands - located on the top of each kidney Critical role in regulating the body’s response to stress Adrenal glands are divided into 2 parts Adrenal medulla – releases epinephrine and norepinephrine when ...
... 2 Adrenal glands - located on the top of each kidney Critical role in regulating the body’s response to stress Adrenal glands are divided into 2 parts Adrenal medulla – releases epinephrine and norepinephrine when ...
Decision Making in Recurrent Neuronal Circuits
... endowed with reward-dependent synaptic plasticity is able to produce adaptive choice behavior. While decision threshold is a core concept for reaction time tasks, it can be dissociated from a general decision rule. Moreover, perceptual decisions and value-based economic choices are described within ...
... endowed with reward-dependent synaptic plasticity is able to produce adaptive choice behavior. While decision threshold is a core concept for reaction time tasks, it can be dissociated from a general decision rule. Moreover, perceptual decisions and value-based economic choices are described within ...
Learning
... Responding decreases when reinforcement stops Reappearance of extinguished response Organism’s response to similar stimuli also reinforced Organism learns that certain responses will be reinforced ...
... Responding decreases when reinforcement stops Reappearance of extinguished response Organism’s response to similar stimuli also reinforced Organism learns that certain responses will be reinforced ...
The Nervous System
... • This polarity reversal travels down the neuron • Neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminals ...
... • This polarity reversal travels down the neuron • Neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminals ...
Slides - Gorman Lab
... Cortical Plasticity – brain modified by experience ! Maps are flexible # ...
... Cortical Plasticity – brain modified by experience ! Maps are flexible # ...
The Nervous System http://www.gmstigers.com/apps/pages/index
... your back. It serves as the main pathway for messages between the brain and the body. In men the spinal cord is about 45 centimeters long. In women it is about 43 centimeters long. Your backbone protects the spinal cord from damage. The organs of the nervous system - brain, neurons, and spinal cord ...
... your back. It serves as the main pathway for messages between the brain and the body. In men the spinal cord is about 45 centimeters long. In women it is about 43 centimeters long. Your backbone protects the spinal cord from damage. The organs of the nervous system - brain, neurons, and spinal cord ...
Operant versus classical conditioning: Law of Effect
... – Raise the criterion or rule for getting a C/T – Build the response in a series of small steps – Think of it as going up a staircase towards your goal. ...
... – Raise the criterion or rule for getting a C/T – Build the response in a series of small steps – Think of it as going up a staircase towards your goal. ...
2002-2003 - Parkinson Canada
... The current project will attempt to study how dopamine is released by brain cells. In particular, an area of the brain called the cerebral cortex seems to play a role in regulating dopamine release. We will use a technique called transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to induce electrical activity ...
... The current project will attempt to study how dopamine is released by brain cells. In particular, an area of the brain called the cerebral cortex seems to play a role in regulating dopamine release. We will use a technique called transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to induce electrical activity ...
THE LIMBIC SYSTEM
... The amygdala is involved in signaling the cortex of motivationally significant stimuli such as those related to reward and fear in addition to social functions such as mating. The amygdala is the limbic structure that assigns the sensory information an emotional interpretation and instructs the bod ...
... The amygdala is involved in signaling the cortex of motivationally significant stimuli such as those related to reward and fear in addition to social functions such as mating. The amygdala is the limbic structure that assigns the sensory information an emotional interpretation and instructs the bod ...
Slide ()
... The functional organization of the motor map of a rat changes rapidly after transection of the facial nerve. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanes et al. 1988 and from Jacobs and Donoghue 1991.) A. A surface view of the rat's frontal cortex shows the normal somatotopic arrangement of areas repres ...
... The functional organization of the motor map of a rat changes rapidly after transection of the facial nerve. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanes et al. 1988 and from Jacobs and Donoghue 1991.) A. A surface view of the rat's frontal cortex shows the normal somatotopic arrangement of areas repres ...
Part II Classical Conditioning
... Animals may use reasoning (cognitive factors) in learning a behavior. Operant conditioning ignores cognitive factors in learning. However, some research has found that animals do use reasoning. For instance, in Mackintosh’s (1994) study, rats pressed the lever in a Skinner box for a food reward. The ...
... Animals may use reasoning (cognitive factors) in learning a behavior. Operant conditioning ignores cognitive factors in learning. However, some research has found that animals do use reasoning. For instance, in Mackintosh’s (1994) study, rats pressed the lever in a Skinner box for a food reward. The ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... skeletal muscle and joints • Or It is the conscious perception of the position and movements of the different parts of the body, particularly the limbs and joints. ...
... skeletal muscle and joints • Or It is the conscious perception of the position and movements of the different parts of the body, particularly the limbs and joints. ...
09. týden Ethology
... Companion animals live in the company of humans; and also provide company to humans. Behavior is the actions & reactions taken for growth, survival & reproduction (also motivations to fulfil needs). Behavioral patterns are organized segments of behavior with a specific aim and function. Animal-assis ...
... Companion animals live in the company of humans; and also provide company to humans. Behavior is the actions & reactions taken for growth, survival & reproduction (also motivations to fulfil needs). Behavioral patterns are organized segments of behavior with a specific aim and function. Animal-assis ...
Abnormal Brain Wiring as a Pathogenetic Mechanism in
... reduced functional coupling of prefrontal regions is related to more severe negative symptoms. Third, depressive symptoms were found to be related to lower levels of global connectivity of the anterior cingulate cortex. Finally, severity of cognitive features (including attention and disorientation) ...
... reduced functional coupling of prefrontal regions is related to more severe negative symptoms. Third, depressive symptoms were found to be related to lower levels of global connectivity of the anterior cingulate cortex. Finally, severity of cognitive features (including attention and disorientation) ...
Conditioning Definitions - No Spaces Between
... sound will diminish. 5. a term used in both classical and operant conditioning. It involves the ability to distinguish between one stimulus and similar stimuli. 7. your teacher's last name. 10. refers to the gradual weakening of a conditioned response that results in the behavior decreasing or disap ...
... sound will diminish. 5. a term used in both classical and operant conditioning. It involves the ability to distinguish between one stimulus and similar stimuli. 7. your teacher's last name. 10. refers to the gradual weakening of a conditioned response that results in the behavior decreasing or disap ...