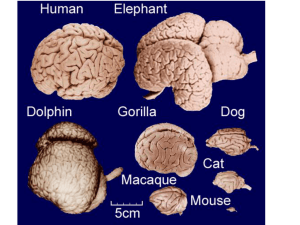
Bio70 Psychobiology Fall 2006 First Midterm October 12 Version A
... a. They exchange information with distant neurons. b. They abide by the all-or-none principle. c. The change in membrane potential increases as it travels. d. They have short dendrites and axons. ...
... a. They exchange information with distant neurons. b. They abide by the all-or-none principle. c. The change in membrane potential increases as it travels. d. They have short dendrites and axons. ...
Midterm 1 - University of California, Berkeley
... psychology -- a set of naive, traditional ideas about the mind and behavior, unsupported by scientific evidence, that are doomed to be replaced by a more sophisticated, truly scientific view. ...
... psychology -- a set of naive, traditional ideas about the mind and behavior, unsupported by scientific evidence, that are doomed to be replaced by a more sophisticated, truly scientific view. ...
The Child’s Growth
... Some cells are analyzing form, while others are analyzing motion, others are analyzing color, and so on. ...
... Some cells are analyzing form, while others are analyzing motion, others are analyzing color, and so on. ...
fixed action patterns
... eggs in their neighbors' nests. In 2003, the researchers showed that coots can count their own eggs and reject ones laid in their nests by other coots. Their latest findings, published this week in Nature, show that coot parents can tell the difference between their own chicks and any impostors that ...
... eggs in their neighbors' nests. In 2003, the researchers showed that coots can count their own eggs and reject ones laid in their nests by other coots. Their latest findings, published this week in Nature, show that coot parents can tell the difference between their own chicks and any impostors that ...
PMHS - Socpsychvita
... Skinner is a major leader in operant conditioning. (OP uses positive and negative reinforcement to get animals/people to voluntarily act a certain way). UNDERLINE POSITIVE INFLUENCES IN CRIB One thing Skinner did was build a conditioning chamber for his daughter as an improvement over the convention ...
... Skinner is a major leader in operant conditioning. (OP uses positive and negative reinforcement to get animals/people to voluntarily act a certain way). UNDERLINE POSITIVE INFLUENCES IN CRIB One thing Skinner did was build a conditioning chamber for his daughter as an improvement over the convention ...
Paper by Daniel Romer (2010) "Adolescent Risk Taking,Impulsivity
... Tannock, 1999). These tasks assess the ability to monitor conflicting cues to action and inhibit prepotent responses when they are no longer adaptive. In young children, a simpler task involves monitoring cues that flank a dominant focus of attention (the flanker task). Children with ADHD do less we ...
... Tannock, 1999). These tasks assess the ability to monitor conflicting cues to action and inhibit prepotent responses when they are no longer adaptive. In young children, a simpler task involves monitoring cues that flank a dominant focus of attention (the flanker task). Children with ADHD do less we ...
Social Science as a Complex Social Science as a
... perspectives, and this multiplicity includes other social sciences without being at all limited to social sciences. A grand strategy of Epistemic Pluralism is what is being advocated here. Minimal epistemic pluralism is not uncommon in most social sciences, more in some than in others. A grand strat ...
... perspectives, and this multiplicity includes other social sciences without being at all limited to social sciences. A grand strategy of Epistemic Pluralism is what is being advocated here. Minimal epistemic pluralism is not uncommon in most social sciences, more in some than in others. A grand strat ...
Social Learning Theory
... A symbol is something that people create and use to stand for something else. (e.g., object, ...
... A symbol is something that people create and use to stand for something else. (e.g., object, ...
The Sensorimotor System
... side of the body contralateral to a brain lesion (not a simple sensory or motor deficit). Often associated with large lesions of the right posterior parietal lobe. ...
... side of the body contralateral to a brain lesion (not a simple sensory or motor deficit). Often associated with large lesions of the right posterior parietal lobe. ...
The Mirror Mechanism: A Mechanism for Understanding Others
... the mirror mechanism in social cognition. I will discuss this issue and will show that, although there are several mechanisms through which one can understand the behaviour of others, the parieto-frontal mechanism is the only one that allows understanding others’ actions from the inside giving the o ...
... the mirror mechanism in social cognition. I will discuss this issue and will show that, although there are several mechanisms through which one can understand the behaviour of others, the parieto-frontal mechanism is the only one that allows understanding others’ actions from the inside giving the o ...
Consumer Behavior
... consumers use to compare competing product alternatives. • Students choosing a university may use many different selection criteria, such as: size, reputation, costs, location, programs, living accommodations, or social life. • Some criteria are more important than others, so we still need to know h ...
... consumers use to compare competing product alternatives. • Students choosing a university may use many different selection criteria, such as: size, reputation, costs, location, programs, living accommodations, or social life. • Some criteria are more important than others, so we still need to know h ...
Chapter 9 Part 3 Central Nervous System
... Neuroendocrine and visceral responses – Coordinated in the hypothalamus and medulla – Hypothalamus contains centers for: • Temperature regulation • Eating • Control of body osmolarity, etc. • Response to stimulation of these centers can be in the form of neural or hormonal reflexes or a behavioral ...
... Neuroendocrine and visceral responses – Coordinated in the hypothalamus and medulla – Hypothalamus contains centers for: • Temperature regulation • Eating • Control of body osmolarity, etc. • Response to stimulation of these centers can be in the form of neural or hormonal reflexes or a behavioral ...
(30 MCQ answers). - Blackwell Publishing
... over days, ingest more of it. This regulation involves learning to associate the sight, taste, smell and texture of the food with the energy that is released from it in the hours after it is eaten. 13) Answer: (d). In the 1950s and 1960s, it was argued that food intake is controlled by two interacti ...
... over days, ingest more of it. This regulation involves learning to associate the sight, taste, smell and texture of the food with the energy that is released from it in the hours after it is eaten. 13) Answer: (d). In the 1950s and 1960s, it was argued that food intake is controlled by two interacti ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM
... not reached, the action potential will not occur at all. If the threshold is reached or exceeded a full action potential will result. ...
... not reached, the action potential will not occur at all. If the threshold is reached or exceeded a full action potential will result. ...
Central Nervous System
... The temporal lobe is responsible for visual memory/object recognition, processing sound and smell, and understanding language. It is located inferior to the lateral sulcus or sylvian fissure, and is positioned between the frontal and occipital lobe. ...
... The temporal lobe is responsible for visual memory/object recognition, processing sound and smell, and understanding language. It is located inferior to the lateral sulcus or sylvian fissure, and is positioned between the frontal and occipital lobe. ...
Sensory Cortex
... brain and some parts the new brain? • A. Old brain parts are what exist in very young children, and new parts develop later • B. Old brain developed first according to evolution. • C. The old brain becomes more active as we grow older • D. The new brain deals with new information, while the old brai ...
... brain and some parts the new brain? • A. Old brain parts are what exist in very young children, and new parts develop later • B. Old brain developed first according to evolution. • C. The old brain becomes more active as we grow older • D. The new brain deals with new information, while the old brai ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_8_lecture_part_1
... 5) This depolarizes the cell and activates NMDA receptor channels (which were inactive due to a Mg2+ blocking the pore). 6) NMDA allows Ca2+ and Na+ in. 7) The Ca2+ binds to a protein called calmodulin, which in turn activates an enzyme called CaMKII. 8) CaMKII causes more AMPA receptors to fuse to ...
... 5) This depolarizes the cell and activates NMDA receptor channels (which were inactive due to a Mg2+ blocking the pore). 6) NMDA allows Ca2+ and Na+ in. 7) The Ca2+ binds to a protein called calmodulin, which in turn activates an enzyme called CaMKII. 8) CaMKII causes more AMPA receptors to fuse to ...
Alzheimer`s Disease: Review Questions
... 1. (D) Temporal lobe, frontal lobe, and hippocampus. The temporal lobe, frontal lobe, and hippocampus are the areas most involved with cortical loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Major association areas are also involved with notable cortical atrophy. Relatively spared areas include the motor and sensory ...
... 1. (D) Temporal lobe, frontal lobe, and hippocampus. The temporal lobe, frontal lobe, and hippocampus are the areas most involved with cortical loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Major association areas are also involved with notable cortical atrophy. Relatively spared areas include the motor and sensory ...
Passive music listening spontaneously engages limbic and
... music [5], the intensity of chills was positively correlated with activations in the ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens), right thalamus, right orbitofrontal cortex, anterior cingulate (BA 24/32), bilateral insula, supplementary motor area, midbrain, and cerebellum. Several of these regions were ac ...
... music [5], the intensity of chills was positively correlated with activations in the ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens), right thalamus, right orbitofrontal cortex, anterior cingulate (BA 24/32), bilateral insula, supplementary motor area, midbrain, and cerebellum. Several of these regions were ac ...
The University of Texas at Dallas Callier Center for Communication
... Communication technologies under investigation include amplification devices (Roeser). In addition, two new Callier initiatives address Autism Spectrum Disorders and the quality of scientific evidence for clinical decision making. For more information about the current research visit our Web site at ...
... Communication technologies under investigation include amplification devices (Roeser). In addition, two new Callier initiatives address Autism Spectrum Disorders and the quality of scientific evidence for clinical decision making. For more information about the current research visit our Web site at ...
Decoupling Neural Networks From Reality: Dissociative Experiences
... dipole density coefficients and dissociation scores. The score on the dissociation scale was significantly and positively related to the density of abnormal slow-wave generators in the left ventral region of the anterior cortical structures (left ventrolateral frontal cortex), r(21) = .41, p < .05, ...
... dipole density coefficients and dissociation scores. The score on the dissociation scale was significantly and positively related to the density of abnormal slow-wave generators in the left ventral region of the anterior cortical structures (left ventrolateral frontal cortex), r(21) = .41, p < .05, ...