Making Sense of Animal Conditioning
... example, morphine is a pain killer (the UR). In contrast, animals become hypersensitive to pain during a CS that predicts morphine (the CR). Siegel went on to argue that classical conditioning may contribute to the build up of tolerance for drugs and to the withdrawal symptoms that are observed when ...
... example, morphine is a pain killer (the UR). In contrast, animals become hypersensitive to pain during a CS that predicts morphine (the CR). Siegel went on to argue that classical conditioning may contribute to the build up of tolerance for drugs and to the withdrawal symptoms that are observed when ...
An architectural model of conscious and unconscious brain
... contents, and (c) low computational efficiency. Thus skilled speakers cannot consciously label the syntax of a sentence, even though they constantly use the results of unconscious syntactic analysis. In contrast to conscious contents, unconscious events showed (a’) much larger capacity limits,6 (b’) ...
... contents, and (c) low computational efficiency. Thus skilled speakers cannot consciously label the syntax of a sentence, even though they constantly use the results of unconscious syntactic analysis. In contrast to conscious contents, unconscious events showed (a’) much larger capacity limits,6 (b’) ...
File - Ms. Beam`s Class
... The Law of Effect • Edward Thorndike • Locked cats in a cage to make them try and escape • Behavior changes because of its consequences. • Rewards strengthen behavior. • If consequences are unpleasant, the StimulusReward connection will weaken. • Called the whole process instrumental learning. ...
... The Law of Effect • Edward Thorndike • Locked cats in a cage to make them try and escape • Behavior changes because of its consequences. • Rewards strengthen behavior. • If consequences are unpleasant, the StimulusReward connection will weaken. • Called the whole process instrumental learning. ...
Spiking Neurons with Boltzmann-like Properties to
... This leaves four parameters to describe the neural model. Threshold theta is 2.2; decay D is 1.12; fatigue increase Fc is 0.45; and fatigue recovery Fr is 0.01. In past simulations, these were free parameters for simulation, but these values have been selected to fit the firing behaviour to biologic ...
... This leaves four parameters to describe the neural model. Threshold theta is 2.2; decay D is 1.12; fatigue increase Fc is 0.45; and fatigue recovery Fr is 0.01. In past simulations, these were free parameters for simulation, but these values have been selected to fit the firing behaviour to biologic ...
Developmental mechanics of the primate cerebral cortex
... we illustrate the substantial impact of mechanical forces on the development, morphology, and functioning of the primate cerebral cortex. Based on the analysis of quantitative structural data for prefrontal cortices of the adult rhesus monkey, we demonstrate that (1) the characteristic shape of cort ...
... we illustrate the substantial impact of mechanical forces on the development, morphology, and functioning of the primate cerebral cortex. Based on the analysis of quantitative structural data for prefrontal cortices of the adult rhesus monkey, we demonstrate that (1) the characteristic shape of cort ...
The basal ganglia and cortex implement optimal decision making
... alternative actions, and the basal ganglia, hypothesised to act as a central ‘switch’ in gating behavioural requests. However, despite our relatively detailed knowledge of basal ganglia biology and its connectivity with the cortex, and numerical simulation studies demonstrating selective function, n ...
... alternative actions, and the basal ganglia, hypothesised to act as a central ‘switch’ in gating behavioural requests. However, despite our relatively detailed knowledge of basal ganglia biology and its connectivity with the cortex, and numerical simulation studies demonstrating selective function, n ...
How Is the Brain Organized?
... instance, they named one region of the brain the gyrus fornicatus because they thought it had a role in sexual function. In fact, most of this region has nothing to do with sexual function. Another area was named the red nucleus because it appears reddish in fresh tissue. This name denotes nothing o ...
... instance, they named one region of the brain the gyrus fornicatus because they thought it had a role in sexual function. In fact, most of this region has nothing to do with sexual function. Another area was named the red nucleus because it appears reddish in fresh tissue. This name denotes nothing o ...
Neurocircuitry of Addiction
... Drug addiction is a chronically relapsing disorder that has been characterized by (1) compulsion to seek and take the drug, (2) loss of control in limiting intake, and (3) emergence of a negative emotional state (eg, dysphoria, anxiety, irritability) reflecting a motivational withdrawal syndrome whe ...
... Drug addiction is a chronically relapsing disorder that has been characterized by (1) compulsion to seek and take the drug, (2) loss of control in limiting intake, and (3) emergence of a negative emotional state (eg, dysphoria, anxiety, irritability) reflecting a motivational withdrawal syndrome whe ...
Ability - WordPress.com
... other way, moving from specific observations to broader generalizations and theories. Informally, we sometimes call this a "bottom up" approach (please note that it's "bottom up" and not "bottoms up" which is the kind of thing the bartender says to customers when he's trying to close for the night!) ...
... other way, moving from specific observations to broader generalizations and theories. Informally, we sometimes call this a "bottom up" approach (please note that it's "bottom up" and not "bottoms up" which is the kind of thing the bartender says to customers when he's trying to close for the night!) ...
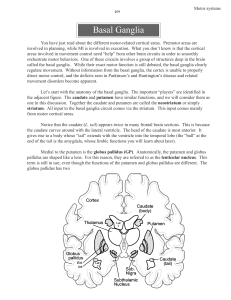
Motor systems Basal ganglia
... the adjacent figure. The caudate and putamen have similar functions, and we will consider them as one in this discussion. Together the caudate and putamen are called the neostriatum or simply striatum. All input to the basal ganglia circuit comes via the striatum. This input comes mainly from motor ...
... the adjacent figure. The caudate and putamen have similar functions, and we will consider them as one in this discussion. Together the caudate and putamen are called the neostriatum or simply striatum. All input to the basal ganglia circuit comes via the striatum. This input comes mainly from motor ...
ch. 9 ppt
... environment? What happens when a learner is punished and cannot escape the punishment? The learner may give up trying to learn. ...
... environment? What happens when a learner is punished and cannot escape the punishment? The learner may give up trying to learn. ...
A non-invasive method to relate the timing of neural activity to white
... reveal white matter pathways that may contribute to interindividual variability in the timing of neural activity. The visual responses were evoked by fixating a saccadic goal and were timelocked to the end point of the saccade. Post-saccadic visual responses may maximize timing variability since prev ...
... reveal white matter pathways that may contribute to interindividual variability in the timing of neural activity. The visual responses were evoked by fixating a saccadic goal and were timelocked to the end point of the saccade. Post-saccadic visual responses may maximize timing variability since prev ...
Neurodevelopmental mechanisms of schizophrenia: understanding
... studies have revealed that both NRG1 and DISC1 are multifunctional in nature, with key roles during neurodevelopment [12–14]. Therefore, systematic studies of these factors from the time of the initial risks in early development to disease onset after puberty is likely to open a window on a mechanis ...
... studies have revealed that both NRG1 and DISC1 are multifunctional in nature, with key roles during neurodevelopment [12–14]. Therefore, systematic studies of these factors from the time of the initial risks in early development to disease onset after puberty is likely to open a window on a mechanis ...
Obsessive–Compulsive Symptoms and Related Sex Differences in
... den Heuvel, 2006; Saxena & Rauch, 2000). It has been hypothesized that an imbalance between these loops, resulting in a hyperactive ventral and hypoactive dorsal ...
... den Heuvel, 2006; Saxena & Rauch, 2000). It has been hypothesized that an imbalance between these loops, resulting in a hyperactive ventral and hypoactive dorsal ...
Chapter 9 PowerPoint - Trimble County Schools
... environment? What happens when a learner is punished and cannot escape the punishment? The learner may give up trying to learn. ...
... environment? What happens when a learner is punished and cannot escape the punishment? The learner may give up trying to learn. ...
Dynamical systems view
... Criticism of the representational approach An epic, twenty-year battle was fought over the cortical representation of movement. Do motor cortex neurons represent the direction of the hand during reaching, or do they represent other features of movement such as joint rotation or muscle output? Grazi ...
... Criticism of the representational approach An epic, twenty-year battle was fought over the cortical representation of movement. Do motor cortex neurons represent the direction of the hand during reaching, or do they represent other features of movement such as joint rotation or muscle output? Grazi ...
Open Questions on Mind, Genes, Consciousness
... and psychological disciplines that cannot be integrated in any other way. Such interdisciplinary in silico research appears to bridge the awkward Cartesian Gap between mind, gene, brain, and body via the concept of information. The genomic revolution made the concept of information the common denomi ...
... and psychological disciplines that cannot be integrated in any other way. Such interdisciplinary in silico research appears to bridge the awkward Cartesian Gap between mind, gene, brain, and body via the concept of information. The genomic revolution made the concept of information the common denomi ...
Circuits through prefrontal cortex, basal ganglia, and ventral anterior
... c New England Primate Research Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Accepted 22 March 2004 ...
... c New England Primate Research Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Accepted 22 March 2004 ...
Ch. 6: Learning through Conditioning compiled by Cetin I. Learning
... A. Skinner coined the term operant conditioning B. He emphasized the role of reinforcement in influencing behavior C. Reinforcement occurs when an event following a response increases an organism’s tendency to make that response D. Common experimental device was the Skinner Box, also called the oper ...
... A. Skinner coined the term operant conditioning B. He emphasized the role of reinforcement in influencing behavior C. Reinforcement occurs when an event following a response increases an organism’s tendency to make that response D. Common experimental device was the Skinner Box, also called the oper ...
xiao-ying-lu-southeast-university
... alcohol concentration rises, the excitation threshold increases quickly. Cell apoptosis occurs rapidly at concentration of 110mM. ...
... alcohol concentration rises, the excitation threshold increases quickly. Cell apoptosis occurs rapidly at concentration of 110mM. ...
Operant Conditioning
... reject the idea that they can be so easily conditioned. This is easily overcome by the generous use of examples of conditioning that occur in everyday life. Some examples include the development of conditioned fears such as to rats, snakes, elevators, open spaces, etc., and the development of habits ...
... reject the idea that they can be so easily conditioned. This is easily overcome by the generous use of examples of conditioning that occur in everyday life. Some examples include the development of conditioned fears such as to rats, snakes, elevators, open spaces, etc., and the development of habits ...
Neural correlates of a decision in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of
... © 1999 Nature America Inc. • http://neurosci.nature.com ...
... © 1999 Nature America Inc. • http://neurosci.nature.com ...
Psych 101
... of learning in which organisms associate their own actions with consequences behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement diminished if followed by punishment ...
... of learning in which organisms associate their own actions with consequences behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement diminished if followed by punishment ...
Prominent Theorist Research
... Skinner had to end up putting his technology in written form. But, with the new technology today some of his programs from the 60s are still being used. Additionally, Skinner wrote numerous books, journals and articles throughout his career that many people still read and study today. Some of them i ...
... Skinner had to end up putting his technology in written form. But, with the new technology today some of his programs from the 60s are still being used. Additionally, Skinner wrote numerous books, journals and articles throughout his career that many people still read and study today. Some of them i ...