Regulation of Respiration
... Respiratory center activity is increased very strongly by changes in blood CO2. A change in blood CO2 has a potent acute effect on controlling respiratory drive and a weak chronic effect so after a few days’ adaptation takes place (its effect gradually declines over the next 1 to 2 days). ...
... Respiratory center activity is increased very strongly by changes in blood CO2. A change in blood CO2 has a potent acute effect on controlling respiratory drive and a weak chronic effect so after a few days’ adaptation takes place (its effect gradually declines over the next 1 to 2 days). ...
vollllllkkks_1
... The somatosensory pathway originates at the sensory receptors in the penile skin, glans, urethra and within the corpus cavernosum. In the human glans penis, there are numerous afferent terminations: free nerve endings and corpuscular receptors with a ratio of 10:1. The free nerve endings are derived ...
... The somatosensory pathway originates at the sensory receptors in the penile skin, glans, urethra and within the corpus cavernosum. In the human glans penis, there are numerous afferent terminations: free nerve endings and corpuscular receptors with a ratio of 10:1. The free nerve endings are derived ...
Notes to Resp. 4
... Control of breathing involves control of the diaphragm, the most important muscle of inspiration. Remember that when our diaphragms contract, air flows into the lungs and when it stops contracting (i.e. when it relaxes), air flows out of the lungs. So the diaphragm has to contract and it also has to ...
... Control of breathing involves control of the diaphragm, the most important muscle of inspiration. Remember that when our diaphragms contract, air flows into the lungs and when it stops contracting (i.e. when it relaxes), air flows out of the lungs. So the diaphragm has to contract and it also has to ...
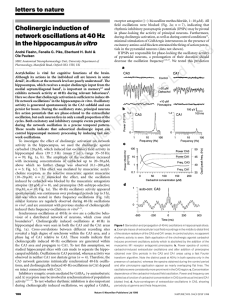
Cholinergic induction of network oscillations at 40 Hz in the
... in the CA1 area7, cholinergically induced oscillations require ionotropic non-NMDA glutamate receptors. In both CA3 and CA1 the oscillatory activity was completely abolished by the non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist 6-nitro-7-sulphamoylbenzo(f)quinoxaline-2,3-dione (NBQX, 20 mM; n ¼ 5; Fig. 2c, ...
... in the CA1 area7, cholinergically induced oscillations require ionotropic non-NMDA glutamate receptors. In both CA3 and CA1 the oscillatory activity was completely abolished by the non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist 6-nitro-7-sulphamoylbenzo(f)quinoxaline-2,3-dione (NBQX, 20 mM; n ¼ 5; Fig. 2c, ...
Paying attention to correlated neural activity
... any cost. They require an inordinate amount of data to be estimated properly and they affect information content of neural codes and downstream processing in ways that are remarkably complicated and counterintuitive1–5. However, we have no choice. If we are to understand how neural activity relates ...
... any cost. They require an inordinate amount of data to be estimated properly and they affect information content of neural codes and downstream processing in ways that are remarkably complicated and counterintuitive1–5. However, we have no choice. If we are to understand how neural activity relates ...
Chapter 15
... Postganglionic axons (unmyelinated)- relatively short - neurotransmitter is acetylcholine Distribution is more specific and less diffuse than sympathetic ...
... Postganglionic axons (unmyelinated)- relatively short - neurotransmitter is acetylcholine Distribution is more specific and less diffuse than sympathetic ...
Paying attention to correlated neural activity
... any cost. They require an inordinate amount of data to be estimated properly and they affect information content of neural codes and downstream processing in ways that are remarkably complicated and counterintuitive1–5. However, we have no choice. If we are to understand how neural activity rela ...
... any cost. They require an inordinate amount of data to be estimated properly and they affect information content of neural codes and downstream processing in ways that are remarkably complicated and counterintuitive1–5. However, we have no choice. If we are to understand how neural activity rela ...
GABAergic Influence on Taste Information in the Central Gustatory
... caused significant partial recovery, but didn’t increase EPSPs when applied alone. Application of baclofen, a GABAB agonist, also reduced EPSPs, but application of CGP55845, a GABAB antagonist, caused only non-significant partial recovery. In contrast to the findings by Du and Bradley, these results ...
... caused significant partial recovery, but didn’t increase EPSPs when applied alone. Application of baclofen, a GABAB agonist, also reduced EPSPs, but application of CGP55845, a GABAB antagonist, caused only non-significant partial recovery. In contrast to the findings by Du and Bradley, these results ...
1 MB - Columbia University
... the phenotypes were often partial and compound supporting a model involving multiple (possibly overlapping) receptors (Lumpkin and Caterina, 2007), some cases were very clear suggesting a 1:1 correspondence between receptor expression and behavior. For example, TRPM8 mutant mice are dramatically imp ...
... the phenotypes were often partial and compound supporting a model involving multiple (possibly overlapping) receptors (Lumpkin and Caterina, 2007), some cases were very clear suggesting a 1:1 correspondence between receptor expression and behavior. For example, TRPM8 mutant mice are dramatically imp ...
Vol. 147, No. 3, 1987 September 30, 1987 BIOCHEMICAL AND
... It is remarkable that the presence of the natural neurotransmitter acetylcholine ...
... It is remarkable that the presence of the natural neurotransmitter acetylcholine ...
Document
... •What is the latency and accuracy of the timed responses? • By examining the mean and the SD for the latency of the first spike, we can make some ...
... •What is the latency and accuracy of the timed responses? • By examining the mean and the SD for the latency of the first spike, we can make some ...
Remembering or Forgetting: The Lifetime of Memories
... the group improves memory while removing them accelerates forgetting. A special type of neuron in the brain controls the size of these groups. We think that this process regulates the lifetime of memories. ...
... the group improves memory while removing them accelerates forgetting. A special type of neuron in the brain controls the size of these groups. We think that this process regulates the lifetime of memories. ...
Synaptic pathways and inhibitory gates in the spinal cord dorsal horn
... mechanical allodynia after loss of GABAergic and glycinergic inhibitory control.4 Inhibitory interneurons in lamina II (black) receiving polysynaptic A fiber input may inhibit neurons that relay non-nociceptive information to NK1R+ neurons.17 Moreover, PKC ␥ + neurons that receive innocuous input v ...
... mechanical allodynia after loss of GABAergic and glycinergic inhibitory control.4 Inhibitory interneurons in lamina II (black) receiving polysynaptic A fiber input may inhibit neurons that relay non-nociceptive information to NK1R+ neurons.17 Moreover, PKC ␥ + neurons that receive innocuous input v ...
Chapter.ID_42624_6x9_GMcB
... work has shown that both the exchanger and the regulatory enzyme of GSH synthesis, -glutamate cysteine ligase (GCL) are under transcriptional control by nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2). This transcription factor, often dubbed the ‘master regulator’ of antioxidant pathways, is its ...
... work has shown that both the exchanger and the regulatory enzyme of GSH synthesis, -glutamate cysteine ligase (GCL) are under transcriptional control by nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2). This transcription factor, often dubbed the ‘master regulator’ of antioxidant pathways, is its ...
Expression and Functional Interaction of Hepatocyte Growth Factor
... During the development, HGF-SF signals were first detected in El2 mouse brain. At that time and throughout further development, HGF-SF mRNA was prominently expressed in the neuroepithelial layer of the telencephalic vesicle. Furthermore, expression was seen in the developing cortical plate, most pro ...
... During the development, HGF-SF signals were first detected in El2 mouse brain. At that time and throughout further development, HGF-SF mRNA was prominently expressed in the neuroepithelial layer of the telencephalic vesicle. Furthermore, expression was seen in the developing cortical plate, most pro ...
III./2.2.: The pathology and etiology of headaches III./2.2.1.: Anatomy
... III./2.2.2.: The pathomechanism of migraine During migraine attacks, the jugular concentration of CGRP is significantly increased, whereas the concentration of substance P, VIP and neuropeptide-Y is unchanged. This phenomenon was observed in both major types of migraine (migraine with and without au ...
... III./2.2.2.: The pathomechanism of migraine During migraine attacks, the jugular concentration of CGRP is significantly increased, whereas the concentration of substance P, VIP and neuropeptide-Y is unchanged. This phenomenon was observed in both major types of migraine (migraine with and without au ...
Name
... A reflex arc is a way of visualizing the direction of transmission of nerve signals. The arc begins with a receptor, a specialized cell which is stimulated by a change in the environment. For example, some receptors in the skin are sensitive to heat, others to pressure, and so on. If stimulation of ...
... A reflex arc is a way of visualizing the direction of transmission of nerve signals. The arc begins with a receptor, a specialized cell which is stimulated by a change in the environment. For example, some receptors in the skin are sensitive to heat, others to pressure, and so on. If stimulation of ...
Regulation of synaptic functions in central nervous system by
... to accumulate, and these studies collectively indicate that leptin, insulin and ghrelin play important roles in synaptic functions (Figures 1 and 2) [3]. In this review, we begin with the current view of synaptic regulation of hypothalamic function in energy homoeostasis, then focus on the cellular ...
... to accumulate, and these studies collectively indicate that leptin, insulin and ghrelin play important roles in synaptic functions (Figures 1 and 2) [3]. In this review, we begin with the current view of synaptic regulation of hypothalamic function in energy homoeostasis, then focus on the cellular ...
Functional Selectivity and Antidepressant Activity of Serotonin 1A
... temperature regulation, pain, and cognition as well as in pathological states including disorders connected to mood, anxiety, psychosis and pain. 5-HT1A receptors has for a long time been considered as an interesting target for the action of antidepressant drugs. It was postulated that postsynaptic ...
... temperature regulation, pain, and cognition as well as in pathological states including disorders connected to mood, anxiety, psychosis and pain. 5-HT1A receptors has for a long time been considered as an interesting target for the action of antidepressant drugs. It was postulated that postsynaptic ...
Substitutions and Deletions in the Cytoplasmic
... The cells were then stained with Wright-Giemsa and the phagocytosis by FcyRIIA is shown in Fig 2. Replacement number of COS-l cells with one or more internalized EA was deterof the first tyrosine (which is not within a typical Y-x-x-L mined in a blinded fashion. Phagocytosis was expressed as phagomo ...
... The cells were then stained with Wright-Giemsa and the phagocytosis by FcyRIIA is shown in Fig 2. Replacement number of COS-l cells with one or more internalized EA was deterof the first tyrosine (which is not within a typical Y-x-x-L mined in a blinded fashion. Phagocytosis was expressed as phagomo ...
Az alvás és ébrenlét, gondolkodás, morális és emocionális
... activate H1 receptors on cortical neurons. The tuberomammillary nucleus play an important role in the arousal mechanism, and activated during the awake state by orexin. ...
... activate H1 receptors on cortical neurons. The tuberomammillary nucleus play an important role in the arousal mechanism, and activated during the awake state by orexin. ...
IHB Endocrine Sys
... Lipid-soluble and water-soluble hormones interact differently with target cells • Steroid Hormones: – Lipid soluble, chemically derived from ...
... Lipid-soluble and water-soluble hormones interact differently with target cells • Steroid Hormones: – Lipid soluble, chemically derived from ...
Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors
... industrial cleaning that is of particular central nervous system toxicity (2). The tox- by a substantial increase in peroxisomal interest to Superfund deanup efforts. It is a icity of these chemicals appears to be 5-oxidation and fatty acid-metabolizing common and persistent environmental enhanced b ...
... industrial cleaning that is of particular central nervous system toxicity (2). The tox- by a substantial increase in peroxisomal interest to Superfund deanup efforts. It is a icity of these chemicals appears to be 5-oxidation and fatty acid-metabolizing common and persistent environmental enhanced b ...
Involvement of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Hippocampal
... The number of offspring per litter in the TNF-KO mice was similar to the wt mice (7 ± 2.74, n = 22 and 8.5 ± 2.9, n = 16, respectively; mean ± SD). TNF-KO mice were analyzed for gross developmental consequences through the first postnatal month. The mice so examined developed normal phenotypes with ...
... The number of offspring per litter in the TNF-KO mice was similar to the wt mice (7 ± 2.74, n = 22 and 8.5 ± 2.9, n = 16, respectively; mean ± SD). TNF-KO mice were analyzed for gross developmental consequences through the first postnatal month. The mice so examined developed normal phenotypes with ...
Understanding the Human Sensory Conduction of Smell
... The olfactory epithelium is the main end organ for the sense of smell in humans and vertebrates. Specially differenciated neuronal cells called olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) play a key role in the olfactory epithelium by expressing the olfactory receptors (ORs) on their apical surface membrane. ...
... The olfactory epithelium is the main end organ for the sense of smell in humans and vertebrates. Specially differenciated neuronal cells called olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) play a key role in the olfactory epithelium by expressing the olfactory receptors (ORs) on their apical surface membrane. ...