PART 1: TRUE OR FALSE (1 point each)
... 59. Which of the following is TRUE regarding sodium channels on a neuron? a. During an action potential, both inactivation or activation gates are never open simultaneously. b. At resting potential, prior to firing an action potential, the inactivation gate is closed and the activation gate is open. ...
... 59. Which of the following is TRUE regarding sodium channels on a neuron? a. During an action potential, both inactivation or activation gates are never open simultaneously. b. At resting potential, prior to firing an action potential, the inactivation gate is closed and the activation gate is open. ...
Circulatory system
... • What is the name given to the maintenance of the body’s internal environment within certain tolerable limits despite changes in the body’s external environment? • Homeostasis ...
... • What is the name given to the maintenance of the body’s internal environment within certain tolerable limits despite changes in the body’s external environment? • Homeostasis ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Discuss the Classification of neurons on the basis of – No of processes – Length of fibers Define a nerve and its coverings Differentiate between myelinated and unmyelinated fibres Enlist various types of Neuroglia and state their functions ...
... Discuss the Classification of neurons on the basis of – No of processes – Length of fibers Define a nerve and its coverings Differentiate between myelinated and unmyelinated fibres Enlist various types of Neuroglia and state their functions ...
Nervous System - Dr. Eric Schwartz
... • Neuromodulators modify both the presynaptic and the postsynaptic cell’s response to specific neurotransmitters, amplifying or dampening the effectiveness of ongoing synaptic activity. • Receptors for neurotransmitters affect ion channels that directly affect excitation or inhibition of the postsyn ...
... • Neuromodulators modify both the presynaptic and the postsynaptic cell’s response to specific neurotransmitters, amplifying or dampening the effectiveness of ongoing synaptic activity. • Receptors for neurotransmitters affect ion channels that directly affect excitation or inhibition of the postsyn ...
Life: The Science of Biology, Ninth Edition
... – the more neurotransmitter released by the receptor cell and – the more frequently the sensory neuron transmits action potentials to the brain. “Hairs” of a receptor cell Neurotransmitter at a synapse Sensory neuron ...
... – the more neurotransmitter released by the receptor cell and – the more frequently the sensory neuron transmits action potentials to the brain. “Hairs” of a receptor cell Neurotransmitter at a synapse Sensory neuron ...
Ch 4: Synaptic Transmission
... When the threshold of excitation is hit, the voltage-activated Na+ channels open & Na+ rushes in The Na+ influx causes the membrane potential to spike to +50mV This triggers the voltage-gated K+ channels to open & K+ flows out After 1ms, Na+ channels close End of rising phase ...
... When the threshold of excitation is hit, the voltage-activated Na+ channels open & Na+ rushes in The Na+ influx causes the membrane potential to spike to +50mV This triggers the voltage-gated K+ channels to open & K+ flows out After 1ms, Na+ channels close End of rising phase ...
The Nervous System
... secrete hormones into the bloodstream where they are carried to the target organ ...
... secrete hormones into the bloodstream where they are carried to the target organ ...
Chapter 10
... • allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information • makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources ...
... • allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information • makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources ...
Human nervous system_Final
... 3. Diffusion: Drifting away the neurotransmitter to out of the synaptic cleft where it can no longer act on a receptor. 4. Reuptake: That the whole neurotransmitter molecule is taken back into the axon terminal that released it. 5. The spinal cord is the extension of the central nervous system and t ...
... 3. Diffusion: Drifting away the neurotransmitter to out of the synaptic cleft where it can no longer act on a receptor. 4. Reuptake: That the whole neurotransmitter molecule is taken back into the axon terminal that released it. 5. The spinal cord is the extension of the central nervous system and t ...
lec#37 by Dalin Mohammad corrected by Bayan
... the neuron (the cell body) itself is in the dorsal root ganglia. So the first order neuron is located in the dorsal root ganglion. The axon will enter the spinal cord, ascends up as the same axon in the posterior column till it reaches the medulla where it will synapse with the second order neuron. ...
... the neuron (the cell body) itself is in the dorsal root ganglia. So the first order neuron is located in the dorsal root ganglion. The axon will enter the spinal cord, ascends up as the same axon in the posterior column till it reaches the medulla where it will synapse with the second order neuron. ...
Neural Tissue - Decker
... Afferent division- brings sensory information to the CNS from receptors in peripheral tissues & organs ...
... Afferent division- brings sensory information to the CNS from receptors in peripheral tissues & organs ...
MS Word - VCU Secrets of the Sequence
... 1. Before conducting this activity, review neuron structure and functions with the students to prepare them for constructing and labeling neurons. Some information is included in the Student Handout but you may wish to expand on this. For example, you may wish to provide more detail on the ‘action p ...
... 1. Before conducting this activity, review neuron structure and functions with the students to prepare them for constructing and labeling neurons. Some information is included in the Student Handout but you may wish to expand on this. For example, you may wish to provide more detail on the ‘action p ...
Schizophrenia II - Psychiatry Training
... • flumazenil (BDZ antagonist) is anxiogenic in panic disorder but not in healthy controls; BDZs are less sedating/impairing in anxious patients than in controls ...
... • flumazenil (BDZ antagonist) is anxiogenic in panic disorder but not in healthy controls; BDZs are less sedating/impairing in anxious patients than in controls ...
Animal Nutrition
... at synapses: gaps between neurons Uses neurotransmitters: substances released from vesicles when action potential reaches end of pre-synaptic axon ...
... at synapses: gaps between neurons Uses neurotransmitters: substances released from vesicles when action potential reaches end of pre-synaptic axon ...
Practice Exam 3 ANSWERS
... b. the somatic and axonal cellular membrane potential c. oligodendrocytes in the PNS and Schwann cells in the CNS d. ependymal CSF 5. The presynaptic axon terminal releases vesicles of neurotransmitter via a. endocytosis b. exocytosis c. phagocytosis d. pinocytosis 6. An excitatory neurotransmitter ...
... b. the somatic and axonal cellular membrane potential c. oligodendrocytes in the PNS and Schwann cells in the CNS d. ependymal CSF 5. The presynaptic axon terminal releases vesicles of neurotransmitter via a. endocytosis b. exocytosis c. phagocytosis d. pinocytosis 6. An excitatory neurotransmitter ...
Ch. 50 - Ltcconline.net
... 2. If you have no prior experience with or memory of a sensation, it stays a sensation. 3. Brain integrates sensation with other information and forms a perception C. Researchers using brain imaging techniques are beginning to find out what the brain actually does 1. communication among neurons arra ...
... 2. If you have no prior experience with or memory of a sensation, it stays a sensation. 3. Brain integrates sensation with other information and forms a perception C. Researchers using brain imaging techniques are beginning to find out what the brain actually does 1. communication among neurons arra ...
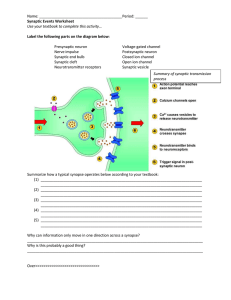
synaptic transmission worksheet
... Synaptic Events Worksheet Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
... Synaptic Events Worksheet Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
the biology of awareness
... level thanks to “neurons.” There are different kinds of neurons. Motor neurons tell muscles whether to contract or not. Sensory neurons have sensory receptors. ...
... level thanks to “neurons.” There are different kinds of neurons. Motor neurons tell muscles whether to contract or not. Sensory neurons have sensory receptors. ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... a. Pain receptors can be stimulated by damaged tissue. b. Pain receptors adapt very little, if at all. 3. Visceral Pain a. Visceral pain receptors respond differently to stimulation than those of surface tissues. b. Pain in visceral organs result from stimulation of mechanoreceptors and from decreas ...
... a. Pain receptors can be stimulated by damaged tissue. b. Pain receptors adapt very little, if at all. 3. Visceral Pain a. Visceral pain receptors respond differently to stimulation than those of surface tissues. b. Pain in visceral organs result from stimulation of mechanoreceptors and from decreas ...
Serotonin Receptors – From Molecular Biology to
... 1999). Although distribution in the brain appears limited, there are distributional similarities with 5-HT1Dβ receptors (Bhalla et al. 2002). 5-HT2 receptors This class has three subtypes – 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C, showing 46-50 % structural homology, preferably linked to Gq11 protein and increasi ...
... 1999). Although distribution in the brain appears limited, there are distributional similarities with 5-HT1Dβ receptors (Bhalla et al. 2002). 5-HT2 receptors This class has three subtypes – 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C, showing 46-50 % structural homology, preferably linked to Gq11 protein and increasi ...
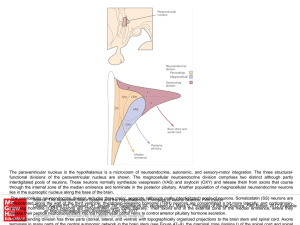
Slide ()
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
CHEMICAL SENSES: SMELL AND TASTE _____ = Olfaction
... ______ of food is a composite of _____________ ________________. - when nose is congested by infection, food “tastes” different because the olfactory system is “blocked” In humans, the senses of taste and smell have lost important survival characteristics In many animal species, taste (especially of ...
... ______ of food is a composite of _____________ ________________. - when nose is congested by infection, food “tastes” different because the olfactory system is “blocked” In humans, the senses of taste and smell have lost important survival characteristics In many animal species, taste (especially of ...
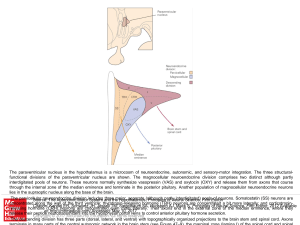
Slide ()
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
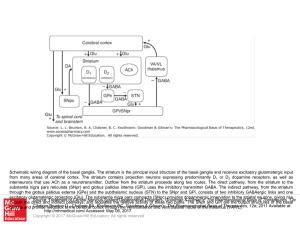
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...