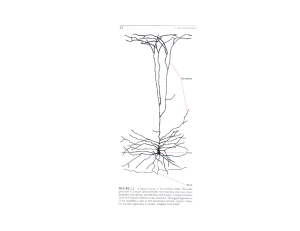
Lecture #21 Date
... To fire an action potential, we have to be at resting potential (-70 mV), maintained by closed Na+ and K+ channels If enough NT molecules are picked up by dendrites, it begins with opening of Na+ channels in axon depolarization as inside of axon becomes more positive More and more Na+ rushes in, s ...
... To fire an action potential, we have to be at resting potential (-70 mV), maintained by closed Na+ and K+ channels If enough NT molecules are picked up by dendrites, it begins with opening of Na+ channels in axon depolarization as inside of axon becomes more positive More and more Na+ rushes in, s ...
Chapter 2, section 2
... • Cycle of events in which information from one step controls or affects a previous ...
... • Cycle of events in which information from one step controls or affects a previous ...
The basic unit of computation - Zador Lab
... implement a very rich class of computations17. Common to all these models is the notion that synapses do more than just provide a substrate for the long-lasting changes underlying learning and memory; they are critical in the computation itself. What is the basic unit of computation in the brain? Fo ...
... implement a very rich class of computations17. Common to all these models is the notion that synapses do more than just provide a substrate for the long-lasting changes underlying learning and memory; they are critical in the computation itself. What is the basic unit of computation in the brain? Fo ...
Neural Decoding www.AssignmentPoint.com Neural decoding is a
... would be represented. This process of decoding neural data forms a loop with neural encoding. First, the organism must be able to perceive a set of stimuli in the world - say a picture of a hat. Seeing the stimuli must result in some internal learning: the encoding stage. After varying the range of ...
... would be represented. This process of decoding neural data forms a loop with neural encoding. First, the organism must be able to perceive a set of stimuli in the world - say a picture of a hat. Seeing the stimuli must result in some internal learning: the encoding stage. After varying the range of ...
Slide 1
... grid cells and more localized sensory input (e.g. vision, smell). Investigate the role of network topology and synaptic learning rules in forming memorized sequences (i.e. navigational routes). Model the effect of changes in the environment (e.g size, features) on hippocampal cell activity, and conn ...
... grid cells and more localized sensory input (e.g. vision, smell). Investigate the role of network topology and synaptic learning rules in forming memorized sequences (i.e. navigational routes). Model the effect of changes in the environment (e.g size, features) on hippocampal cell activity, and conn ...
PPT
... Neural networks learn by experience, generalize from previous experiences to new ones, and can make decisions. The human nervous system consists of cells called neurons. There are hundreds of billions of neurons, each connected to hundreds or thousands of other neurons. Each neuron receives, process ...
... Neural networks learn by experience, generalize from previous experiences to new ones, and can make decisions. The human nervous system consists of cells called neurons. There are hundreds of billions of neurons, each connected to hundreds or thousands of other neurons. Each neuron receives, process ...
chapter3Weiten
... Antagonist – opposes action of a neurotransmitter 15 – 20 neurotransmitters known at present Interactions between neurotransmitter circuits ...
... Antagonist – opposes action of a neurotransmitter 15 – 20 neurotransmitters known at present Interactions between neurotransmitter circuits ...
CHAPTER 28 Nervous Systems
... interconnected functions – Sensory input: receptors-structures specialized to detect certain stimuli – Integration: through the spinal cord & brain – Motor output: effectors-respond to a stimulus such as muscles or glands ...
... interconnected functions – Sensory input: receptors-structures specialized to detect certain stimuli – Integration: through the spinal cord & brain – Motor output: effectors-respond to a stimulus such as muscles or glands ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... • Agonist – mimics neurotransmitter action • Antagonist – opposes action of a neurotransmitter • 15 – 20 neurotransmitters known at present • Interactions between neurotransmitter circuits ...
... • Agonist – mimics neurotransmitter action • Antagonist – opposes action of a neurotransmitter • 15 – 20 neurotransmitters known at present • Interactions between neurotransmitter circuits ...
The Nervous System
... or electrical signal. Electrical synapses cross gap junctions, such as in cardiac and smooth muscle. Neurotransmitters are used in nervous system synapses. They are released from the axon. Bouton / knobs / presynaptic terminal Neuromodulators – can influence an action potential ...
... or electrical signal. Electrical synapses cross gap junctions, such as in cardiac and smooth muscle. Neurotransmitters are used in nervous system synapses. They are released from the axon. Bouton / knobs / presynaptic terminal Neuromodulators – can influence an action potential ...
1-nervous_system
... Schwann Cells – form myelin sheaths around axons Holds neurons in place Speeds up transmission Can repair if damaged Keeps messages from being scrambled ...
... Schwann Cells – form myelin sheaths around axons Holds neurons in place Speeds up transmission Can repair if damaged Keeps messages from being scrambled ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 9. The white fatty substance around the neurons that speeds up impulse transmission is called _________________________. 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an _______________________. 11. Indentations between the Sch ...
... 9. The white fatty substance around the neurons that speeds up impulse transmission is called _________________________. 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an _______________________. 11. Indentations between the Sch ...
Nervous System
... electrochemical nerve impulses to other neurons. • Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and neuroglial cells. • Neuroglial cells provide support, insulation, and nutrients to neurons • Neurons consist of a cell body and extensions called dendrites and axons • Axons send information in the form of n ...
... electrochemical nerve impulses to other neurons. • Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and neuroglial cells. • Neuroglial cells provide support, insulation, and nutrients to neurons • Neurons consist of a cell body and extensions called dendrites and axons • Axons send information in the form of n ...
Health - Nervous System Review
... 1. Largest part of the brain where learning, intelligence, and judgment occur 3. Sweet, sour, salty, and bitter 5. Nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal column 6. Carries messages to your brain and spinal cord from receptors in your skin 8. Special cell in our skin that allows us to s ...
... 1. Largest part of the brain where learning, intelligence, and judgment occur 3. Sweet, sour, salty, and bitter 5. Nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal column 6. Carries messages to your brain and spinal cord from receptors in your skin 8. Special cell in our skin that allows us to s ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... _____ – receive messages and give to cell body (can collect from many sources) _____ – carries message away from cell body (can go to many other cells from 1 cell) Impulse – message carried by a neuron Receptors – in all sense organs Respond to _____ Sensory – _____ Interneurons – _____ ...
... _____ – receive messages and give to cell body (can collect from many sources) _____ – carries message away from cell body (can go to many other cells from 1 cell) Impulse – message carried by a neuron Receptors – in all sense organs Respond to _____ Sensory – _____ Interneurons – _____ ...
Introduction to Psychology
... the brain’s sensory switchboard directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
... the brain’s sensory switchboard directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
Chapter 2 PPT Neuroscience and Behavior
... the brain’s sensory switchboard directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
... the brain’s sensory switchboard directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾ Some aspects of brain research that are interesting include: arousal & sleep; lateralization, language, & speech; emotions; memory & learning; and consciousness. ¾ An electroencephalogram records the different patterns in the electrical activity of the brain produced during sleep and arousal. ...
... ¾ Some aspects of brain research that are interesting include: arousal & sleep; lateralization, language, & speech; emotions; memory & learning; and consciousness. ¾ An electroencephalogram records the different patterns in the electrical activity of the brain produced during sleep and arousal. ...
Review #2 - Course Notes
... 31. The surgical removal of a large tumor from Allen's occipital lobe resulted in extensive loss of brain tissue. Allen is most likely to suffer some loss of: a. muscular coordination. b. language comprehension. c. speaking ability. d. visual perception. e. pain sensations. 32. The part of a neuron ...
... 31. The surgical removal of a large tumor from Allen's occipital lobe resulted in extensive loss of brain tissue. Allen is most likely to suffer some loss of: a. muscular coordination. b. language comprehension. c. speaking ability. d. visual perception. e. pain sensations. 32. The part of a neuron ...
Practice Test #2
... 31. The surgical removal of a large tumor from Allen's occipital lobe resulted in extensive loss of brain tissue. Allen is most likely to suffer some loss of: a. muscular coordination. b. language comprehension. c. speaking ability. d. visual perception. e. pain sensations. 32. The part of a neuron ...
... 31. The surgical removal of a large tumor from Allen's occipital lobe resulted in extensive loss of brain tissue. Allen is most likely to suffer some loss of: a. muscular coordination. b. language comprehension. c. speaking ability. d. visual perception. e. pain sensations. 32. The part of a neuron ...
nervous system
... Dendrite- sensitive process that receives info from other neurons Axon- passes electrical impulses (action potential) and ends with synaptic terminals Synapse- area where 2 nerves meet, neurotransmitters are used for communication ...
... Dendrite- sensitive process that receives info from other neurons Axon- passes electrical impulses (action potential) and ends with synaptic terminals Synapse- area where 2 nerves meet, neurotransmitters are used for communication ...
Robotic/Human Loops - Computer Science & Engineering
... – Understand scientific basis for superiority of human intelligence over current machine learning and AI – Create neurally-based cognitively intelligent systems – Develop neuromorphic robots which interact with humans – Complement Neuroscience wet lab and cognitive research ...
... – Understand scientific basis for superiority of human intelligence over current machine learning and AI – Create neurally-based cognitively intelligent systems – Develop neuromorphic robots which interact with humans – Complement Neuroscience wet lab and cognitive research ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... a. am individual reflexively withdraws from a pain stimulus. b. an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. c. a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. d. dendrites transmit more electrical signals to axons. e. positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membran ...
... a. am individual reflexively withdraws from a pain stimulus. b. an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. c. a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. d. dendrites transmit more electrical signals to axons. e. positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membran ...