Human Biology Human Body Systems Nervous System
... (spinal nerves, cranial nerves, ganglia, motor and sensory neurons.) ...
... (spinal nerves, cranial nerves, ganglia, motor and sensory neurons.) ...
Slide 1
... Stem cells are the foundation cells for every organ and tissue in the body. They are like a blank microchip that can ultimately be programmed to perform particular tasks. Under proper conditions, stem cells begin to develop or ‘differentiate’ into specialized cells that carry out a specific function ...
... Stem cells are the foundation cells for every organ and tissue in the body. They are like a blank microchip that can ultimately be programmed to perform particular tasks. Under proper conditions, stem cells begin to develop or ‘differentiate’ into specialized cells that carry out a specific function ...
Nervous System
... central nervous system (CNS) – All the nervous tissue outside the brain and spinal cord make up the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
... central nervous system (CNS) – All the nervous tissue outside the brain and spinal cord make up the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems
... your body (periphery) toward the central nervous system. Motor neurons: (motoneurons) (Efferent) Carry signals away from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body. Receptors: Sense the environment (chemicals, light, sound, touch) and encode this information i ...
... your body (periphery) toward the central nervous system. Motor neurons: (motoneurons) (Efferent) Carry signals away from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body. Receptors: Sense the environment (chemicals, light, sound, touch) and encode this information i ...
consciousness
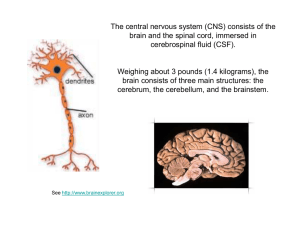
... cortex, white matter and the spinal cord. The brainstem contributes to the control of breathing, sleep and circulation. ...
... cortex, white matter and the spinal cord. The brainstem contributes to the control of breathing, sleep and circulation. ...
Nervous System
... Myelinated nerves – have a coat of white fatty material, interrupted along the length of the nerve at regularly spaced intervals -found mostly in the CNS Nonmyelinated nerves – have a thin coat of myelin – found in the autonomic nervous system ...
... Myelinated nerves – have a coat of white fatty material, interrupted along the length of the nerve at regularly spaced intervals -found mostly in the CNS Nonmyelinated nerves – have a thin coat of myelin – found in the autonomic nervous system ...
nervous system power point
... • Unipolar – one process that splits into axon with dendrite endings (sensory) ...
... • Unipolar – one process that splits into axon with dendrite endings (sensory) ...
- Krest Technology
... radio communications technology did not take off in a big way. Equipment was large and these radio communications systems were not convenient to use or carry around. ...
... radio communications technology did not take off in a big way. Equipment was large and these radio communications systems were not convenient to use or carry around. ...
Chapter 2A Practice Test
... B) a 1a1rer of fatty tissue that encases the fibers of many neurons. Ci * antagonist molecule that blocks neurotransmitter receptor sites' Oj tire extJnsion of a neuron that carries messages away from the ce1l body E) a junction between ...
... B) a 1a1rer of fatty tissue that encases the fibers of many neurons. Ci * antagonist molecule that blocks neurotransmitter receptor sites' Oj tire extJnsion of a neuron that carries messages away from the ce1l body E) a junction between ...
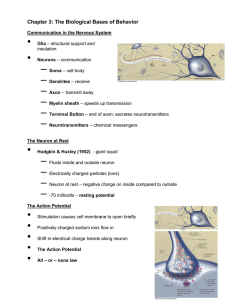
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Voltage change at receptor site – postsynaptic potential (PSP) ...
... Voltage change at receptor site – postsynaptic potential (PSP) ...
The Brain
... • The newest evolutionary development and is most highly developed in primates (especially humans). • Incredibly complex, it has many structures and interconnections and is the locus (center) of planning and decision-making. ...
... • The newest evolutionary development and is most highly developed in primates (especially humans). • Incredibly complex, it has many structures and interconnections and is the locus (center) of planning and decision-making. ...
Test Question 1 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive
... c) Why do researchers not always use more direct representations of the neural activity from EEG or MEG? AW: Less good spatial resolution. Does not see the deeper sources very well Test Question 3 Why is the term “EMG investigation” strictly speaking not correct for a routine electro-diagnostic inve ...
... c) Why do researchers not always use more direct representations of the neural activity from EEG or MEG? AW: Less good spatial resolution. Does not see the deeper sources very well Test Question 3 Why is the term “EMG investigation” strictly speaking not correct for a routine electro-diagnostic inve ...
The Nervous System – Use notebook paper if
... Draw a neuron and describe the three types of neurons. ...
... Draw a neuron and describe the three types of neurons. ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. The self-examination of
... c) observable relationship between specific independent and dependent variables. d) set of principles that organizes observations and explains newly discovered facts. 9. In a written report of their research, psychologists specify exactly how anxiety is assessed, thus providing their readers with a( ...
... c) observable relationship between specific independent and dependent variables. d) set of principles that organizes observations and explains newly discovered facts. 9. In a written report of their research, psychologists specify exactly how anxiety is assessed, thus providing their readers with a( ...
Introduction to Machine Intelligence
... 1957 – first cochlear implant by Djourno and Eyries – consisted of electrodes placed in the auditory nerve, which were stimulated at different pulse rates 1970s – clinical trials begun in USA 1961 – first motor prosthesis for foot drop in hemiplegics 1980s – Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) o ...
... 1957 – first cochlear implant by Djourno and Eyries – consisted of electrodes placed in the auditory nerve, which were stimulated at different pulse rates 1970s – clinical trials begun in USA 1961 – first motor prosthesis for foot drop in hemiplegics 1980s – Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) o ...
Introduction to Machine Intelligence
... 1957 – first cochlear implant by Djourno and Eyries – consisted of electrodes placed in the auditory nerve, which were stimulated at different pulse rates 1970s – clinical trials begun in USA 1961 – first motor prosthesis for foot drop in hemiplegics 1980s – Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) o ...
... 1957 – first cochlear implant by Djourno and Eyries – consisted of electrodes placed in the auditory nerve, which were stimulated at different pulse rates 1970s – clinical trials begun in USA 1961 – first motor prosthesis for foot drop in hemiplegics 1980s – Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) o ...
A1984SR69800001
... new search for possible transmitter substances. By more precise electrophysiological techniques, it became possible to release minute amounts of various substances from microelectrodes inserted into the brain and spinal cord and thus examine their effects on individual nerve cells. Numerous such ‘io ...
... new search for possible transmitter substances. By more precise electrophysiological techniques, it became possible to release minute amounts of various substances from microelectrodes inserted into the brain and spinal cord and thus examine their effects on individual nerve cells. Numerous such ‘io ...
Intro-ANN - Computer Science
... Neural Networks Computational model inspired by the brain Brain ...
... Neural Networks Computational model inspired by the brain Brain ...
Lecture notes
... represented in the figure from Gilbert6 and in this movie (1.6Mbytes). (by RMH) 3. Morphogenetic movements are summarized in this summary figure. The neural plate narrows, by the convergent extension of cells to the midline. This brings the folds closer together, so that the folds can reach each oth ...
... represented in the figure from Gilbert6 and in this movie (1.6Mbytes). (by RMH) 3. Morphogenetic movements are summarized in this summary figure. The neural plate narrows, by the convergent extension of cells to the midline. This brings the folds closer together, so that the folds can reach each oth ...
BOX 2.1 THE NEURON DOCTRINE The cell theory, which states
... The cell theory, which states that all organisms are composed of individual cells, was developed around the middle of the nineteenth century by Mattias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, this unitary vision of the cellular nature of life was not immediately applied to the nervous system, as mos ...
... The cell theory, which states that all organisms are composed of individual cells, was developed around the middle of the nineteenth century by Mattias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, this unitary vision of the cellular nature of life was not immediately applied to the nervous system, as mos ...
The Nervous System
... Paralysis – loss of neurological communication (movement, feeling, etc) Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – ...
... Paralysis – loss of neurological communication (movement, feeling, etc) Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – ...