File
... integrate many body functions. The nervous tissue includes neurological cells. These cells support and bind components of nervous tissue, carry on phagocytosis, and help support nutrients to neurons by connecting them to blood vessels. Function: These cells are the structural and functional units of ...
... integrate many body functions. The nervous tissue includes neurological cells. These cells support and bind components of nervous tissue, carry on phagocytosis, and help support nutrients to neurons by connecting them to blood vessels. Function: These cells are the structural and functional units of ...
Unit 3 Notes
... Motor Cortex: an area at the head of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Mapping the Motor Cortex ...
... Motor Cortex: an area at the head of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Mapping the Motor Cortex ...
The Nervous System
... • Sensory function- Sensory receptors detect changes called stimuli that occur inside and outside the body. They monitor outside things, such as temperature, light, and sound. Inside the body they monitor pressure, pH, carbon dioxide concentration, and levels of electrolytes. All of this gathered in ...
... • Sensory function- Sensory receptors detect changes called stimuli that occur inside and outside the body. They monitor outside things, such as temperature, light, and sound. Inside the body they monitor pressure, pH, carbon dioxide concentration, and levels of electrolytes. All of this gathered in ...
Nervous System & Senses
... Messages jump across Drugs and the synapse alcohol disrupts like the an electrical communication current between neurons ...
... Messages jump across Drugs and the synapse alcohol disrupts like the an electrical communication current between neurons ...
2016 department of medicine research day
... threshold] or cervical VNS [20 Hz; 1.2x threshold]. Cardiac nodose neural activity was also assessed at progressive levels of VNS [2 Hz; 1-8 mA]. Results: 65% of cardiac-related nodose neurons responded to LAD CAO, with activity increasing ~140% (0.33±0.08 to 0.79±0.19 impulses/sec, p=0.001). The ne ...
... threshold] or cervical VNS [20 Hz; 1.2x threshold]. Cardiac nodose neural activity was also assessed at progressive levels of VNS [2 Hz; 1-8 mA]. Results: 65% of cardiac-related nodose neurons responded to LAD CAO, with activity increasing ~140% (0.33±0.08 to 0.79±0.19 impulses/sec, p=0.001). The ne ...
Inkwell @ SMUG - Indiana University
... Information Is What Matters • "Life is a pattern in spacetime, rather than a specific material object.” - Farmer & Belin (ALife II, 1990) • Schrödinger speaks of life being characterized by and feeding on “negative entropy” (What Is Life? 1944) • Von Neumann describes brain activity in terms of inf ...
... Information Is What Matters • "Life is a pattern in spacetime, rather than a specific material object.” - Farmer & Belin (ALife II, 1990) • Schrödinger speaks of life being characterized by and feeding on “negative entropy” (What Is Life? 1944) • Von Neumann describes brain activity in terms of inf ...
Chapter 2
... receiving neuron tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap Neurotransmitters chemical messengers that travel the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neuro-transmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron--influencing ...
... receiving neuron tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap Neurotransmitters chemical messengers that travel the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neuro-transmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron--influencing ...
PDF
... express an inducible mutated RAS gene – RAS family members are the most commonly mutated oncogenes in human cancers and the RAS pathway is a key developmental pathway during embryogenesis. The researchers then use one of the genes that is upregulated by RAS expression to screen for small molecules t ...
... express an inducible mutated RAS gene – RAS family members are the most commonly mutated oncogenes in human cancers and the RAS pathway is a key developmental pathway during embryogenesis. The researchers then use one of the genes that is upregulated by RAS expression to screen for small molecules t ...
PDF
... express an inducible mutated RAS gene – RAS family members are the most commonly mutated oncogenes in human cancers and the RAS pathway is a key developmental pathway during embryogenesis. The researchers then use one of the genes that is upregulated by RAS expression to screen for small molecules t ...
... express an inducible mutated RAS gene – RAS family members are the most commonly mutated oncogenes in human cancers and the RAS pathway is a key developmental pathway during embryogenesis. The researchers then use one of the genes that is upregulated by RAS expression to screen for small molecules t ...
PPt #2 Human Body Nervous system
... how they transmit electrochemical impulses. • 3. I can compare and contrast the central and peripheral nervous systems • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and their functions. • 5. I can explain how the nervous system passes information between the external environment and t ...
... how they transmit electrochemical impulses. • 3. I can compare and contrast the central and peripheral nervous systems • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and their functions. • 5. I can explain how the nervous system passes information between the external environment and t ...
nervous system outline PPT
... Directs the functions of all human body systems – 100 Billion Nerve cells ...
... Directs the functions of all human body systems – 100 Billion Nerve cells ...
Essential Questions and Vocabulary
... How is the neural system organized? What are the lobes and localizations of the brain? How is the cerebral cortex organized? What experimental methods are used to study brain function? What are the differences between the right and left hemispheres? VOCABULARY: Biological psychology, neuro ...
... How is the neural system organized? What are the lobes and localizations of the brain? How is the cerebral cortex organized? What experimental methods are used to study brain function? What are the differences between the right and left hemispheres? VOCABULARY: Biological psychology, neuro ...
Structure of neuron
... The term was introduced in nineteenth century by the British neurophysiologist Charles Sherrington ...
... The term was introduced in nineteenth century by the British neurophysiologist Charles Sherrington ...
C! **D!**E!**F! - Amherst College
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
The Peripheral Nervous System The P.N.S.
... Consequences of Damage to Nerve Cells A. The nerve does not ___________________ B. The transmission of impulses may _______ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ C. Interpretation of the impulse may be ___________________________________ __________________________ ...
... Consequences of Damage to Nerve Cells A. The nerve does not ___________________ B. The transmission of impulses may _______ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ C. Interpretation of the impulse may be ___________________________________ __________________________ ...
Nervous Dia rams
... 5. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. 6. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. ...
... 5. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. 6. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. ...
Nerve Chips
... Nanotechnology – design of new “impossible” materials Electrode coatings that contain brain molecules, “trick” cells into acting like electrode is part of brain Polymer chains that can enter the cell Conductive polymer chains that place your electrode inside a cell without hurting it Components that ...
... Nanotechnology – design of new “impossible” materials Electrode coatings that contain brain molecules, “trick” cells into acting like electrode is part of brain Polymer chains that can enter the cell Conductive polymer chains that place your electrode inside a cell without hurting it Components that ...
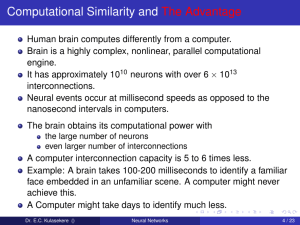
Neural Networks
... To build a neuron based computer with as little as 0.1% of the performance of the human brain. Use this model to perform tasks that would be difficult to achieve using conventional computations. ...
... To build a neuron based computer with as little as 0.1% of the performance of the human brain. Use this model to perform tasks that would be difficult to achieve using conventional computations. ...
Tehnici de optimizare – Programare Genetica
... buttons. They are interconnected to a form of an extensive network that electrochemical processes information. All electrochemical and electrical impulses are transmitted by neurons with synapses. ...
... buttons. They are interconnected to a form of an extensive network that electrochemical processes information. All electrochemical and electrical impulses are transmitted by neurons with synapses. ...
File
... of failure of primitive streak regression. In the United States the occurrence is about 1 in 40,000 live births. Teratomas from any origin are benign tumors that arise from germ cells. They may contain a variety of structures such as skin, neurons, glands, and cartilage. These may be seen grossly or ...
... of failure of primitive streak regression. In the United States the occurrence is about 1 in 40,000 live births. Teratomas from any origin are benign tumors that arise from germ cells. They may contain a variety of structures such as skin, neurons, glands, and cartilage. These may be seen grossly or ...
Neuroembryology of Neural Tube Defects
... of the spinal cord and/or meninges through the defect in the vertebral arch. Referred to as s.b. cystica because of the cystlike sac that is associated with these anomalies. Occur in about 1/1,000 births. Types: Spina bifida with meningocele Spina bifida with meningomyelocele Spina bifida with myelo ...
... of the spinal cord and/or meninges through the defect in the vertebral arch. Referred to as s.b. cystica because of the cystlike sac that is associated with these anomalies. Occur in about 1/1,000 births. Types: Spina bifida with meningocele Spina bifida with meningomyelocele Spina bifida with myelo ...
for neural fate
... Gastrulation : Gastrulation can be defined as the process by which the embryo acquires 2-3 germ layers. There are extensive cell movements and rearrangements. Ectoderm Major tissues of the Nervous System, ...
... Gastrulation : Gastrulation can be defined as the process by which the embryo acquires 2-3 germ layers. There are extensive cell movements and rearrangements. Ectoderm Major tissues of the Nervous System, ...
IV. PSYCHOBIOLOGY
... Other “3/4” of cerebral cortex. Integrates, interprets, acts on information. (i.e. important to communication). Areas and their associated behaviors have been identified based on what happens when those areas are damaged. ...
... Other “3/4” of cerebral cortex. Integrates, interprets, acts on information. (i.e. important to communication). Areas and their associated behaviors have been identified based on what happens when those areas are damaged. ...