Neural Crest Cells and Axonal Specificity
... type of neuron? position of neuronal precursor within neural tube when it forms (birthday) ...
... type of neuron? position of neuronal precursor within neural tube when it forms (birthday) ...
Slide ()
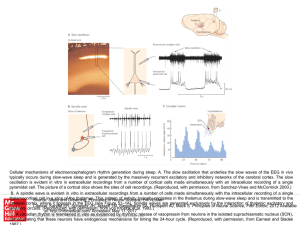
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
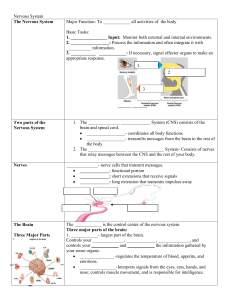
The nervous system
... The soma (cell body) is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus of the cell, and therefore is where most protein synthesis occurs. The nucleus ranges from 3 to 18 micrometers in diameter. The dendrites of a neuron are cellular extensions with many branches, and metaphorically this o ...
... The soma (cell body) is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus of the cell, and therefore is where most protein synthesis occurs. The nucleus ranges from 3 to 18 micrometers in diameter. The dendrites of a neuron are cellular extensions with many branches, and metaphorically this o ...
Nervous System Test Review After you accidentally touch a hot pan
... 10. Where do sense organs send information about the environment? a. To the Brain 11. What is a concussion? a. A bruise like injury to the brain ...
... 10. Where do sense organs send information about the environment? a. To the Brain 11. What is a concussion? a. A bruise like injury to the brain ...
Ch 3 lec 1
... fuses to form the neural tube… Walls of the neural tube become the CNS Neural crest becomes the PNS Figure 3.7 ...
... fuses to form the neural tube… Walls of the neural tube become the CNS Neural crest becomes the PNS Figure 3.7 ...
Nerve Notes
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
Development of the CNS - Yeasting
... Take up residency within neural tube, and take up phagocyticic function Is multipotential Differentiate into: o Glial cells (almost all) Oligodendrocytes Astrocytes Fibrous o Stronger, have intracellular fibers within them o Are more supportive o Found largely within tract areas Protop ...
... Take up residency within neural tube, and take up phagocyticic function Is multipotential Differentiate into: o Glial cells (almost all) Oligodendrocytes Astrocytes Fibrous o Stronger, have intracellular fibers within them o Are more supportive o Found largely within tract areas Protop ...
Slide 1
... • 1 neuron cell body = 10 microns wide 85,000,000,000 neurons = 850 km • If you use a basketball (diameter = ~24 cm) as the cell body, then your axon would have to be 240,000 cm (2.4 kilometers) in length! ...
... • 1 neuron cell body = 10 microns wide 85,000,000,000 neurons = 850 km • If you use a basketball (diameter = ~24 cm) as the cell body, then your axon would have to be 240,000 cm (2.4 kilometers) in length! ...
Brain Cell or Neuron
... part of PNS consisting of motor neurons that control internal organs. controls muscles in the heart, the smooth muscle in internal organs such as the intestine, bladder, and uterus. two subsystems. o Sympathetic Nervous System involved in the fight or flight response. o Parasympathetic Nervous Syste ...
... part of PNS consisting of motor neurons that control internal organs. controls muscles in the heart, the smooth muscle in internal organs such as the intestine, bladder, and uterus. two subsystems. o Sympathetic Nervous System involved in the fight or flight response. o Parasympathetic Nervous Syste ...
Inner Ear
... stimulate different areas along the basilar membrane and the membrane rubs against hair cells. Each ear contains thousands of hair cells. The hair cells are arranged by frequency (pitch) just like the keyboard of a piano. Nerves are attached to the bottom of these hair cells so when the hair cells m ...
... stimulate different areas along the basilar membrane and the membrane rubs against hair cells. Each ear contains thousands of hair cells. The hair cells are arranged by frequency (pitch) just like the keyboard of a piano. Nerves are attached to the bottom of these hair cells so when the hair cells m ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Functional MRI (fMRI) ...
... Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Functional MRI (fMRI) ...
Slide ()
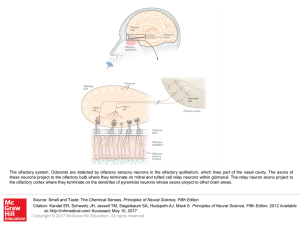
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
HONORS BIOLOGY Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... o Ganglia (clusters of cell bodies of the neurons) Sensory neurons ...
... o Ganglia (clusters of cell bodies of the neurons) Sensory neurons ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... Autonomic NS controls glands and organs. Sympathetic NS arouses a person. Parasympathetic NS conserves energy and calms. ...
... Autonomic NS controls glands and organs. Sympathetic NS arouses a person. Parasympathetic NS conserves energy and calms. ...
Where does breathing start?
... It comes from the respiratory centres called medulla oblongata and the pons which are located in the lower brainstem. The medulla oblongata contains the Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG) and the Dorsal Respiratory Group and the pons contains the Pneumotaxic (PNG) and the Apneustic centres (APN). The f ...
... It comes from the respiratory centres called medulla oblongata and the pons which are located in the lower brainstem. The medulla oblongata contains the Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG) and the Dorsal Respiratory Group and the pons contains the Pneumotaxic (PNG) and the Apneustic centres (APN). The f ...
Quiz 1 - Suraj @ LUMS
... parameters that may be adapted during learning. A neural network is said to learn if its free parameters are adapted in response to experience in order to improve performance at learning an input-output mapping. The free parameters can be: weights Activation function parameters Architectural p ...
... parameters that may be adapted during learning. A neural network is said to learn if its free parameters are adapted in response to experience in order to improve performance at learning an input-output mapping. The free parameters can be: weights Activation function parameters Architectural p ...
Neurobiologically Inspired Robotics: Enhanced Autonomy through
... This Special Issue includes eleven papers that represent the current state of the art in neurobiologically inspired robotics. In general, the collection of papers takes on three major issues that are of the utmost importance for research in neuroscience and cognitive science, as well as advancing ro ...
... This Special Issue includes eleven papers that represent the current state of the art in neurobiologically inspired robotics. In general, the collection of papers takes on three major issues that are of the utmost importance for research in neuroscience and cognitive science, as well as advancing ro ...
Slide ()
... A perceptron implementing the Hubel-Wiesel model of selectivity and invariance. The network in Figure E–2C can be extended to grids of many cells by specifying synaptic connectivity at all locations in the visual field. The resulting network can be repeated four times, one for each preferred orienta ...
... A perceptron implementing the Hubel-Wiesel model of selectivity and invariance. The network in Figure E–2C can be extended to grids of many cells by specifying synaptic connectivity at all locations in the visual field. The resulting network can be repeated four times, one for each preferred orienta ...
Slide ()
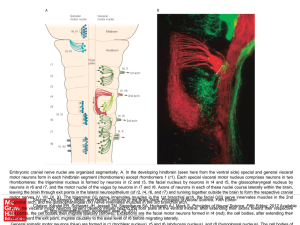
... motor nerves (V, VII, IX, X). The trigeminal (V) nerve innervates muscles in the 1st branchial arch, the facial (VII) nerve innervates muscles in the 2nd Source: The Sensory, Motor, and Reflex Functions of the Brain Stem, Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon branchial arch, and the glossophary ...
... motor nerves (V, VII, IX, X). The trigeminal (V) nerve innervates muscles in the 1st branchial arch, the facial (VII) nerve innervates muscles in the 2nd Source: The Sensory, Motor, and Reflex Functions of the Brain Stem, Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon branchial arch, and the glossophary ...
Nervous System
... controls thought, language, learning, judgment, & voluntary action 2. Cerebellum controls involuntary functions of muscles & maintains balance and posture 3. Brain stem (Pons & Medulla Oblongata) Controls involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate, and swallowing 4. Thalamus, Hypothalamus C ...
... controls thought, language, learning, judgment, & voluntary action 2. Cerebellum controls involuntary functions of muscles & maintains balance and posture 3. Brain stem (Pons & Medulla Oblongata) Controls involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate, and swallowing 4. Thalamus, Hypothalamus C ...
Slide ()
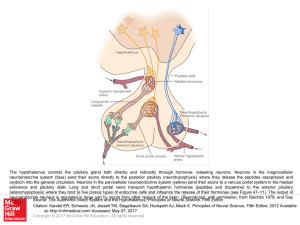
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
Nervous System Cells
... Functional Classification • Neurons can be classified according to the direction in which they conduct impulses • Afferent neurons – transmit to the spinal cord or brain • Efferent neurons – transmit away from the brain or spinal cord • Interneurons – conduct impulses toward motor neurons (entirely ...
... Functional Classification • Neurons can be classified according to the direction in which they conduct impulses • Afferent neurons – transmit to the spinal cord or brain • Efferent neurons – transmit away from the brain or spinal cord • Interneurons – conduct impulses toward motor neurons (entirely ...
Review Senses and Nervous System Test
... 5. What is pathway of light thru eye 6. What is visual field and visual pathway to brain 7. Eye reflexes (pupil dialate/photpupillary reflex) 8. Mecahnoreceptors in hearing 9. Ottis media 10. Mechanisms of hearing 11. Mechanisms of equilibrium (static and dynamic) 12. Types of deafness 13. What are ...
... 5. What is pathway of light thru eye 6. What is visual field and visual pathway to brain 7. Eye reflexes (pupil dialate/photpupillary reflex) 8. Mecahnoreceptors in hearing 9. Ottis media 10. Mechanisms of hearing 11. Mechanisms of equilibrium (static and dynamic) 12. Types of deafness 13. What are ...