Optogenetics: Molecular and Optical Tools for Controlling Life with
... cannulas [26], or coupled to fibers that are chronically implanted into the brain. As optics is a rapidly changing field, we are maintaining a web page with current part numbers and best-practices method for assembling, calibrating, and utilizing these fibercoupled lasers and accessory parts [27]. W ...
... cannulas [26], or coupled to fibers that are chronically implanted into the brain. As optics is a rapidly changing field, we are maintaining a web page with current part numbers and best-practices method for assembling, calibrating, and utilizing these fibercoupled lasers and accessory parts [27]. W ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... for newly incoming data. Competing makes it possible that even after new neurons have been added to the architecture, existing neurons can still learn if the incoming data is similar to that of the stored information, and this sets up a major difference with the existing constructive neural network ...
... for newly incoming data. Competing makes it possible that even after new neurons have been added to the architecture, existing neurons can still learn if the incoming data is similar to that of the stored information, and this sets up a major difference with the existing constructive neural network ...
Development of NS_20..
... Department of Histology and Embryology, P. J. Šafárik University, Medical Faculty, Košice ...
... Department of Histology and Embryology, P. J. Šafárik University, Medical Faculty, Košice ...
Chapter 12-13 Summary
... parts overlap with 2401. I’ve added additional references. Use this knowing it may not cover everything. Nervous System: (These are very important chapters.) ...
... parts overlap with 2401. I’ve added additional references. Use this knowing it may not cover everything. Nervous System: (These are very important chapters.) ...
Nervous Tissue
... Receptors monitor both external and internal environments. Integration: Process the information (at synapses) and often integrate it with stored information. Motor output: If necessary, signal effector organs to make an appropriate response. ...
... Receptors monitor both external and internal environments. Integration: Process the information (at synapses) and often integrate it with stored information. Motor output: If necessary, signal effector organs to make an appropriate response. ...
Chapter 2 - davis.k12.ut.us
... E) axons 6. In its resting state, the inside of a neuron carries a slight _____ charge with respect to the outside. A) positive B) negative C) active D) depolarized E) antagonistic 7. The minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse is called the A) reflex. B) threshold. C) syna ...
... E) axons 6. In its resting state, the inside of a neuron carries a slight _____ charge with respect to the outside. A) positive B) negative C) active D) depolarized E) antagonistic 7. The minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse is called the A) reflex. B) threshold. C) syna ...
SompolinskyAug09
... describing a cellular process by which sensory neurons in the brain can automatically adjust their perceptual clocks and thus correct large temporal variations in the rate of sounds and speech that arrive from the environment. According to their findings, which were recently published in the PLoS Bi ...
... describing a cellular process by which sensory neurons in the brain can automatically adjust their perceptual clocks and thus correct large temporal variations in the rate of sounds and speech that arrive from the environment. According to their findings, which were recently published in the PLoS Bi ...
Theoretical Neuroscience - Neural Dynamics and Computation Lab
... deal now about how single neurons transform inputs to outputs, and how single plastic synapses change their efficacies in an activity dependent manner, the question of how many such relatively simple biophysical units interact with each other to give rise to complex higher level cognitive phenomena ...
... deal now about how single neurons transform inputs to outputs, and how single plastic synapses change their efficacies in an activity dependent manner, the question of how many such relatively simple biophysical units interact with each other to give rise to complex higher level cognitive phenomena ...
The Nervous System
... muscles, memory and the senses. •Cerebellum- maintains balance. •Medulla- controls and coordinates involuntary muscle functions. ...
... muscles, memory and the senses. •Cerebellum- maintains balance. •Medulla- controls and coordinates involuntary muscle functions. ...
Slide ()
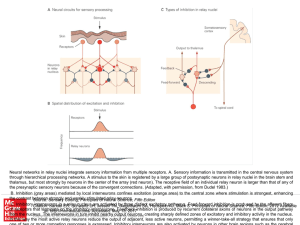
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
______ 1
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
The basics of brain communication
... The Neuron: The Basic Unit of Communication Neuron: The basic units of the nervous system; cells that receive, integrate, and transmit information in the nervous system. They operate through electrical impulses, communicate with other neurons through chemical signals, and form neural networks. (page ...
... The Neuron: The Basic Unit of Communication Neuron: The basic units of the nervous system; cells that receive, integrate, and transmit information in the nervous system. They operate through electrical impulses, communicate with other neurons through chemical signals, and form neural networks. (page ...
Psychology 101 Exam 1
... c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcu ...
... c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcu ...
The NERVOUS System
... System 1. Monitors stimuli (Sensory input) 2. Processes, makes decisions about how to respond to stimuli. 3. Causes a response by activating muscles, or glands (motor output) ...
... System 1. Monitors stimuli (Sensory input) 2. Processes, makes decisions about how to respond to stimuli. 3. Causes a response by activating muscles, or glands (motor output) ...
Brain Muscle Interface
... Neurological disorders may involve the Central Nervous System or the Peripheral Nervous System, both of which can involve sensory and/or motor loss. Motor loss means impairment in motor function such as contraction of muscles and movement of the limbs leading to significant Functional disability. Im ...
... Neurological disorders may involve the Central Nervous System or the Peripheral Nervous System, both of which can involve sensory and/or motor loss. Motor loss means impairment in motor function such as contraction of muscles and movement of the limbs leading to significant Functional disability. Im ...
C13 Lesson 2 extra credit
... 1. How are a stimulus and a response related? 2. How do the three different types of neurons function? 3. What is a nerve net? How many specialized neurons does a nerve net include? 4. What are the three functions of a brain? 5. How are animals with many sense organs able to process many stimuli at ...
... 1. How are a stimulus and a response related? 2. How do the three different types of neurons function? 3. What is a nerve net? How many specialized neurons does a nerve net include? 4. What are the three functions of a brain? 5. How are animals with many sense organs able to process many stimuli at ...
Ray pavloski
... levels. Evidence from my recent research shows how simulations of model neural networks produce self-organized patterns of clusters of neurons that are both stable and hidden, and illustrates how the structure of these hidden patterns can be inferred from the network-wide structure of the effects of ...
... levels. Evidence from my recent research shows how simulations of model neural networks produce self-organized patterns of clusters of neurons that are both stable and hidden, and illustrates how the structure of these hidden patterns can be inferred from the network-wide structure of the effects of ...
Artificial Neural Networks
... splits into thousands of branches. At the end of the branch, a structure called a synapse converts the activity from the axon into electrical effects that inhibit or excite activity in the connected neurons. When a neuron receives excitatory input that is sufficiently large compared with its inhibit ...
... splits into thousands of branches. At the end of the branch, a structure called a synapse converts the activity from the axon into electrical effects that inhibit or excite activity in the connected neurons. When a neuron receives excitatory input that is sufficiently large compared with its inhibit ...
brain and spinal cord
... The human brain is the most complex system, natural or man made, in the world. About 3 lbs.; About the size of a grapefruit;Pinkish/gray in color; About 100 billion nerve cells; At a loss rate of 200,000 per day during our adult lives we still end up with over 98% of or brain cells. ...
... The human brain is the most complex system, natural or man made, in the world. About 3 lbs.; About the size of a grapefruit;Pinkish/gray in color; About 100 billion nerve cells; At a loss rate of 200,000 per day during our adult lives we still end up with over 98% of or brain cells. ...
N1 - Kůra mozku HE
... cells : 1.neurons and 2.glial cells • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vascul ...
... cells : 1.neurons and 2.glial cells • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vascul ...
Neuroscience, Genetics, and Behavior
... • Summing Up • Terms and Concepts to Remember • Critical Thinking Exercise • For Further Information Myers 5e ...
... • Summing Up • Terms and Concepts to Remember • Critical Thinking Exercise • For Further Information Myers 5e ...