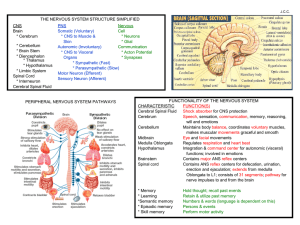
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Co ...
... Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Co ...
Fundamentals of Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... going to skeletal muscles and Visceral Motor – going to smooth or cardiac muscles. Inter-neurons receive information from sensory neurons and integrate it, interpret the meaning and pass instructions to motor neurons to act. Neurons (on basis # of appendages) Multipolar Neurons – many dendrites and ...
... going to skeletal muscles and Visceral Motor – going to smooth or cardiac muscles. Inter-neurons receive information from sensory neurons and integrate it, interpret the meaning and pass instructions to motor neurons to act. Neurons (on basis # of appendages) Multipolar Neurons – many dendrites and ...
Connecting cortex to machines: recent advances in brain interfaces
... to the point where recordings can be made in tens to hundreds of neurons for months. Assemblies of small wires, termed ‘microwires’, have been used for many years for chronic cortical recordings. These have proven to be a very useful experimental tool to study cortical activity1,9,10. More advanced ...
... to the point where recordings can be made in tens to hundreds of neurons for months. Assemblies of small wires, termed ‘microwires’, have been used for many years for chronic cortical recordings. These have proven to be a very useful experimental tool to study cortical activity1,9,10. More advanced ...
Study Guide 1
... 19. Under what conditions does neurotransmitter release cause an action potential? 20. Define spatial summation and temporal summation. 21. Define convergence and divergence as these terms would apply to a neural circuit. 22. What is the difference between an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) ...
... 19. Under what conditions does neurotransmitter release cause an action potential? 20. Define spatial summation and temporal summation. 21. Define convergence and divergence as these terms would apply to a neural circuit. 22. What is the difference between an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) ...
Brain Messages - rm13brainwaves
... system is divided into two main systems, the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The spinal cord and the brain make up the CNS (central nervous system) and all nerves and ‘wiring’ make up the PNS (peripheral nervous system. There is also another system called the Ecrodine or Ho ...
... system is divided into two main systems, the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The spinal cord and the brain make up the CNS (central nervous system) and all nerves and ‘wiring’ make up the PNS (peripheral nervous system. There is also another system called the Ecrodine or Ho ...
File
... binds to receptors which have an inhibitory effect, reducing rate and strength of the muscle contraction. by enzyme degradation and re-uptake ...
... binds to receptors which have an inhibitory effect, reducing rate and strength of the muscle contraction. by enzyme degradation and re-uptake ...
Cognitive neuroscience
... event is occurring • EEG, MEG, TMS and single-cell recording = millisecond resolution • PET and fMRI = minutes and seconds Spatial resolution: Measure where an event is occurring • Lesion and functional imaging = millimetre • Single-cell recordings = level of the neuron (The Student's Guide to Cogni ...
... event is occurring • EEG, MEG, TMS and single-cell recording = millisecond resolution • PET and fMRI = minutes and seconds Spatial resolution: Measure where an event is occurring • Lesion and functional imaging = millimetre • Single-cell recordings = level of the neuron (The Student's Guide to Cogni ...
Slide 1
... Nanowire is also a good candidate for the research into neural network. (especially in electrical, chemical, and biological signal detection.) ...
... Nanowire is also a good candidate for the research into neural network. (especially in electrical, chemical, and biological signal detection.) ...
Circulatory System Directs blood from the heart to the rest of the
... 2. The nerve cell is stimulated by an electric current, change in pH, or a pinch, causing an action potential 3. Upon stimulation, Sodium gates in the nerve cell membrane open and sodium rushes into the cell. This rush of positive ions causes the cell’s charge to rise and spike (from -65mv to +40mv) ...
... 2. The nerve cell is stimulated by an electric current, change in pH, or a pinch, causing an action potential 3. Upon stimulation, Sodium gates in the nerve cell membrane open and sodium rushes into the cell. This rush of positive ions causes the cell’s charge to rise and spike (from -65mv to +40mv) ...
Nervous System
... out from the cell body; receive and carry impulses to the cell body 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another ...
... out from the cell body; receive and carry impulses to the cell body 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another ...
Nerves Part 1 Powerpoint
... • Interneurons form the central nervous system (CNS) • Sensory and motor neurons form the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
... • Interneurons form the central nervous system (CNS) • Sensory and motor neurons form the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
Chapter 6 - TeacherWeb
... - nerve- a tissue inside an organ in the nervous system that is made up of nerve fibers - neuron- a cell in the nerve tissue in the nervous system that carries information * nerve impulse- message that the neuron carries * dendrites – a nerve fiber in the neuron that caries impulses towards the neur ...
... - nerve- a tissue inside an organ in the nervous system that is made up of nerve fibers - neuron- a cell in the nerve tissue in the nervous system that carries information * nerve impulse- message that the neuron carries * dendrites – a nerve fiber in the neuron that caries impulses towards the neur ...
Neurons, Neurons, Neurons!
... When myelin is damaged, dense, scar-like tissue forms around nerve fibers throughout the brain and spinal cord. These scars, sometimes referred to as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spina ...
... When myelin is damaged, dense, scar-like tissue forms around nerve fibers throughout the brain and spinal cord. These scars, sometimes referred to as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spina ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 13.1 Ectodermis subdivided into
... FIGURE 13.3 The BMP signaling pathway and its role in DV patterning of the ectoderm. (A) Experiments in Xenopus embryos that led to the default model: culture of animal cap explant results in epidermis differentiation; dissociation for several hours followed by reaggregation of animal cap tissue res ...
... FIGURE 13.3 The BMP signaling pathway and its role in DV patterning of the ectoderm. (A) Experiments in Xenopus embryos that led to the default model: culture of animal cap explant results in epidermis differentiation; dissociation for several hours followed by reaggregation of animal cap tissue res ...
Ch. 12 Nervous Tissue
... types of cells that are found in nervous tissue • Know the anatomy of a neuron and the structural and functional types of neurons • Understand what a potential is and how this can transmit an impulse • Understand what occurs at the synapse ...
... types of cells that are found in nervous tissue • Know the anatomy of a neuron and the structural and functional types of neurons • Understand what a potential is and how this can transmit an impulse • Understand what occurs at the synapse ...
Project Self-Discovery
... a) They don’t call it “dope” for nothin’! b) Cocaine is a reuptake inhibitor for dopamine c) What does that mean? Quick write what the video taught you about how cocaine interacts with our brains at the neural level ...
... a) They don’t call it “dope” for nothin’! b) Cocaine is a reuptake inhibitor for dopamine c) What does that mean? Quick write what the video taught you about how cocaine interacts with our brains at the neural level ...
The Nervous System
... a ventral and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, and retina. The peripheral nervous system consists of all the other singular nerves and neurons, the nerve clusters, and the nerves that connects to the central nervous system. This whole system i ...
... a ventral and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, and retina. The peripheral nervous system consists of all the other singular nerves and neurons, the nerve clusters, and the nerves that connects to the central nervous system. This whole system i ...
Nervous System
... Bilateral symmetry usually demonstrate cephalization, nervous system concentration in the head and centralization, presence of CNS and PNS Platyhelminthes with nerve cords to control animal movements is simplest Subsequent phyla see an increase in neuron number and segmentation ...
... Bilateral symmetry usually demonstrate cephalization, nervous system concentration in the head and centralization, presence of CNS and PNS Platyhelminthes with nerve cords to control animal movements is simplest Subsequent phyla see an increase in neuron number and segmentation ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... 24. Mature neurons do not divide. If damage to a neuron occurs to the axon and the cell body remains intact, cut or compressed axons can: – A. regenerate. – B. never regenerate. ...
... 24. Mature neurons do not divide. If damage to a neuron occurs to the axon and the cell body remains intact, cut or compressed axons can: – A. regenerate. – B. never regenerate. ...
jeopardy bio psych review
... The part of the neuron that conducts an electrical signal during an action potential. ...
... The part of the neuron that conducts an electrical signal during an action potential. ...
Project Self-Discovery
... human being. When the operation is over and the anesthetic wears off, the body opens its eyes. Who is looking out of the eyes? Who is processing the information coming into the eyes, ears, skin, nose, mouth? Quick talk #2: You suffer a traumatic brain injury in a car accident. After months of physic ...
... human being. When the operation is over and the anesthetic wears off, the body opens its eyes. Who is looking out of the eyes? Who is processing the information coming into the eyes, ears, skin, nose, mouth? Quick talk #2: You suffer a traumatic brain injury in a car accident. After months of physic ...
Study Questions - Nervous System
... 20. If a neuron can only send an ON or OFF signal, how can information about stimulus intensity be contained in that signal? (11.3) 21. How does an action potential from one neuron create a graded potential in a target neuron? (11.5) 22. Explain how a neurotransmitter can be excitatory (meaning what ...
... 20. If a neuron can only send an ON or OFF signal, how can information about stimulus intensity be contained in that signal? (11.3) 21. How does an action potential from one neuron create a graded potential in a target neuron? (11.5) 22. Explain how a neurotransmitter can be excitatory (meaning what ...
MAPPINGS BETWEEN BRAINS - Wichita State University
... the thought process? What determines the process? Do the neurons fire just once or do they continue to take in input and evaluate it and fire another decision until the decisions are irrelevant? Why are the brains neurons able to receive many inputs at the same time, but only give one output at a ti ...
... the thought process? What determines the process? Do the neurons fire just once or do they continue to take in input and evaluate it and fire another decision until the decisions are irrelevant? Why are the brains neurons able to receive many inputs at the same time, but only give one output at a ti ...