Axia College Material Appendix B Structures of the Nervous System
... CNS is a part of the nervous system of all vertebrates. It is located in the spine and skull. This is the center of metabolic activity within each neuron. The cell body is also called the soma. This is the part of the vertebrate nervous system which is located outside the CNS (i.e. outside the spine ...
... CNS is a part of the nervous system of all vertebrates. It is located in the spine and skull. This is the center of metabolic activity within each neuron. The cell body is also called the soma. This is the part of the vertebrate nervous system which is located outside the CNS (i.e. outside the spine ...
Brain Structure - Updated 14
... neighboring neuron. (use the text to help you understand what each role does) • Group – Students line up in the correct order of neural transmission. • Facilitator – Orchestrate the group to ‘act out’ each of the steps and have each student act out their parts as you are going through the steps. Do ...
... neighboring neuron. (use the text to help you understand what each role does) • Group – Students line up in the correct order of neural transmission. • Facilitator – Orchestrate the group to ‘act out’ each of the steps and have each student act out their parts as you are going through the steps. Do ...
Name
... 1. What is homeostasis? Give examples. 2. What are the functions of the nervous system? 3. What is the structure of a neuron and what kinds of neurons are found in the body? 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous sys ...
... 1. What is homeostasis? Give examples. 2. What are the functions of the nervous system? 3. What is the structure of a neuron and what kinds of neurons are found in the body? 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous sys ...
Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... Neurons = nerve cells, the building blocks of our neural information system. Soma or cyton or cell body = cell body of the neuron, the nucleus or brain of the cell Dendrites = bushy fibers that receive neural information Axon = the elongated-tail ending in branchlike axon terminals that transmit inf ...
... Neurons = nerve cells, the building blocks of our neural information system. Soma or cyton or cell body = cell body of the neuron, the nucleus or brain of the cell Dendrites = bushy fibers that receive neural information Axon = the elongated-tail ending in branchlike axon terminals that transmit inf ...
Zika may cause brain damage in adults, too August 19, 2016 By
... mice, the researchers found Zika affected only regions specific to neural progenitor cells—though they have yet to test the results of their study in humans. ...
... mice, the researchers found Zika affected only regions specific to neural progenitor cells—though they have yet to test the results of their study in humans. ...
Notes - The Nervous System
... – Messages come in from different stimuli and trigger electrical impulses. – At the end of the axon it is changed into a chemical message so it can cross over the synapse – neurotransmitters. ...
... – Messages come in from different stimuli and trigger electrical impulses. – At the end of the axon it is changed into a chemical message so it can cross over the synapse – neurotransmitters. ...
Nervous System
... As chemicals dissolve in mucus in area of smell receptors, the impulses are transferred to the olfactory ...
... As chemicals dissolve in mucus in area of smell receptors, the impulses are transferred to the olfactory ...
Chapter 3
... from donors into the damaged area. Human research - Parkinson’s disease patients have partial recovery of motor ability from transplanted fetal tissue. Ethics - a major debate over the use fetal stem cells exists, acceptance might be higher for adult stem cell use ...
... from donors into the damaged area. Human research - Parkinson’s disease patients have partial recovery of motor ability from transplanted fetal tissue. Ethics - a major debate over the use fetal stem cells exists, acceptance might be higher for adult stem cell use ...
Chapter 48 p. 1040-1053
... long-term depression (LTD): postsynaptic cell’s decreased responsiveness to action potential long-term potentiation(LTP): enhanced responsiveness to action potentials; associated with release of neurotransmitter glutamate (binds with receptors to open gated channels that let in a lot of calcium, ...
... long-term depression (LTD): postsynaptic cell’s decreased responsiveness to action potential long-term potentiation(LTP): enhanced responsiveness to action potentials; associated with release of neurotransmitter glutamate (binds with receptors to open gated channels that let in a lot of calcium, ...
Nervous System Formative Study Guide File
... carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce (effect) movement. b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, sound, feeling, etc.). They are activated by sensory input, and send projections to other elements of the nervous system, ultim ...
... carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce (effect) movement. b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, sound, feeling, etc.). They are activated by sensory input, and send projections to other elements of the nervous system, ultim ...
activities unit 5 - Junta de Andalucía
... a) Reflex actions can happen with/without the participation of the brain. b) Grey matter is shaped like the wings of a bird/butterfly. c) Grey matter is found in the centre/on the outside of the spinal cord. 7. Name the different parts of the brain. 8. What is the function of the skull? 9. Complete ...
... a) Reflex actions can happen with/without the participation of the brain. b) Grey matter is shaped like the wings of a bird/butterfly. c) Grey matter is found in the centre/on the outside of the spinal cord. 7. Name the different parts of the brain. 8. What is the function of the skull? 9. Complete ...
Chapter 40
... 3. Specialized function into peripheral afferent and efferent nerves, connecting to the CNS 4. An increased number of association neurons and other synaptic connections 5. Cephalization, with a concentration of nervous (including sensory) tissue at the head end D. Flatworms have cerebral ganglia tha ...
... 3. Specialized function into peripheral afferent and efferent nerves, connecting to the CNS 4. An increased number of association neurons and other synaptic connections 5. Cephalization, with a concentration of nervous (including sensory) tissue at the head end D. Flatworms have cerebral ganglia tha ...
corticospinal tract
... • corticospinal tract – humans - ~ 1,000,000 axons – originate in motor cortex; pyramidal motor system – makes monosynaptic connections with motor neurons ...
... • corticospinal tract – humans - ~ 1,000,000 axons – originate in motor cortex; pyramidal motor system – makes monosynaptic connections with motor neurons ...
Chapter 3
... • Brain lesions are the most common causes of sensory and motor defects • Lesions are tissue that has been altered by: – Chemical imbalance in the brain – Physical injury – Infection ...
... • Brain lesions are the most common causes of sensory and motor defects • Lesions are tissue that has been altered by: – Chemical imbalance in the brain – Physical injury – Infection ...
15_Neuro
... – senses changes in internal and external environment – interprets these changes – coordinates appropriate response in order to maintain homeostasis ...
... – senses changes in internal and external environment – interprets these changes – coordinates appropriate response in order to maintain homeostasis ...
Ch. 35.3
... of the brain and spinal cord Skull and vertebrae protect brain and spinal cord • Wrapped in MENINGES connective tissue • CEREBROSPINAL FLUID is in between the layers Acts as a shock absorber and protects the CNS ...
... of the brain and spinal cord Skull and vertebrae protect brain and spinal cord • Wrapped in MENINGES connective tissue • CEREBROSPINAL FLUID is in between the layers Acts as a shock absorber and protects the CNS ...
Neural tube formation: Previously- apical constriction, convergence
... SHH non-responsive “barrier” to a relay) proves that SHH can move over a distance as a morphogen, and is not activating a relay system. Dorsal fates occur in cells that cannot respond to SHH. Importantly, ventral fates result in cells beyond the “barrier” of smo-/-, and can even occur at distances l ...
... SHH non-responsive “barrier” to a relay) proves that SHH can move over a distance as a morphogen, and is not activating a relay system. Dorsal fates occur in cells that cannot respond to SHH. Importantly, ventral fates result in cells beyond the “barrier” of smo-/-, and can even occur at distances l ...
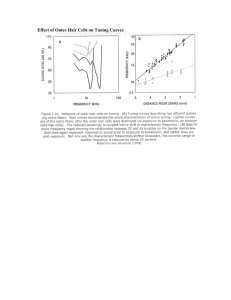
Effect of Outer Hair Cells on Tuning Curves
... release. The locations of neurons with high spike rates and the period between clusters of spikes for groups of active neurons convey frequency information to the brain. ...
... release. The locations of neurons with high spike rates and the period between clusters of spikes for groups of active neurons convey frequency information to the brain. ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... prepare for action + parasympathetic - enhance activity to gain and conserve energy ...
... prepare for action + parasympathetic - enhance activity to gain and conserve energy ...
The brain is the body`s most complex organ. Neurons communicate
... Some injuries harm nerve cells, but the brain often recovers from stress, damage, or disease. ...
... Some injuries harm nerve cells, but the brain often recovers from stress, damage, or disease. ...
The Nervous System allows communication
... radioactive substances to produce three-dimensional colored images of those substances functioning within the body. These images are called PET scans and the technique is termed PET scanning. PET scanning provides information about the body's chemistry not available through other procedures. Unlike ...
... radioactive substances to produce three-dimensional colored images of those substances functioning within the body. These images are called PET scans and the technique is termed PET scanning. PET scanning provides information about the body's chemistry not available through other procedures. Unlike ...