Lecture 7 (Jan 31): BRAIN DEVELOPMENT and EVOLUTION
... specific part of the Optic Tectum Evidence for Chemical Markers (in vitro experiments) TOPDV, high concentration in Dorsal Retina, low in Ventral Retina AND high in Ventral Tectum, low in Dorsal Tectum ….. forms a chemical gradient ...
... specific part of the Optic Tectum Evidence for Chemical Markers (in vitro experiments) TOPDV, high concentration in Dorsal Retina, low in Ventral Retina AND high in Ventral Tectum, low in Dorsal Tectum ….. forms a chemical gradient ...
Myers Module Four
... axon and speeds up the tranmission of neural impulses. After age 25, this sheath deteriorates, leading in extreme cases to multiple sclerosis. ...
... axon and speeds up the tranmission of neural impulses. After age 25, this sheath deteriorates, leading in extreme cases to multiple sclerosis. ...
sensationandperception_PP_Vision_Mods 18 and 19
... sends it to its own specialized processing region of the brain. ...
... sends it to its own specialized processing region of the brain. ...
read more
... techniques, which allow us to instantaneously perturb neural activity and record the response. We do not yet have a theoretical framework to adequately describe the neural response to such optogenetic perturbations, nor do we understand how neural networks can perform computations amid a background ...
... techniques, which allow us to instantaneously perturb neural activity and record the response. We do not yet have a theoretical framework to adequately describe the neural response to such optogenetic perturbations, nor do we understand how neural networks can perform computations amid a background ...
Ch. 11: Machine Learning: Connectionist
... If the potential reaches a certain threshold, an electrical pulse, or action potential, will travel down the axon, eventually reaching all the branches, causing them to release their neurotransmitters. And so on ... ...
... If the potential reaches a certain threshold, an electrical pulse, or action potential, will travel down the axon, eventually reaching all the branches, causing them to release their neurotransmitters. And so on ... ...
Chapter Summary Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception • Sensation
... several principles by which we recognize stimuli even when visual inputs are limited. We use binocular and monocular cues for depth perception. Perceptual constancies, based on learning from previous experiences, help us to see things as stable despite constant shifts in our visual inputs. These top ...
... several principles by which we recognize stimuli even when visual inputs are limited. We use binocular and monocular cues for depth perception. Perceptual constancies, based on learning from previous experiences, help us to see things as stable despite constant shifts in our visual inputs. These top ...
Brain Questions
... 1- State three functions of the nervous system 2- What, kind of neurons carry signals to the central nervous system? What, kind of neurons interpret these signals? What, kind of neurons send signals out to the peripheral nervous system? 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripher ...
... 1- State three functions of the nervous system 2- What, kind of neurons carry signals to the central nervous system? What, kind of neurons interpret these signals? What, kind of neurons send signals out to the peripheral nervous system? 3- The central nervous system is composed of what? The peripher ...
Study Guide
... Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you want to do something (like throw a ball, ride a bike.) When you react to something without thinking, your action is called a reflex. The part of the brain that controls involuntary act ...
... Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you want to do something (like throw a ball, ride a bike.) When you react to something without thinking, your action is called a reflex. The part of the brain that controls involuntary act ...
Neural Development
... Each location in space is seen by a different location on the retina of the frog Each different location on the retina is connected by the optic nerve to a different location in the brain Each of these different locations in the brain causes a different movement direction. In a normal animal, a reti ...
... Each location in space is seen by a different location on the retina of the frog Each different location on the retina is connected by the optic nerve to a different location in the brain Each of these different locations in the brain causes a different movement direction. In a normal animal, a reti ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... comprised of the brain and spinal chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in ...
... comprised of the brain and spinal chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in ...
Madison Pejsa Pd.4
... Brain Stem- The portion of the brain that is continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and parts of the hypothalamus, functioning in the control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion ...
... Brain Stem- The portion of the brain that is continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and parts of the hypothalamus, functioning in the control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion ...
Powerpoint slides
... Excitatory postsynaptic potentials Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials Temporal summation Spatial summation ...
... Excitatory postsynaptic potentials Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials Temporal summation Spatial summation ...
Overview of the Day
... Peripheral Nervous System (carries info. to and from the CNS) somatic/skeletal nervous system (controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles autonomic nervous system (controls glands and muscles of internal organs [e.g., heart]). The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work together to k ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (carries info. to and from the CNS) somatic/skeletal nervous system (controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles autonomic nervous system (controls glands and muscles of internal organs [e.g., heart]). The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work together to k ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... respiratory, and digestive system activities) Cerebellum o Coordinates complex somatic motor patterns o Adjusts output of other somatic motor centers in brain and spinal cord How does the CNS get its adult shape? Embryonic Development of the Nervous System Understanding the embryology helps to ...
... respiratory, and digestive system activities) Cerebellum o Coordinates complex somatic motor patterns o Adjusts output of other somatic motor centers in brain and spinal cord How does the CNS get its adult shape? Embryonic Development of the Nervous System Understanding the embryology helps to ...
Neuron Summary - MsHughesPsychology
... incoming neural information (neural impulses) 2. Soma – cell body, the section that determines whether the neuron will be activated and thus transmit (pass on) the neural stimulation to other neurons 3. Axon – a single tube like extension that transmits messages (neural impulses) from the soma to ot ...
... incoming neural information (neural impulses) 2. Soma – cell body, the section that determines whether the neuron will be activated and thus transmit (pass on) the neural stimulation to other neurons 3. Axon – a single tube like extension that transmits messages (neural impulses) from the soma to ot ...
Vocabulary: Chapter 1 Body Control Systems Neuron
... Peripheral nervous system, part of the nervous system that connects the central nervous system with all the other parts of the body. Cerebrum- the part of the brain that controls thinking and voluntary movements and receives information from the senses. Cerebellum- the part of the brain that coordin ...
... Peripheral nervous system, part of the nervous system that connects the central nervous system with all the other parts of the body. Cerebrum- the part of the brain that controls thinking and voluntary movements and receives information from the senses. Cerebellum- the part of the brain that coordin ...
Artificial Neural Networks - Introduction -
... Artificial neural networks Tasks to be solved by artificial neural networks: • controlling the movements of a robot based on selfperception and other information (e.g., visual information); • deciding the category of potential food items (e.g., edible or non-edible) in an artificial world; ...
... Artificial neural networks Tasks to be solved by artificial neural networks: • controlling the movements of a robot based on selfperception and other information (e.g., visual information); • deciding the category of potential food items (e.g., edible or non-edible) in an artificial world; ...
PSY110 Psychology
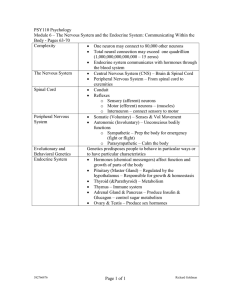
... Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System – From spinal cord to exremities Spinal Cord Conduit Reflexes o Sensory (afferent) neurons o Motor (efferent) neurons – (musc ...
... Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System – From spinal cord to exremities Spinal Cord Conduit Reflexes o Sensory (afferent) neurons o Motor (efferent) neurons – (musc ...
AP Psychology - HOMEWORK 9
... MULTIPLE ANSWER: Biological psychologists study behavior and mental processes from multiple levels, noting how____________________, ______________________________and ______________________-_____________________________ systems work and interact. (0.5 pt each) ...
... MULTIPLE ANSWER: Biological psychologists study behavior and mental processes from multiple levels, noting how____________________, ______________________________and ______________________-_____________________________ systems work and interact. (0.5 pt each) ...
Perspective Research of Specific Neural Projection with
... Perspective Brain is the most complex organ of human body and the cerebral cortex is the most component of the brain. The cerebral cortex itself is divided into different regions, each containing specific neuron types. During development, these neurons project to different target region and establis ...
... Perspective Brain is the most complex organ of human body and the cerebral cortex is the most component of the brain. The cerebral cortex itself is divided into different regions, each containing specific neuron types. During development, these neurons project to different target region and establis ...
Neural Development - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... brain abnormalities, such as mental retardation and other brain disorders, can be prevented or treated. ...
... brain abnormalities, such as mental retardation and other brain disorders, can be prevented or treated. ...