UNIT 3A: Biological Bases of Behavior – Neural Processing and the
... Correctly focused attention on the fact that various parts of the brain have different functions C. Biological psychology ...
... Correctly focused attention on the fact that various parts of the brain have different functions C. Biological psychology ...
Chapter 2 - The Brain (Part II)
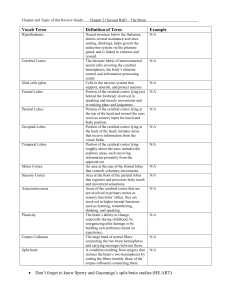
... roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. Areas o ...
... roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. Areas o ...
1. Which of the following is the component of the limbic system that
... 2. An axon is A) a cell that serves as the basic building block of the nervous system. B) a layer of fatty tissue that encases the fibers of many neurons. C) an antagonist molecule that blocks neurotransmitter receptor sites. D) the extension of a neuron that carries messages away from the cell body ...
... 2. An axon is A) a cell that serves as the basic building block of the nervous system. B) a layer of fatty tissue that encases the fibers of many neurons. C) an antagonist molecule that blocks neurotransmitter receptor sites. D) the extension of a neuron that carries messages away from the cell body ...
File
... •Credited with the idea that learning involves the establishment and strengthening of neural connections at the synapse •Learning results in the creation of ‘cell assemblies’ (interconnected groups of neurons that form networks or pathways) • When neurotransmitter is repeatedly sent across the synap ...
... •Credited with the idea that learning involves the establishment and strengthening of neural connections at the synapse •Learning results in the creation of ‘cell assemblies’ (interconnected groups of neurons that form networks or pathways) • When neurotransmitter is repeatedly sent across the synap ...
nervous system
... sheath which provides the electrical insulation for certain neurons in the CNS ...
... sheath which provides the electrical insulation for certain neurons in the CNS ...
Artificial Intelligence Connectionist Models Inspired by the brain
... to analyze neural networks and applies them to new problems 1985: Backpropagation training rule for muli-layer neural networks is rediscovered 1987: First IEEE conference on neural networks. Over 2000 attend. The revival is underway! ...
... to analyze neural networks and applies them to new problems 1985: Backpropagation training rule for muli-layer neural networks is rediscovered 1987: First IEEE conference on neural networks. Over 2000 attend. The revival is underway! ...
Nervous System functions
... 1. Sensory Function • Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral neurons: – Gather info by detecting changes inside and outside the body. • Inside: temperature and oxygen concentration • Outside: light and sound intensities ...
... 1. Sensory Function • Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral neurons: – Gather info by detecting changes inside and outside the body. • Inside: temperature and oxygen concentration • Outside: light and sound intensities ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to the Health Science Program
... Impulses from one neuron are transmitted across the synapse to another neuron by a chemical called a neurotransmitter ...
... Impulses from one neuron are transmitted across the synapse to another neuron by a chemical called a neurotransmitter ...
PDF version
... The World's No.1 Science & Technology News Service Moving brain implant seeks out signals 19:00 10 November 04 Exclusive from New Scientist Print Edition. Subscribe and get 4 free issues. ...
... The World's No.1 Science & Technology News Service Moving brain implant seeks out signals 19:00 10 November 04 Exclusive from New Scientist Print Edition. Subscribe and get 4 free issues. ...
Slide 1
... thoughts and personality • Large memory storehouse. • Each portion of the nervous system performs specific functions, but it is the cortex that opens the world up for one’s mind. ...
... thoughts and personality • Large memory storehouse. • Each portion of the nervous system performs specific functions, but it is the cortex that opens the world up for one’s mind. ...
Slide ()
... The activity of functionally distinct parietal motor neurons varies with the purpose of a grasping action. (Modified, with permission, from Fogassi et al. ...
... The activity of functionally distinct parietal motor neurons varies with the purpose of a grasping action. (Modified, with permission, from Fogassi et al. ...
The role of the nervous system in detecting and
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
Lies outside the central nervous system
... Consists of the spinal cord and the brain Both covered with a protective membrane called meningens Impulses are received at the spinal cord and the brain via the PNS- initiates voluntary motor control ...
... Consists of the spinal cord and the brain Both covered with a protective membrane called meningens Impulses are received at the spinal cord and the brain via the PNS- initiates voluntary motor control ...
File
... 1. This lobe of the cerebrum houses your intellect, emotions, and consciousness: 2. This region of the brain acts as a relay station for sensory input: 3. These neurons transfer impulses from the brain to skeletal muscle: 4. This allows communication between the left and right hemispheres of the cer ...
... 1. This lobe of the cerebrum houses your intellect, emotions, and consciousness: 2. This region of the brain acts as a relay station for sensory input: 3. These neurons transfer impulses from the brain to skeletal muscle: 4. This allows communication between the left and right hemispheres of the cer ...
Brain Learning
... from another. As exposure continues, the listener (and the brain) learns to differentiate among different sounds and even among short sequences of sounds that correspond to words or parts of words. Neural connections that reflect this learning process are formed in the auditory (temporal) cortex of ...
... from another. As exposure continues, the listener (and the brain) learns to differentiate among different sounds and even among short sequences of sounds that correspond to words or parts of words. Neural connections that reflect this learning process are formed in the auditory (temporal) cortex of ...
48.5, .6, .7
... Lateralization of Cortical Function • During brain development after birth, competing functions segregate and displace each other in the cortex of the left and right cerebral hemispheres • The left hemisphere becomes more adept to language, math, logical operations, and the serial processing of seq ...
... Lateralization of Cortical Function • During brain development after birth, competing functions segregate and displace each other in the cortex of the left and right cerebral hemispheres • The left hemisphere becomes more adept to language, math, logical operations, and the serial processing of seq ...
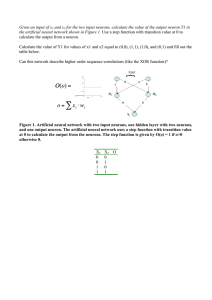
Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the
... Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the value of the output neuron Y1 in the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0 ...
... Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the value of the output neuron Y1 in the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0 ...
Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
... Excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excita ...
... Excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excita ...
The Nervous System
... • The CNS (central nervous system) – Consists of the brain and spinal cord ...
... • The CNS (central nervous system) – Consists of the brain and spinal cord ...
Biopsychology revision 2
... What makes you, you? What makes you unique from every other person? ...
... What makes you, you? What makes you unique from every other person? ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 1. What are the three major overlapping functions of the nervous system? a) Sensory input—information gathered from stimuli inside and outside the body b) Integration—processes and interprets sensory input and decides what should be done c) Motor output—response performed by activating muscle or gla ...
... 1. What are the three major overlapping functions of the nervous system? a) Sensory input—information gathered from stimuli inside and outside the body b) Integration—processes and interprets sensory input and decides what should be done c) Motor output—response performed by activating muscle or gla ...
File
... 12. Sir Charles Sherrington observed that impulses took more time to travel a neural pathway than he might have anticipated. His observation provided evidence for the existence of: A) association areas. B) synaptic gaps. C) interneurons. D) neural networks. ...
... 12. Sir Charles Sherrington observed that impulses took more time to travel a neural pathway than he might have anticipated. His observation provided evidence for the existence of: A) association areas. B) synaptic gaps. C) interneurons. D) neural networks. ...