The Induction and Patterning of the Nervous System
... forebrain: follistatin, noggin, chordin more posterior: FGF family protein hindbrain and spinal cord: retinoic acid ...
... forebrain: follistatin, noggin, chordin more posterior: FGF family protein hindbrain and spinal cord: retinoic acid ...
HP Authorized Customer
... It is accountable for the treatments of memory, thought, and perception and serves like the seat of problem solving, language, social capabilities, and advanced motor function. Cells of the nervous system that transmit messages via electrochemical signs. It is a slim, normally branched projection of ...
... It is accountable for the treatments of memory, thought, and perception and serves like the seat of problem solving, language, social capabilities, and advanced motor function. Cells of the nervous system that transmit messages via electrochemical signs. It is a slim, normally branched projection of ...
Review questions: Neuroanatomy
... Review questions: Neuroanatomy 1. Classify the structures of the nervous system into divisions. CNS – Brain and Spinal Cord PNS – Nerves: 31 spinal, 12 cranial. Ganglia: Collection of nerve cell bodies in PNS. Cells which perform similar functions. Receptors: Pick up stimulus at end of nerves (dendr ...
... Review questions: Neuroanatomy 1. Classify the structures of the nervous system into divisions. CNS – Brain and Spinal Cord PNS – Nerves: 31 spinal, 12 cranial. Ganglia: Collection of nerve cell bodies in PNS. Cells which perform similar functions. Receptors: Pick up stimulus at end of nerves (dendr ...
The Nervous System
... • Neither of these chemicals can pass through the cell membrane. They are attracted to each other because of their opposite charge. ...
... • Neither of these chemicals can pass through the cell membrane. They are attracted to each other because of their opposite charge. ...
ppt
... potential after ions “leak” down their concentration gradient - 3 Na+ ions are actively pumped out while 2 K+ ions are pumped in. ...
... potential after ions “leak” down their concentration gradient - 3 Na+ ions are actively pumped out while 2 K+ ions are pumped in. ...
Nervous System PPT
... What is the nervous system? Each day, you use verbal and nonverbal communication as a signal to others. For example, to signal a student has a question, he/she would raise his/her hand. The teacher would recognize this signal and direct his/her attention to the student. Your body works in much the ...
... What is the nervous system? Each day, you use verbal and nonverbal communication as a signal to others. For example, to signal a student has a question, he/she would raise his/her hand. The teacher would recognize this signal and direct his/her attention to the student. Your body works in much the ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... What name is given to the electrical-type message that travels along a neuron? ...
... What name is given to the electrical-type message that travels along a neuron? ...
nerve net
... – Series of smaller nerves that branch to all parts of organism – Impulses are generated by receptors and travel through the nerves to reach muscles and glands ...
... – Series of smaller nerves that branch to all parts of organism – Impulses are generated by receptors and travel through the nerves to reach muscles and glands ...
Bradley`s.
... Its unique ability to send and receive specific signals from specific parts of the body using nerve cells, chemicals, and electrical impulses is simply amazing ...
... Its unique ability to send and receive specific signals from specific parts of the body using nerve cells, chemicals, and electrical impulses is simply amazing ...
Chapter 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
... • Electrical signals can’t jump this gap. Instead, the neuron that is sending the message across the gap (the _21_ neuron) releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. This occurs when the action potential gets to the terminal button and causes the _22_ (2 words), the storage sacs for the neu ...
... • Electrical signals can’t jump this gap. Instead, the neuron that is sending the message across the gap (the _21_ neuron) releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. This occurs when the action potential gets to the terminal button and causes the _22_ (2 words), the storage sacs for the neu ...
1. The diagram below is of a nerve cell or neuron. i. Add the following
... 3. The connection between adjacent neurons. ...
... 3. The connection between adjacent neurons. ...
Unit 10 Chapter 36 The Nervous System
... to the spinal cord & brain Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord & brain to the body Interneurons are found within the spinal cord & brain, pass response impulses between sensory & motor ...
... to the spinal cord & brain Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord & brain to the body Interneurons are found within the spinal cord & brain, pass response impulses between sensory & motor ...
Modeling working memory and decision making using generic
... attractor” states can be held by generic neural microcircuits on the time-scales of several seconds, which is obviously a requirement for tasks involving working memory ...
... attractor” states can be held by generic neural microcircuits on the time-scales of several seconds, which is obviously a requirement for tasks involving working memory ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... • Relay station for tracts passing between the cerebrum and the spinal cord or cerebellum • Has reflex centers for visual, auditory, and tactile responses • Contains the cerebral peduncles and corpora ...
... • Relay station for tracts passing between the cerebrum and the spinal cord or cerebellum • Has reflex centers for visual, auditory, and tactile responses • Contains the cerebral peduncles and corpora ...
The Nervous System and The Brain
... with a vacuum or scalpel. It can also be transected, meaning isolated or cut. ...
... with a vacuum or scalpel. It can also be transected, meaning isolated or cut. ...
Neurons - Scott Melcher
... How Neurons Communicate Neurons are intricately interwoven, but do not actually touch. The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving cell is called a synapse. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or cleft. When neurons are ...
... How Neurons Communicate Neurons are intricately interwoven, but do not actually touch. The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving cell is called a synapse. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or cleft. When neurons are ...
Nervous System PPT - Effingham County Schools
... • picks up sensory information and delivers it to the CNS Motor Division • carries information to muscles and glands Divisions of the Motor Division • Somatic – carries information to skeletal muscle • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
... • picks up sensory information and delivers it to the CNS Motor Division • carries information to muscles and glands Divisions of the Motor Division • Somatic – carries information to skeletal muscle • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
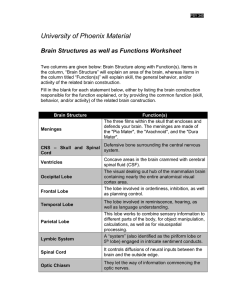
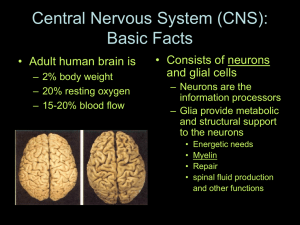
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
Neural Coalition and Main Theorem
... • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obtained by solving for the minimum of the Gibbs/Helmholtz Fre ...
... • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obtained by solving for the minimum of the Gibbs/Helmholtz Fre ...
The Nervous System - Volunteer State Community College
... Signal transmission along a neuron depends on voltages created by ionic fluxes across neuron plasma membranes. Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. All cells have an electrical potential or voltage across their plasma ...
... Signal transmission along a neuron depends on voltages created by ionic fluxes across neuron plasma membranes. Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. All cells have an electrical potential or voltage across their plasma ...
A Guided Tour of the Brain
... primal neural cells has formed. This sheet curls to form the hollow neural tube. The neural stem cells divide and multiply, creating specific cells that eventually produce neurons and glial cells. As the neural tube expands, the cavities develop, called the ventricles. During peak periods in the bra ...
... primal neural cells has formed. This sheet curls to form the hollow neural tube. The neural stem cells divide and multiply, creating specific cells that eventually produce neurons and glial cells. As the neural tube expands, the cavities develop, called the ventricles. During peak periods in the bra ...
File
... Cranial nerves: __ pairs of nerves that originate in the brain and relay impulses to and from the PNS Craniosacral division: the _____________ nervous system, in which nerves originate in the brain stem or sacral region of the spinal cord Dorsal ramus: the division of __________ spinal nerves that ...
... Cranial nerves: __ pairs of nerves that originate in the brain and relay impulses to and from the PNS Craniosacral division: the _____________ nervous system, in which nerves originate in the brain stem or sacral region of the spinal cord Dorsal ramus: the division of __________ spinal nerves that ...