Neurons
... Classes of Neurons Afferent- do not have dendrites: transmit impulses from specialized structures to the Central Nervous System Efferent- conduct electrical signals from the CNS to muscle or glad cells Inter- reside entirely within the CNS and make up about 99% of all neurons ...
... Classes of Neurons Afferent- do not have dendrites: transmit impulses from specialized structures to the Central Nervous System Efferent- conduct electrical signals from the CNS to muscle or glad cells Inter- reside entirely within the CNS and make up about 99% of all neurons ...
Editorial overview: Neurobiology of cognitive behavior: Complexity
... thus arise from the involvement of both local and distributed networks. The recent ability to simultaneously monitor activity of large groups of neurons has given us an even deeper look at the richness and complexity of neural representations in cognitive tasks. Advances in high-density probe design ...
... thus arise from the involvement of both local and distributed networks. The recent ability to simultaneously monitor activity of large groups of neurons has given us an even deeper look at the richness and complexity of neural representations in cognitive tasks. Advances in high-density probe design ...
Neural Networks 2 - Monash University
... how such topology-preserving mappings might arise in neural networks It is probable that in biological systems that much of the organization of such maps is genetically determined, BUT: The brain is estimated to have ~1013 synapses (connections), so it would be impossible to produce this organiz ...
... how such topology-preserving mappings might arise in neural networks It is probable that in biological systems that much of the organization of such maps is genetically determined, BUT: The brain is estimated to have ~1013 synapses (connections), so it would be impossible to produce this organiz ...
Document
... • the interneurons are arranged in tracts which connect the spinal cord to the brain. • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected b ...
... • the interneurons are arranged in tracts which connect the spinal cord to the brain. • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected b ...
Chapter 12 - Marion ISD
... Sodium potassium pump (active transport)-produces slight excess of pos. ions outside. Transports sodium/potassium ...
... Sodium potassium pump (active transport)-produces slight excess of pos. ions outside. Transports sodium/potassium ...
CNS
... • the interneurons are arranged in tracts which connect the spinal cord to the brain. • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected b ...
... • the interneurons are arranged in tracts which connect the spinal cord to the brain. • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected b ...
Chapter 9
... between a nerve and a neuron? Chapter 12- The Brain and Cranial Nerves 1. Name and describe the function of the principal parts of the brain. 2. Know the names and functions of the 12 cranial nerves. What division of the nervous system do cranial nerves belong to? 3. Where does CSF come from? What i ...
... between a nerve and a neuron? Chapter 12- The Brain and Cranial Nerves 1. Name and describe the function of the principal parts of the brain. 2. Know the names and functions of the 12 cranial nerves. What division of the nervous system do cranial nerves belong to? 3. Where does CSF come from? What i ...
Nervous System
... 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. ...
... 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. ...
Psychology312-2_001 - Northwestern University
... Hundreds of cats, rats, humans have been trained to self-control all sorts of ERPs as we’ll see. 2. Obvious clinical applications? (If you change a visual EP, do you change vision? We’ll come back to this. 3. OCNE uniquely can work out neural code/mechanisms of voluntary movement in an unrestrai ...
... Hundreds of cats, rats, humans have been trained to self-control all sorts of ERPs as we’ll see. 2. Obvious clinical applications? (If you change a visual EP, do you change vision? We’ll come back to this. 3. OCNE uniquely can work out neural code/mechanisms of voluntary movement in an unrestrai ...
The Nervous System
... • A nerve cell or neuron is: a specialized cell that uses electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous syst ...
... • A nerve cell or neuron is: a specialized cell that uses electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous syst ...
Organization of the Nervous system. Physiology of neurons and glial
... Nerve cells: neurons and neuroglial cells. • ~1011 neurons in the human brain • and 10 x more neuroglia Neurons have special shapes, physiological properties, and connections (~1000 synapses/each neuron & other connecting mechanisms !) • information transmission throughout the nervous system • uniqu ...
... Nerve cells: neurons and neuroglial cells. • ~1011 neurons in the human brain • and 10 x more neuroglia Neurons have special shapes, physiological properties, and connections (~1000 synapses/each neuron & other connecting mechanisms !) • information transmission throughout the nervous system • uniqu ...
Neural Crest - bthsresearch
... • Define “Neural Crest” & identify the adult structures formed by these cells ...
... • Define “Neural Crest” & identify the adult structures formed by these cells ...
Slide ()
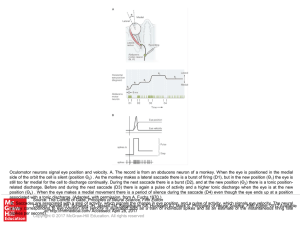
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
2806nn1
... Network Design? 1) Restricting the network architecture through the use of local connections known as receptive fields. 2) Constraining the choice of synaptic weights through the use of weight-sharing. ...
... Network Design? 1) Restricting the network architecture through the use of local connections known as receptive fields. 2) Constraining the choice of synaptic weights through the use of weight-sharing. ...
PDF
... Wnt signalling is known to be involved in NC migration, but is it, like canonical Wnt signalling, required for NC specification? On p. 5441, Olga Ossipova and Sergei Sokol implicate noncanonical Wnt11-like proteins in NC specification in Xenopus embryos. They show that Wnt11R, which is expressed in ...
... Wnt signalling is known to be involved in NC migration, but is it, like canonical Wnt signalling, required for NC specification? On p. 5441, Olga Ossipova and Sergei Sokol implicate noncanonical Wnt11-like proteins in NC specification in Xenopus embryos. They show that Wnt11R, which is expressed in ...
Neurons
... • Has two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • BOTH are composed of neurons, or nerve cells, that transmit messages to different parts of the body. • Neurons have three main parts: cell body (produces energy), dendrites (DELIVERS info to the cell body), and axo ...
... • Has two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • BOTH are composed of neurons, or nerve cells, that transmit messages to different parts of the body. • Neurons have three main parts: cell body (produces energy), dendrites (DELIVERS info to the cell body), and axo ...
The Neuron
... Although neurons are typically defined as nerve cells, they are not actually the only cells in the nervous system. In fact, they are supported by a large number of other cells apply named supporting cells. While the neurons are important for carrying the neural message, the supporting cells are impo ...
... Although neurons are typically defined as nerve cells, they are not actually the only cells in the nervous system. In fact, they are supported by a large number of other cells apply named supporting cells. While the neurons are important for carrying the neural message, the supporting cells are impo ...
Understanding-the.. - Windsor C
... 1. Sensory- afferent- receives messages from sense organs 2. Motor- efferent- sends messages to other parts of the body 3. Inter- communicates between sensory and motor neurons ...
... 1. Sensory- afferent- receives messages from sense organs 2. Motor- efferent- sends messages to other parts of the body 3. Inter- communicates between sensory and motor neurons ...
600 Kb PDF
... Abstract. The brain is perhaps the most advanced and robust computation system known. We are creating a method to study how information is processed and encoded in living cultured neuronal networks by interfacing them to a computer-generated animal, the Neurally-Controlled Animat, within a virtual w ...
... Abstract. The brain is perhaps the most advanced and robust computation system known. We are creating a method to study how information is processed and encoded in living cultured neuronal networks by interfacing them to a computer-generated animal, the Neurally-Controlled Animat, within a virtual w ...
Learning, Memory and Perception.
... evolved to detect meaningful patterns (e.g., correlated rather than uncorrelated motion), to learn, memorize and recall them, and to act adaptively. In a subset of species, many of them social ones, brains can also produce and/or decode communication signals. This deceptively simple constellation of ...
... evolved to detect meaningful patterns (e.g., correlated rather than uncorrelated motion), to learn, memorize and recall them, and to act adaptively. In a subset of species, many of them social ones, brains can also produce and/or decode communication signals. This deceptively simple constellation of ...
1 Bio 3411, Fall 2007, Lecture 17: Neuroembryology.
... However, later stages resemble the blastodisc of telolecithal eggs (reptile/bird/fish-like) ...
... However, later stages resemble the blastodisc of telolecithal eggs (reptile/bird/fish-like) ...
Human Physiology
... Drugs change how the brain works, by changing the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that are generated. Drugs that make a person feel relaxed or tired. Reduce the ability of neurons (nerve cells) to generate action potentials (send messages). Block neurotransmitters (stops/slows messages ...
... Drugs change how the brain works, by changing the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that are generated. Drugs that make a person feel relaxed or tired. Reduce the ability of neurons (nerve cells) to generate action potentials (send messages). Block neurotransmitters (stops/slows messages ...
Module 3 Brain`s Building Blocks
... There are about 30,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that equal about 300,000 pages of written instructions Genes program the development of individual parts into a complex body & brain ...
... There are about 30,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that equal about 300,000 pages of written instructions Genes program the development of individual parts into a complex body & brain ...
The Induction and Patterning of the Nervous System
... forebrain: follistatin, noggin, chordin more posterior: FGF family protein hindbrain and spinal cord: retinoic acid ...
... forebrain: follistatin, noggin, chordin more posterior: FGF family protein hindbrain and spinal cord: retinoic acid ...