Ch 21 Sec 3 Guided Reading
... This section explains how an electric current can be produced in a conductor. It also describes how generators and transformers work. ...
... This section explains how an electric current can be produced in a conductor. It also describes how generators and transformers work. ...
Hall Probe CYHP881
... can be used to measure magnetic field strength of permanent magnet materials, electromagnets, motors, loudspeakers, magnetic sensors/ transducer and other machines and instruments etc. It needs a power supply voltage of +5VDC to give an output voltage of 0 - 4.5VDC in a magnetic measuring range of 0 ...
... can be used to measure magnetic field strength of permanent magnet materials, electromagnets, motors, loudspeakers, magnetic sensors/ transducer and other machines and instruments etc. It needs a power supply voltage of +5VDC to give an output voltage of 0 - 4.5VDC in a magnetic measuring range of 0 ...
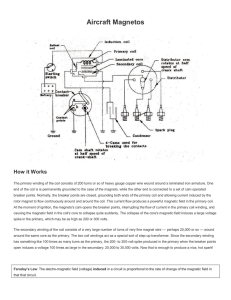
Magneto Diagram - Take Flight San Diego
... causing the magnetic field in the coil's core to collapse quite suddenly. The collapse of the core's magnetic field induces a large voltage spike in the primary, which may be as high as 200 or 300 volts. The secondary winding of the coil consists of a very large number of turns of very fine magnet w ...
... causing the magnetic field in the coil's core to collapse quite suddenly. The collapse of the core's magnetic field induces a large voltage spike in the primary, which may be as high as 200 or 300 volts. The secondary winding of the coil consists of a very large number of turns of very fine magnet w ...
Chapter 5 Electrostatics
... • Induced current flows in a direction such that it opposes the action that induces it – Two ways to induce current: • Self induction – single coil of wire with a current running through it – OPPOSES the magnetic forces it produces • Mutual induction – inducing a current flow through a secondary coi ...
... • Induced current flows in a direction such that it opposes the action that induces it – Two ways to induce current: • Self induction – single coil of wire with a current running through it – OPPOSES the magnetic forces it produces • Mutual induction – inducing a current flow through a secondary coi ...
Chapter 5 Electrostatics
... • Induced current flows in a direction such that it opposes the action that induces it – Two ways to induce current: • Self induction – single coil of wire with a current running through it – OPPOSES the magnetic forces it produces • Mutual induction – inducing a current flow through a secondary coi ...
... • Induced current flows in a direction such that it opposes the action that induces it – Two ways to induce current: • Self induction – single coil of wire with a current running through it – OPPOSES the magnetic forces it produces • Mutual induction – inducing a current flow through a secondary coi ...
Chapter 5 Electrostatics
... • Induced current flows in a direction such that it opposes the action that induces it – Two ways to induce current: • Self induction – single coil of wire with a current running through it – OPPOSES the magnetic forces it produces • Mutual induction – inducing a current flow through a secondary coi ...
... • Induced current flows in a direction such that it opposes the action that induces it – Two ways to induce current: • Self induction – single coil of wire with a current running through it – OPPOSES the magnetic forces it produces • Mutual induction – inducing a current flow through a secondary coi ...
Slide 1 - Cobb Learning
... When an electric current is passed through a coil of wire wrapped around a metal core, a very strong magnetic field is produced. This is called an electromagnet. The more coils wrapped around the core, the stronger the magnetic field that is produced. This stronger magnetic field leads to a stro ...
... When an electric current is passed through a coil of wire wrapped around a metal core, a very strong magnetic field is produced. This is called an electromagnet. The more coils wrapped around the core, the stronger the magnetic field that is produced. This stronger magnetic field leads to a stro ...