Learning Objectives
... • Current produced in a simple dynamo can flow in two ways, if it flows in the same direction and is called direct current (DC). • If it flows and keeps changing direction it is called alternating current(AC). ...
... • Current produced in a simple dynamo can flow in two ways, if it flows in the same direction and is called direct current (DC). • If it flows and keeps changing direction it is called alternating current(AC). ...
Inductor Basics notes
... An inductor is a series of turns of wire around a core material. The core can be air, soft iron in solid of powdered form, graphite or alloys of different metals chosen for their magnetic properties. The inductance of a coil (inductor) is dependant on: 1. Number of turns 2. Area (How close the turns ...
... An inductor is a series of turns of wire around a core material. The core can be air, soft iron in solid of powdered form, graphite or alloys of different metals chosen for their magnetic properties. The inductance of a coil (inductor) is dependant on: 1. Number of turns 2. Area (How close the turns ...
BASIC INDUSTRIAL ELECTRICITY
... introduce the physical laws which govern electricity and how they apply in industry. It will present series and parallel circuits, magnetism and electromagnetism, resistance, capacitance and induction. Relay Logic. The student will learn to use the most common industrial electrical test equipment. ...
... introduce the physical laws which govern electricity and how they apply in industry. It will present series and parallel circuits, magnetism and electromagnetism, resistance, capacitance and induction. Relay Logic. The student will learn to use the most common industrial electrical test equipment. ...
This Course
... coil auxiliary contact (aux contact) motor leads (T leads) • Re-install the coil and wire the circuit using wire provided. Tag each wire with either a sticky label or other means using the numbers assigned above. • Have the circuit checked by the instructor. Do not attempt to hook up to any availabl ...
... coil auxiliary contact (aux contact) motor leads (T leads) • Re-install the coil and wire the circuit using wire provided. Tag each wire with either a sticky label or other means using the numbers assigned above. • Have the circuit checked by the instructor. Do not attempt to hook up to any availabl ...
Magnetism and Induction
... electric current will produce a magnetic field. The field is just like that of a bar magnet. Can make a very strong magnet with only one D cell. And electromagnets can be turned off! ...
... electric current will produce a magnetic field. The field is just like that of a bar magnet. Can make a very strong magnet with only one D cell. And electromagnets can be turned off! ...
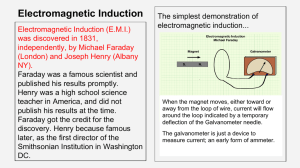
How electricity is made
... The current produced changes direction every half turn (180 degrees ). This is called alternating current or AC. The generators at large power stations produce nearly all the electricity we use in this way. ...
... The current produced changes direction every half turn (180 degrees ). This is called alternating current or AC. The generators at large power stations produce nearly all the electricity we use in this way. ...