What is a transformer?
... What is a transformer? The voltage of an alternating current can be changed using a device called a transformer. A transformer contains two coils that are wound around a soft iron core. ...
... What is a transformer? The voltage of an alternating current can be changed using a device called a transformer. A transformer contains two coils that are wound around a soft iron core. ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... can be produced by (batteries, motion of electric current). More specifically, voltage is induced in a loop of wire if there is a change in the (batteries, magnetic field in the loop). This phenomenon is called (electromagnetic waves, electromagnetic induction). When a magnet is plunged in and out o ...
... can be produced by (batteries, motion of electric current). More specifically, voltage is induced in a loop of wire if there is a change in the (batteries, magnetic field in the loop). This phenomenon is called (electromagnetic waves, electromagnetic induction). When a magnet is plunged in and out o ...
transformer - Madison County Schools
... alternating current. The other coil - called the secondary coil - is not connected to a source of electricity. ...
... alternating current. The other coil - called the secondary coil - is not connected to a source of electricity. ...
Theory of Heating by Induction
... Heating by Induction INDUCTION HEATING was first noted when it was found that heat was produced in transformer and motor windings, as mentioned in the Chapter “Heat Treating of Metal” in this book. Accordingly, the theory of induction heating was studied so that motors and transformers could be buil ...
... Heating by Induction INDUCTION HEATING was first noted when it was found that heat was produced in transformer and motor windings, as mentioned in the Chapter “Heat Treating of Metal” in this book. Accordingly, the theory of induction heating was studied so that motors and transformers could be buil ...
VOICE OVER FOR TLM for Project 5 - Class CBSE
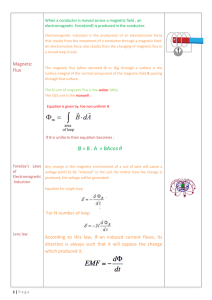
... calculate the magnetic induction ‘dB’ at point P due to one such element of the current-carrying conductor. Then, to obtain the magnetic induction due to all the elements of the conductor, we calculate the sum of the magnetic inductions due to all the elements at point P. ...
... calculate the magnetic induction ‘dB’ at point P due to one such element of the current-carrying conductor. Then, to obtain the magnetic induction due to all the elements of the conductor, we calculate the sum of the magnetic inductions due to all the elements at point P. ...
GENERATORS AND TRANSFORMERS
... 120 degrees from each other. If you were to look at the three phases on a graph, they would look like this relative to ground: ...
... 120 degrees from each other. If you were to look at the three phases on a graph, they would look like this relative to ground: ...