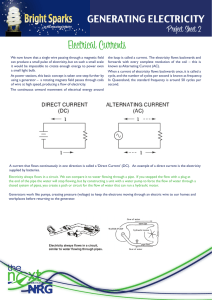
Notes: Magnetism
... Magnets that do not make their own magnetic fields and lose the field when it disappears Ex. Electromagnets Nails & Paper Clips ...
... Magnets that do not make their own magnetic fields and lose the field when it disappears Ex. Electromagnets Nails & Paper Clips ...
Electromagnets and Induction
... Motors that run on AC electricity are easier to make because the current switches direction all by itself. All electric motors must have three parts: 1. Rotor 2. Fixed Magnet 3. Commutator ...
... Motors that run on AC electricity are easier to make because the current switches direction all by itself. All electric motors must have three parts: 1. Rotor 2. Fixed Magnet 3. Commutator ...
Electromagnetic Induction(EMI)
... with magnitude B = 0.60 T, directed into the page. We lay a metal rod with length L = 0.10 m across the two arms of the conductor, forming a conducting loop, and move the rod to the right with constant speed v = 2.5 m/s. What is the magnitude of the resulting emf? ...
... with magnitude B = 0.60 T, directed into the page. We lay a metal rod with length L = 0.10 m across the two arms of the conductor, forming a conducting loop, and move the rod to the right with constant speed v = 2.5 m/s. What is the magnitude of the resulting emf? ...
Exercises
... by simply moving a magnet into or out of a wire coil. a. Einstein and Faraday b. Faraday and Henry c. Henry and Newton d. Maxwell and Newton 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Voltage is induced whether the magnetic field of a magnet moves past a stationary conductor, or the conductor moves ...
... by simply moving a magnet into or out of a wire coil. a. Einstein and Faraday b. Faraday and Henry c. Henry and Newton d. Maxwell and Newton 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Voltage is induced whether the magnetic field of a magnet moves past a stationary conductor, or the conductor moves ...
Physics Gang Signs Review
... • A GENERATOR uses electromagnetic induction, it turns mechanical energy into electrical energy. • As the coil enters the magnetic field, voltage is induced one direction, as the coil leaves the magnet, voltage is induced the other direction. – This produces current that travels one direction in a w ...
... • A GENERATOR uses electromagnetic induction, it turns mechanical energy into electrical energy. • As the coil enters the magnetic field, voltage is induced one direction, as the coil leaves the magnet, voltage is induced the other direction. – This produces current that travels one direction in a w ...