* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download E & M
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
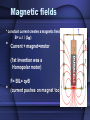
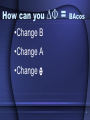
E & M Induction Flux, Induction, Faraday, & Lenz 1 Magnetic fields * constant current creates a magnetic field B= uo I / (2pr) • Current + magnet=motor (1st Invention was a Homopolar motor) • F= BIL= qvB (current pushes on magnet too) 2 EM Induction - Discovery • Symmetry if I B,then B I? • 1831 Faraday discovers the switch ( DB I …. Key is change) I= V/R V= emf = flux change / time • = D (NBA/time) N=#loops Source: Hecht’s Physics w/ Algebra & Trig. 3 EM Induction & B Flux • Magnetic Flux = magnetic field passing to area x that area • M=B A =BA =BAcos Back to Flux Questions 4 Flux • The figure below shows 5 loops in a B field. Rank the magnetic flux (Φ)from largest to smallest. 1. 2=4, 1, 3, 5 2. 1=4, 2=3=5 3. 4, 2, 1, 3, 5 4. 4=2, 1, 5, 3 From Knight’s Physics for Scientists & Engineers Flux Instruction Slide is # 5 5 How can you D = BAcos •Change B •Change A •Change 6 How is induction done? •Move magnet or wire •Change current in wire •Rotate wire or magnet 7 Changing Flux Voltage Call it: voltage,“emf”, or potential = - N(DM)/Dt = V • How Is energy conserved? • Lenz’s Law: Induced EMF must produce current that opposes the change that caused it 8 Lenz law check A bar magnet is positioned below a horizontal loop of wire with its North pole pointing toward the loop. Then the magnet is pulled down, away from the loop. As viewed from above, is the induced current in the loop clockwise or counterclockwise? Answer: The B-field from a bar magnet points out of the North pole. As seen from above, the field through the loop is out (toward the observer). As the magnet is pulled away, the flux is decreasing. To fight the decrease, the induced B-field should add to the original B-field, and also be out (toward the observer). The induced current will be (B), counterclockwise, in order to make an induced B-field out. Answer Induction check A loop of wire lies in the plane of the page. A decreasing magnetic field is directed into the page. The induced current in the loop is: 1.counterclockwise 2.clockwise 3.zero 4.depends upon whether or not B is decreasing at a steady rate Question modified from unknown source Induction Instruction 11 Faraday’s Law • Does the loop of wire have a 1-clockwise, 2counter-clockwise, or 3no current when: 1. The B field strength is increasing. 2. The B field strength is constant. 3. The B field strength is decreasing. 1. 1 2. 3 3. 2 12 From Knight’s Physics for Scientists & Engineers Induction tips • There is always voltage (only current if closed wire or conductive) • Earth’s field can induce in moving things • There is also induced an electric force F= qE where E =V/d (d is length of wire) this is the resistive force you must overcome to start induction, ie. takes work to get energy! 13 Tranformers: 2 ac solenoids • Ac current: already changing B field (B= uIN/L where L= solenoid length • transfers voltage w/o connecting them • New voltage depends on N turns (2x turns, 2x voltage, but ½ current) 14 Transformer You have a transformer with Np=6 primary windings, and Ns=3 secondary windings, as shown. If Vp=120 V AC, what is the current measured by the ammeter "A" in the secondary circuit? A) 120 A B) 60 A C) 240 A D) Nothing is measured because the fuse in the ammeter blows! Answer The fuse in the ammeter blows! The secondary voltage is 60 VAC (it's a step-down transformer). The internal resistance of the ammeter is zero. So the ammeter current is I = V/R = 60 V/(0 ohms) = infinite current. The fuse will blow. (that’s what she said- mitch)