
Chapter 10: The Endocrine System
... produces hormones that control other glands and their secretion of hormones, which in return decrease the amount of hormones the hypothalamus secretes. 29. Discuss the role of the pancreas in the regulation of glucose levels in the blood. Ans: The pancreas secretes insulin, which enables cells to us ...
... produces hormones that control other glands and their secretion of hormones, which in return decrease the amount of hormones the hypothalamus secretes. 29. Discuss the role of the pancreas in the regulation of glucose levels in the blood. Ans: The pancreas secretes insulin, which enables cells to us ...
Chapter 10: The Endocrine System
... produces hormones that control other glands and their secretion of hormones, which in return decrease the amount of hormones the hypothalamus secretes. 29. Discuss the role of the pancreas in the regulation of glucose levels in the blood. Ans: The pancreas secretes insulin, which enables cells to us ...
... produces hormones that control other glands and their secretion of hormones, which in return decrease the amount of hormones the hypothalamus secretes. 29. Discuss the role of the pancreas in the regulation of glucose levels in the blood. Ans: The pancreas secretes insulin, which enables cells to us ...
Ch 10 ES 207 Notes
... o The (neurons in the) hypothalamus releases special stimulating hormones called “releasing hormones”. These releasing hormones stimulate cells in the anterior pituitary to release their hormones. These hormones are going to be in the general circulation/go everywhere in the body. They’re then gonna ...
... o The (neurons in the) hypothalamus releases special stimulating hormones called “releasing hormones”. These releasing hormones stimulate cells in the anterior pituitary to release their hormones. These hormones are going to be in the general circulation/go everywhere in the body. They’re then gonna ...
Endocrine System - HCC Learning Web
... the mechanisms involved, and compare the modes of intercellular communication that occur in the endocrine and nervous systems. Compare the cellular components of the endocrine system with those of other systems, contrast the major structural classes of hormones, and explain the general mechanisms ...
... the mechanisms involved, and compare the modes of intercellular communication that occur in the endocrine and nervous systems. Compare the cellular components of the endocrine system with those of other systems, contrast the major structural classes of hormones, and explain the general mechanisms ...
Physiology_12_Endocrine
... Estrogens in females and testosterone in males suppresses release of GnRH and FSH through negative feedback systems. ...
... Estrogens in females and testosterone in males suppresses release of GnRH and FSH through negative feedback systems. ...
Antidiuretic Hormone
... • Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands • Absorbed into blood vessels and will contact all cells of the body. ...
... • Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands • Absorbed into blood vessels and will contact all cells of the body. ...
Anat3_09_Endocrine_System
... Estrogens in females and testosterone in males suppresses release of GnRH and FSH through negative feedback systems. ...
... Estrogens in females and testosterone in males suppresses release of GnRH and FSH through negative feedback systems. ...
The Pathology of Pituitary
... In general, clinical evidence of excess hormones is rare and tumors usually present with symptoms secondary to the mass effects of the tumor In young women, may present as primary ovarian ...
... In general, clinical evidence of excess hormones is rare and tumors usually present with symptoms secondary to the mass effects of the tumor In young women, may present as primary ovarian ...
What is Endocrine Surgery?
... The thyroid gland is a butterfly shaped gland in the center of the neck. The thyroid gland produces the thyroid hormones T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). These hormones regulate the growth and function of many systems of the body and they set the pace of the metabolism. Hypothyroidism is wh ...
... The thyroid gland is a butterfly shaped gland in the center of the neck. The thyroid gland produces the thyroid hormones T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). These hormones regulate the growth and function of many systems of the body and they set the pace of the metabolism. Hypothyroidism is wh ...
Quick Review of Feedback Systems
... • Source (what organ/cell produces and/or secretes it?) • What is its target cell(s)? • What is the effect on target cells? • What regulates its production/secretion? • What type of chemical structure? • Details of transport/metabolism? • What type of receptor/signal transduction? ...
... • Source (what organ/cell produces and/or secretes it?) • What is its target cell(s)? • What is the effect on target cells? • What regulates its production/secretion? • What type of chemical structure? • Details of transport/metabolism? • What type of receptor/signal transduction? ...
2 Types of neurotransmitters Classical small molecules
... Long-term, genomic effects of N.R. hormones Because the nuclear receptors bind to DNA, their effects are necessarily genomic (e.g. not directly ionotropic or metabotropic) They induce protein synthesis. It can take hours or days before an effect is seen. ...
... Long-term, genomic effects of N.R. hormones Because the nuclear receptors bind to DNA, their effects are necessarily genomic (e.g. not directly ionotropic or metabotropic) They induce protein synthesis. It can take hours or days before an effect is seen. ...
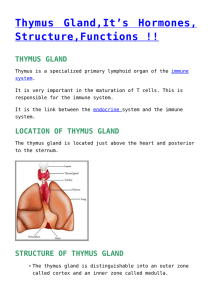
thymus gland - Biology Notes Help
... Thyroid produce thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) with the help of pituitary gland. Thyroid hormones also helpful to brain and muscle development. Thyroid individually produces two main hormones T3 and T4. Thyroid hormones regulate the body glucose metabolism. Increase protein synthesis. Increase ox ...
... Thyroid produce thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) with the help of pituitary gland. Thyroid hormones also helpful to brain and muscle development. Thyroid individually produces two main hormones T3 and T4. Thyroid hormones regulate the body glucose metabolism. Increase protein synthesis. Increase ox ...
Endocrine System
... initiating signal transduction pathways like G protein and phosphorylation cascade (water soluble hormones) ...
... initiating signal transduction pathways like G protein and phosphorylation cascade (water soluble hormones) ...
TSH Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Thyotropin
... It is produced when the hypothalamus releases the tripeptide TRH (thyrotropinreleasing hormone) ...
... It is produced when the hypothalamus releases the tripeptide TRH (thyrotropinreleasing hormone) ...
Biochemistry, Secretion, and Transport of Hormones
... Remember the formation of cortisol is enzymatically driven as it is with all hormones. Steroids are formed on an “as needed” basis and are not stored like TH or some catecholamines. ...
... Remember the formation of cortisol is enzymatically driven as it is with all hormones. Steroids are formed on an “as needed” basis and are not stored like TH or some catecholamines. ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... Remember the formation of cortisol is enzymatically driven as it is with all hormones. Steroids are formed on an “as needed” basis and are not stored like TH or some catecholamines. ...
... Remember the formation of cortisol is enzymatically driven as it is with all hormones. Steroids are formed on an “as needed” basis and are not stored like TH or some catecholamines. ...
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... Hypothalamus: makes hormones that stimulate other glands to release hormones Pituitary: controls growth and water in blood Thyroid: metabolism, energy levels, digestion Thymus: helps white blood cells fight off infection Adrenal Glands: breathe faster, increase blood pressure- heart increases streng ...
... Hypothalamus: makes hormones that stimulate other glands to release hormones Pituitary: controls growth and water in blood Thyroid: metabolism, energy levels, digestion Thymus: helps white blood cells fight off infection Adrenal Glands: breathe faster, increase blood pressure- heart increases streng ...
comp3_unit7_lecture_slides
... Thyroid Diseases • Four main types of disease – Hyperthyroidism – Hypothyroidism – Benign (non-cancerous) thyroid disease – Thyroid cancer • Risk Factors • Symptoms • Treatments – Surgery, radioactive iodine, hormone treatment, radiation therapy or chemotherapy. Some patients receive a combination ...
... Thyroid Diseases • Four main types of disease – Hyperthyroidism – Hypothyroidism – Benign (non-cancerous) thyroid disease – Thyroid cancer • Risk Factors • Symptoms • Treatments – Surgery, radioactive iodine, hormone treatment, radiation therapy or chemotherapy. Some patients receive a combination ...
Slide 1
... Posterior Pituitary • Cells within the posterior lobe of the pituitary do not produce any hormones – Neurons of the hypothalamus manufacture antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT) – They travel down the nerve cells into the posterior pituitary, where they are stored and released ...
... Posterior Pituitary • Cells within the posterior lobe of the pituitary do not produce any hormones – Neurons of the hypothalamus manufacture antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT) – They travel down the nerve cells into the posterior pituitary, where they are stored and released ...
Secretsto Exceptional Health
... overworking, chronic disease, sleep deprivation, guilt, blood sugar fluctuations, toxic exposures, medications and others. Hormones, such as cortisol and Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) secreted by the adrenal glands, are an essential part of the stress response physiology. While the body’s complex ho ...
... overworking, chronic disease, sleep deprivation, guilt, blood sugar fluctuations, toxic exposures, medications and others. Hormones, such as cortisol and Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) secreted by the adrenal glands, are an essential part of the stress response physiology. While the body’s complex ho ...
Endocrine Flashcards
... children) is more serious. It is caused by destruction of pancreatic islets by autoimmune disorders. They must have insulin injections daily throughout life. It is a consequence of obesity. They produce insulin, but their cells are less sensitive to the effects of insulin Diet and exercise Progester ...
... children) is more serious. It is caused by destruction of pancreatic islets by autoimmune disorders. They must have insulin injections daily throughout life. It is a consequence of obesity. They produce insulin, but their cells are less sensitive to the effects of insulin Diet and exercise Progester ...
9 Endocrine Physiology
... iodination. After TSH stimulation, the follicular cells drink it back into the cell, and another enzyme comes along and chops up the long thyroglobulin protein into smaller pieces, each with some iodine on them. • If a segment has two iodines, it is called T2. If there are 3 iodines attached, it is ...
... iodination. After TSH stimulation, the follicular cells drink it back into the cell, and another enzyme comes along and chops up the long thyroglobulin protein into smaller pieces, each with some iodine on them. • If a segment has two iodines, it is called T2. If there are 3 iodines attached, it is ...
[j26] Chapter 11#
... You may recall from anatomy that tissues that secrete hormones are derived from specialized epithelium, known as glandular epithelium. During embryonic growth, glandular epithelium directs the formation of both exocrine (with ducts) and endocrine (without ducts) glands in various regions of the body ...
... You may recall from anatomy that tissues that secrete hormones are derived from specialized epithelium, known as glandular epithelium. During embryonic growth, glandular epithelium directs the formation of both exocrine (with ducts) and endocrine (without ducts) glands in various regions of the body ...



















![[j26] Chapter 11#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015022681_1-426d04e8814a7328aae37c166b315c2a-300x300.png)