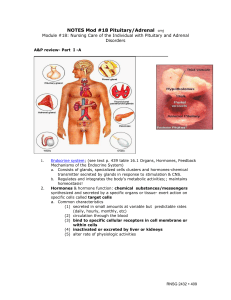
Secretions and Glands Endocrine System Classes of Hormones
... ● Released in response to gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from hypothalamus 1)Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) ● Females: promotes ovarian follicle development and (in concert with LH) stimulates secretion of estrogens ● Males: promotes maturation of sperm ● Inhibited by inhibin (peptide rel ...
... ● Released in response to gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from hypothalamus 1)Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) ● Females: promotes ovarian follicle development and (in concert with LH) stimulates secretion of estrogens ● Males: promotes maturation of sperm ● Inhibited by inhibin (peptide rel ...
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 10: Endocrine System
... then "attaches" itself to the posterior pituitary gland. b. The anterior pituitary gland is indirectly connected to the hypothalamus by means of a venous portal system. By "portal," we mean that the veins carry substances from the capillaries at one point to the capillaries at another point (hypotha ...
... then "attaches" itself to the posterior pituitary gland. b. The anterior pituitary gland is indirectly connected to the hypothalamus by means of a venous portal system. By "portal," we mean that the veins carry substances from the capillaries at one point to the capillaries at another point (hypotha ...
Hormonal response to physical exercise Răspunsul hormonal la
... the case of aerobic exercise; after aerobic exercise, cortisol values remained unchanged; the cessation of anaerobic exercise was followed by an increase of cortisolemia (Balsalobre-Fernandez et al., 2014). In contradiction to the previous study, Kemmler demonstrated in postmenopausal women with ost ...
... the case of aerobic exercise; after aerobic exercise, cortisol values remained unchanged; the cessation of anaerobic exercise was followed by an increase of cortisolemia (Balsalobre-Fernandez et al., 2014). In contradiction to the previous study, Kemmler demonstrated in postmenopausal women with ost ...
Endocrine System
... (target cells) because only the hormone’s target cells have the appropriate receptor to fit it; • Endocrine control slower than nervous system • Endocrine and nervous systems interact i.e. timing of growth and sexual maturation involves a complex sequence of changes in both endocrine and nerve signa ...
... (target cells) because only the hormone’s target cells have the appropriate receptor to fit it; • Endocrine control slower than nervous system • Endocrine and nervous systems interact i.e. timing of growth and sexual maturation involves a complex sequence of changes in both endocrine and nerve signa ...
Notes - Austin Community College
... neurons-extend downward as large bundle behind anterior pituitarylso forms so-called pituitary stalk-appears to suspend anterior gland from hypothalamus. 3) intermediate (pars intermedia) *secretes MSH (melanocytes for skin pigmentation ...
... neurons-extend downward as large bundle behind anterior pituitarylso forms so-called pituitary stalk-appears to suspend anterior gland from hypothalamus. 3) intermediate (pars intermedia) *secretes MSH (melanocytes for skin pigmentation ...
Overivew notes
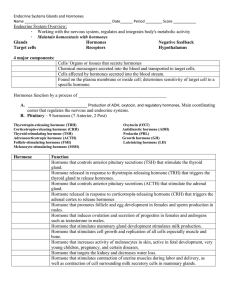
... Found on the plasma membrane or inside cell; determines sensitivity of target cell to a specific hormone. Hormones function by a process of _______________________________________ A. __________________________ Production of ADH, oxytocin, and regulatory hormones, Main coordinating center that regula ...
... Found on the plasma membrane or inside cell; determines sensitivity of target cell to a specific hormone. Hormones function by a process of _______________________________________ A. __________________________ Production of ADH, oxytocin, and regulatory hormones, Main coordinating center that regula ...
Endocrinology - mededcoventry.com
... Secretion is increased by stress,sepsis,trauma, hypoglycemia, beta agonists. Secretion is inhibited by hyperglycemia, somatostatin, insulin, FFA, alpha agonists. Increase plasma levels of fatty acids & glycerol [activates lipase]. ...
... Secretion is increased by stress,sepsis,trauma, hypoglycemia, beta agonists. Secretion is inhibited by hyperglycemia, somatostatin, insulin, FFA, alpha agonists. Increase plasma levels of fatty acids & glycerol [activates lipase]. ...
Endocrinology
... through releasing and/or inhibiting hormones. These hormones either stimulate release of the tropic hormone or inhibit it as part of feedback control. Growth Hormone (GH) and Prolactin (PTH) are not considered tropic hormones proper because they do not stimulate second tier endocrine glands, but rat ...
... through releasing and/or inhibiting hormones. These hormones either stimulate release of the tropic hormone or inhibit it as part of feedback control. Growth Hormone (GH) and Prolactin (PTH) are not considered tropic hormones proper because they do not stimulate second tier endocrine glands, but rat ...
Ch 5 Cell Signaling and the Hormonal Responses to Exercise
... Influences on Growth Hormone Release 1. Stimulates release of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) -IGF-1 in muscle responsible for muscle growth 2. Essential growth of all tissues -Amino Acid uptake and protein synthesis ...
... Influences on Growth Hormone Release 1. Stimulates release of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) -IGF-1 in muscle responsible for muscle growth 2. Essential growth of all tissues -Amino Acid uptake and protein synthesis ...
Sudabeh Moein, M.D. | 4060 4th Ave., Suite 510, San Diego, CA
... The answer is yes to both but that doesn't mean Bio‐identical Hormones are perfect. The great appeal of Bio‐identical Hormones is that they are natural, and our bodies can metabolize them as it was designed to do, minimizing side effects. Synthetic hormones are quite strong and often produce int ...
... The answer is yes to both but that doesn't mean Bio‐identical Hormones are perfect. The great appeal of Bio‐identical Hormones is that they are natural, and our bodies can metabolize them as it was designed to do, minimizing side effects. Synthetic hormones are quite strong and often produce int ...
Synthesis of Steroid Hormones
... ACTH continues to drive steroid biosynthesis adrenal hyperplasia & accumulation of cortisol precursors (depending on which enzyme is lacking) Cannot secrete aldosterone electrolyte disturbances ...
... ACTH continues to drive steroid biosynthesis adrenal hyperplasia & accumulation of cortisol precursors (depending on which enzyme is lacking) Cannot secrete aldosterone electrolyte disturbances ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Stephen G
... ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Introduction 1 What two systems work together to regulate and coordinate the activity of cells? 2 How does the effect of hormones differ from that of the nervous system? 3 What is the difference between exocrine and endocrine glands? Hormones 4. What are hormones? What are the two m ...
... ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Introduction 1 What two systems work together to regulate and coordinate the activity of cells? 2 How does the effect of hormones differ from that of the nervous system? 3 What is the difference between exocrine and endocrine glands? Hormones 4. What are hormones? What are the two m ...
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE OUTLINE COMPARISON of CONTROL by
... B. Histologically, the thyroid consists of the thyroid follicles composed of follicular cells, which secrete the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), and parafollicular cells, which secrete calcitonin (CT) (Figure 18.10). C. Formation, Storage, and Release of Thyroid Hormones ...
... B. Histologically, the thyroid consists of the thyroid follicles composed of follicular cells, which secrete the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), and parafollicular cells, which secrete calcitonin (CT) (Figure 18.10). C. Formation, Storage, and Release of Thyroid Hormones ...
hormones
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
Slide 1
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
Glands - cloudfront.net
... “tell” the pituitary gland either to secrete or to stop secreting its hormones. In this way, the hypothalamus provides a link between the nervous and endocrine systems. The hypothalamus also produces hormones that directly regulate body processes. These hormones travel to the pituitary gland, which ...
... “tell” the pituitary gland either to secrete or to stop secreting its hormones. In this way, the hypothalamus provides a link between the nervous and endocrine systems. The hypothalamus also produces hormones that directly regulate body processes. These hormones travel to the pituitary gland, which ...
Endocrine System
... secretion a. Hormonal stimuli b. Humoral stimuli c. Neural stimuli C. Negative Feedback 1. Endocrine glands tend to over-secrete their hormones so the target organ has enough to function properly 2. When too much function occurs, some factor feeds back to the endocrine gland to cause a negative effe ...
... secretion a. Hormonal stimuli b. Humoral stimuli c. Neural stimuli C. Negative Feedback 1. Endocrine glands tend to over-secrete their hormones so the target organ has enough to function properly 2. When too much function occurs, some factor feeds back to the endocrine gland to cause a negative effe ...
Endocrine System
... complex, because the glands themselves are target organs of a regulatory system called the hypothalamic-pituitary-target gland axis. The major mechanisms in this regulatory system consist of complex interconnecting negative feedback loops that involve the hypothalamus (a structure located at the bas ...
... complex, because the glands themselves are target organs of a regulatory system called the hypothalamic-pituitary-target gland axis. The major mechanisms in this regulatory system consist of complex interconnecting negative feedback loops that involve the hypothalamus (a structure located at the bas ...
Understanding Delayed Puberty in Boys
... Our evaluation of your son’s delayed puberty begins with a discussion about your son’s signs of puberty and a physical exam. If your son has signs of delayed puberty, we will have him get an X-ray of his left hand and wrist called a bone age. A bone age tells us how much his bones have matured. It c ...
... Our evaluation of your son’s delayed puberty begins with a discussion about your son’s signs of puberty and a physical exam. If your son has signs of delayed puberty, we will have him get an X-ray of his left hand and wrist called a bone age. A bone age tells us how much his bones have matured. It c ...
I. General Characteristics of the Endocrine System
... o. Hormones whose actions require cyclic AMP include releasinghormones from the hypothalamus, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, ADH, PTH, norepinephrine, epinephrine, glucagon, and calcitonin. p. An example of another second messenger is DAG. q. In another mechanism, a hormone binding its receptor increases calci ...
... o. Hormones whose actions require cyclic AMP include releasinghormones from the hypothalamus, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, ADH, PTH, norepinephrine, epinephrine, glucagon, and calcitonin. p. An example of another second messenger is DAG. q. In another mechanism, a hormone binding its receptor increases calci ...
Chemical Control of the Animal Body: The Endocrine System
... – Occurs when insulin cannot be secreted or if target cells are unresponsive – Causes circulatory problems that result in heart attacks, blindness, and kidney failure – Human insulin (synthesized by bacteria) is administered when a patient cannot produce their own ...
... – Occurs when insulin cannot be secreted or if target cells are unresponsive – Causes circulatory problems that result in heart attacks, blindness, and kidney failure – Human insulin (synthesized by bacteria) is administered when a patient cannot produce their own ...
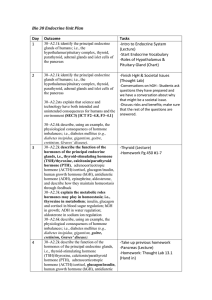
Bio 30 Endocrine Unit Plan Day Outcome Tasks 1 30–A2.1k identify
... 30–A2.6k describe, using an example, the physiological consequences of hormone imbalances; i.e., diabetes mellitus (e.g., diabetes insipidus, gigantism, goitre, cretinism, Graves’ disease). 30–A2.2k describe the function of the -ADH (Lecture) hormones of the principal endocrine glands, -Adrenal Glan ...
... 30–A2.6k describe, using an example, the physiological consequences of hormone imbalances; i.e., diabetes mellitus (e.g., diabetes insipidus, gigantism, goitre, cretinism, Graves’ disease). 30–A2.2k describe the function of the -ADH (Lecture) hormones of the principal endocrine glands, -Adrenal Glan ...