* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Overivew notes
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
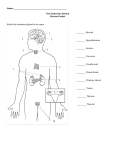
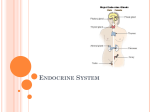
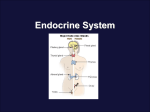
Endocrine Systems Glands and Hormones Name __________________________________________ Date______ Period ________ Score ___________ Endocrine System Overview: • Working with the nervous system, regulates and integrates body's metabolic activity • Maintain homeostasis with hormones Glands Hormones Negative feedback Target cells Receptors Hypothalamus 4 major components: Cells/ Organs or tissues that secrete hormones Chemical messengers secreted into the blood and transported to target cells. Cells affected by hormones secreted into the blood stream. Found on the plasma membrane or inside cell; determines sensitivity of target cell to a specific hormone. Hormones function by a process of _______________________________________ A. __________________________ Production of ADH, oxytocin, and regulatory hormones, Main coordinating center that regulates the nervous and endocrine systems. B. Pituitary – 9 hormones (7 Anterior, 2 Post) Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) Hormone Oxytocin (OXT) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Prolactin (PRL) Growth hormone (GH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Function Hormone that controls anterior pituitary secretions (TSH) that stimulate the thyroid gland. Hormone released in response to thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) that triggers the thyroid gland to release hormones. Hormone that controls anterior pituitary secretions (ACTH) that stimulate the adrenal gland. Hormone released in response to corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) that triggers the adrenal cortex to release hormones Hormone that promotes follicle and egg development in females and sperm production in males. Hormone that induces ovulation and secretion of progestins in females and androgens such as testosterone in males. Hormone that stimulates mammary gland development stimulates milk production. Hormone that stimulates cell growth and replication of all cells especially muscle and bone. Hormone that increases activity of melanocytes in skin, active in fetal development, very young children, pregnancy, and certain diseases. Hormone that targets the kidney and decreases water loss. Hormone that stimulates contraction of uterine muscles during labor and delivery, as well as contraction of cell surrounding milk secretory cells in mammary glands. Endocrine Systems Glands and Hormones Name __________________________________________ Date______ Period ________ Score _______ C. Thyroid and Parathyroid 1. Hormones that adjust tissue metabolic rates 2. Hormones that usually plays a minor role in calcium ion homeostasis by opposing the action of parathyroid hormone Thyroxine (T4) & Triiodothyronine (T3) Hormone Calcitonin Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Function Hormone(s) that increase the rate of ATP production in mitochondria, therefore increasing the rate of metabolism. Hormone(s) that are essential for normal bone growth in children and in the last trimester of pregnancy; stimulated by an increase in the plasma Ca2+, inhibits osteoclasts in bone, and stimulates calcium excretion by kidneys. Hormone(s) stimulated by a decrease in the plasma Ca2+, activates osteoclasts in bone, and reduces calcium excretion by kidneys D. Adrenal gland – metabolic functions Mineralocorticoids Glucocorticoids Androgens Epinephrine (E, or adrenaline) & Norepinephrine (NE, or noradrenaline) Hormones Function Hormone (s) that affects electrolyte balance in body fluids. Hormone (s) that affects glucose metabolism; also an anti-inflammatory Hormone (s) that can be converted to estrogens in plasma; in normal amounts do not affect sexual characteristics. Hormone (s) that trigger metabolic changes to increase availability of energy molecules; supports and prolongs the overall sympathetic response. E. Pineal Gland and Pancreas _________________ Inhibition of reproductive function, antioxidant activity, day/night cycle _________________ Digestive organ whose exocrine cells make digestive enzymes Melatonin Alpha cells Hormone Cell Beta cells Glucagon Insulin Function Hormone that plays a role in maintaining Circadian rhythms (day-night cycles). Hormone released upon a decrease in BGL, resulting in the breakdown of glycogen in liver and muscles into glucose and an increase in BGL. Hormone released upon an increase in BGL, resulting in cell uptake of glucose and a decrease in BGL. Function Cells that secrete glucagon. Cells that secrete insulin. 2 Endocrine Systems Glands and Hormones Name __________________________________________ Date______ Period ________ Score _______ Secondary Endocrine Functions : Calcitrol Erythropoietin Renin Atrial Natriuietic Peptide (ANP) Thymosins Leptin F. Intestines – process and absorb nutrients G. Kidneys – urinary system Hormone Function Hormone stimulated by PTH, derived from Vitamin D3 that increases the absorption of calcium and phosphate. Hormone stimulated by the kidneys that causes an increase in Red Blood Cell production. An enzyme that triggers a hormonal chain reaction to increase Blood Pressure and blood volume. H. Heart, Cardiovascular system Hormone Function Hormone that detects excessive stretching in the right atrium of the heart; causes a loss of sodium and water and a decrease in Blood Pressure an blood volume I. Thymus lymphatic system Hormone Function Hormones that aid in the development and maintenance of immune defenses. J. Adipose Tissue Hormone Function Hormone secreted from Adipose Tissue that provides negative feedback control of appetite; increases fertility K. Gonads - Reproductive system Testes Testosterone Ovaries Estrogen Hormone Progesterone Inhibin Function Male Gonads Hormone that promotes sperm production Female Gonads Hormone that supports maturation of ova and growth of uterine lining Hormone released from corpus luteum that accelerates fertilized egg movement through the uterine tube; prepares for arrival of developing embryo Hormone that provides negative feedback to FSH. 3 Endocrine Systems Glands and Hormones Name __________________________________________ Date______ Period ________ Score _______ 4