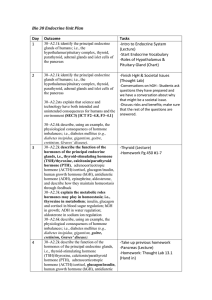
Bio 30 Endocrine Unit Plan Day Outcome Tasks 1 30–A2.1k identify
... 30–A2.6k describe, using an example, the physiological consequences of hormone imbalances; i.e., diabetes mellitus (e.g., diabetes insipidus, gigantism, goitre, cretinism, Graves’ disease). 30–A2.2k describe the function of the -ADH (Lecture) hormones of the principal endocrine glands, -Adrenal Glan ...
... 30–A2.6k describe, using an example, the physiological consequences of hormone imbalances; i.e., diabetes mellitus (e.g., diabetes insipidus, gigantism, goitre, cretinism, Graves’ disease). 30–A2.2k describe the function of the -ADH (Lecture) hormones of the principal endocrine glands, -Adrenal Glan ...
Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology
... Cushing’s syndrome: A relatively rare endocrine disorder resulting from excessive exposure to the hormone cortisol, which leads to a variety of symptoms and physical abnormalities. Diabetes Insipidus: A disorder that causes the patient to produce tremendous quantities of urine. The massively incr ...
... Cushing’s syndrome: A relatively rare endocrine disorder resulting from excessive exposure to the hormone cortisol, which leads to a variety of symptoms and physical abnormalities. Diabetes Insipidus: A disorder that causes the patient to produce tremendous quantities of urine. The massively incr ...
F13_Endocrine1
... Unlike the nervous system with which the endocrine works similarly to and in some cases with, the endocrine system sends messages to cells to perform a necessary action. Hormones are messenger molecules. The endocrines system is comprised of small organs dispersed throughout the body and secrete hor ...
... Unlike the nervous system with which the endocrine works similarly to and in some cases with, the endocrine system sends messages to cells to perform a necessary action. Hormones are messenger molecules. The endocrines system is comprised of small organs dispersed throughout the body and secrete hor ...
I. Introduction and
... o. Hormones whose actions require cyclic AMP include releasinghormones from the hypothalamus, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, ADH, PTH, norepinephrine, epinephrine, glucagon, and calcitonin. p. An example of another second messenger is DAG. q. In another mechanism, a hormone binding its receptor increases calci ...
... o. Hormones whose actions require cyclic AMP include releasinghormones from the hypothalamus, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, ADH, PTH, norepinephrine, epinephrine, glucagon, and calcitonin. p. An example of another second messenger is DAG. q. In another mechanism, a hormone binding its receptor increases calci ...
Unit 7_Endocrine System
... Stimulates follicle development in ovaries (oogenesis) Stimulates sperm development in testes (spermatogenesis) ...
... Stimulates follicle development in ovaries (oogenesis) Stimulates sperm development in testes (spermatogenesis) ...
Endocrine System
... 1. Mainly protein in nature & can be glycoprotein. 2. Most of the receptors are bound to the cell membrane but it can be intracellular receptor. E. g. of intracellular receptor hormone:- Steroid hormone , Thyroid hormone , Vit. D 3. Combine with high affinity with the hormone concentrate the hormo ...
... 1. Mainly protein in nature & can be glycoprotein. 2. Most of the receptors are bound to the cell membrane but it can be intracellular receptor. E. g. of intracellular receptor hormone:- Steroid hormone , Thyroid hormone , Vit. D 3. Combine with high affinity with the hormone concentrate the hormo ...
Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones
... • Four (4) of these ones are called Tropic Hormones as they stimulate the growth, nutrition and function of : • other endocrine glands • TSH : regulates Thyroid gland secretion • ACTH : controls secretion of Adrenal Cortex • FSH : maintains female sex hormones level and follicle growth • LH : regula ...
... • Four (4) of these ones are called Tropic Hormones as they stimulate the growth, nutrition and function of : • other endocrine glands • TSH : regulates Thyroid gland secretion • ACTH : controls secretion of Adrenal Cortex • FSH : maintains female sex hormones level and follicle growth • LH : regula ...
1. Endocrine Glands of the Body
... production. Results in less pituitary LH & FSH. Causes ↓testes growth and ↓ testosterone and estrogen production. In male child – can interfere with development of penis, testes, sperm production, ...
... production. Results in less pituitary LH & FSH. Causes ↓testes growth and ↓ testosterone and estrogen production. In male child – can interfere with development of penis, testes, sperm production, ...
Biochemistry of hormones derived from amino acids and proteins
... 3. Lipid metabolism: GH promotes the release of free fatty acids and glycerol from adipose tissue, increases circulating free fatty acids, causes increased oxidation of free fatty acids in the liver 4. Mineral metabolism: GH promotes a positive calcium, magnesium, and phosphate balance (promotes gro ...
... 3. Lipid metabolism: GH promotes the release of free fatty acids and glycerol from adipose tissue, increases circulating free fatty acids, causes increased oxidation of free fatty acids in the liver 4. Mineral metabolism: GH promotes a positive calcium, magnesium, and phosphate balance (promotes gro ...
Unit 22.2: The Endocrine System
... • The pineal gland is a tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleep-wake cycles and several other processes. • The pancreas is located near the stomach. Its hormones include insulin and glucagon. These two hormones work together to cont ...
... • The pineal gland is a tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleep-wake cycles and several other processes. • The pancreas is located near the stomach. Its hormones include insulin and glucagon. These two hormones work together to cont ...
fill in blank key
... 2. Adrenal cortex 3. Oxytocin 4. Prolactin 5. Adrenal medulla 6. Insulin 7. Estrogen 8. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone 9. Epinephrine 10. Testosterone 1. Cell clusters in pancreas producing insulin 2. Hormone assisting body to deal with stress 3. Hormone stimulating skin pigment 4. Hormone stimulati ...
... 2. Adrenal cortex 3. Oxytocin 4. Prolactin 5. Adrenal medulla 6. Insulin 7. Estrogen 8. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone 9. Epinephrine 10. Testosterone 1. Cell clusters in pancreas producing insulin 2. Hormone assisting body to deal with stress 3. Hormone stimulating skin pigment 4. Hormone stimulati ...
Chapter 11: The Endocrine System (pp
... Chapter 11: The Endocrine System (pp. 276) Overview The endocrine system, like the nervous system, controls body activities to maintain a relatively constant internal environment. The methods used by these two systems are different. This chapter describes the location of the endocrine glands and the ...
... Chapter 11: The Endocrine System (pp. 276) Overview The endocrine system, like the nervous system, controls body activities to maintain a relatively constant internal environment. The methods used by these two systems are different. This chapter describes the location of the endocrine glands and the ...
Chapter 10: Endocrine System
... hypothalamus through the hypothalamicpituitary portal system to the anterior pituitary. The releasing hormone binds to and stimulates cells that secrete ACTH into the general circulation. ...
... hypothalamus through the hypothalamicpituitary portal system to the anterior pituitary. The releasing hormone binds to and stimulates cells that secrete ACTH into the general circulation. ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM: MATCHING EXERCISE
... 2. Adrenal cortex 3. Oxytocin 4. Prolactin 5. Adrenal medulla 6. Insulin 7. Estrogen 8. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone 9. Epinephrine 10. Testosterone ...
... 2. Adrenal cortex 3. Oxytocin 4. Prolactin 5. Adrenal medulla 6. Insulin 7. Estrogen 8. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone 9. Epinephrine 10. Testosterone ...
The Endocrine System
... Aldosterone is a hormone that helps to regulate the sodium and potassium levels in the blood which helps regulate blood pressure and the balance of electrolytes in blood. ...
... Aldosterone is a hormone that helps to regulate the sodium and potassium levels in the blood which helps regulate blood pressure and the balance of electrolytes in blood. ...
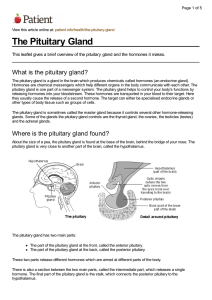
The Pituitary Gland
... Disclaimer: This article is for information only and should not be used for the diagnosis or treatment of medical conditions. EMIS has used all reasonable care in compiling the information but makes no warranty as to its accuracy. Consult a doctor or other healthcare professional for diagnosis and t ...
... Disclaimer: This article is for information only and should not be used for the diagnosis or treatment of medical conditions. EMIS has used all reasonable care in compiling the information but makes no warranty as to its accuracy. Consult a doctor or other healthcare professional for diagnosis and t ...
The Endocrine System
... 2. There are three ways that endocrine glands can be activated: A. Hormonal- activation from other hormones B. Humoral- activation by changing blood levels of certain ions (like calcium) C. Neural- activation by nerve impulses ...
... 2. There are three ways that endocrine glands can be activated: A. Hormonal- activation from other hormones B. Humoral- activation by changing blood levels of certain ions (like calcium) C. Neural- activation by nerve impulses ...
Control and Coordination
... It initiates and maintains the secretion of milk by the mammary glands in mothers. Thus it is necessary for initiation and maintaining lactation. The presence of this hormone in blood reduces the changes of pregnancy so long as mother is feeding her baby. 5. Gonadrotropins /Gonadotrophic hormones As ...
... It initiates and maintains the secretion of milk by the mammary glands in mothers. Thus it is necessary for initiation and maintaining lactation. The presence of this hormone in blood reduces the changes of pregnancy so long as mother is feeding her baby. 5. Gonadrotropins /Gonadotrophic hormones As ...
Hormones-Receptors
... • Steroid Hormones: inactivated in liver where enzymes in the smooth ER convert them to polar derivatives that are filtered but not reabsorbed by the kidney. Testicular Feminization Syndrome: Failure to synthesize a functional androgen receptor testis of an XY individual produces testosterone, but ...
... • Steroid Hormones: inactivated in liver where enzymes in the smooth ER convert them to polar derivatives that are filtered but not reabsorbed by the kidney. Testicular Feminization Syndrome: Failure to synthesize a functional androgen receptor testis of an XY individual produces testosterone, but ...
Chapter 14
... Many organs house clusters of cells that secrete hormones. The kidney, for example, contains scattered cells that secrete erythropoietin, a hormone essential for production of red blood cells. Even the heart contains cells that produce atrial naturetic hormone, which is important in sodium and water ...
... Many organs house clusters of cells that secrete hormones. The kidney, for example, contains scattered cells that secrete erythropoietin, a hormone essential for production of red blood cells. Even the heart contains cells that produce atrial naturetic hormone, which is important in sodium and water ...
Lect E1 - Endocrine intro 1
... • Type II receptors (No HSP association) – Vitamin A receptor (vitamin A) – Vitamin D receptor (vitamin D) – Retinoid receptor – Thyroid hormone receptor ...
... • Type II receptors (No HSP association) – Vitamin A receptor (vitamin A) – Vitamin D receptor (vitamin D) – Retinoid receptor – Thyroid hormone receptor ...
Chapter Summary- Notes
... hormones produced by the adrenal cortex provides an excellent opportunity to examine steroid use from exogenous sources. Persons who abuse anabolic steroids for athletic or appearance purposes are aging body tissues such as the liver at a much faster rate. Males may never again be able to endogenous ...
... hormones produced by the adrenal cortex provides an excellent opportunity to examine steroid use from exogenous sources. Persons who abuse anabolic steroids for athletic or appearance purposes are aging body tissues such as the liver at a much faster rate. Males may never again be able to endogenous ...
The Endocrine System - healingenergies-at
... but can only grow and develop and function properly if there is co-ordinated interaction between these various kinds of cells. One of the ways in which cells communicate with each other is by chemical signals. The chemical signals are carried in the blood stream to the cells which they act upon by m ...
... but can only grow and develop and function properly if there is co-ordinated interaction between these various kinds of cells. One of the ways in which cells communicate with each other is by chemical signals. The chemical signals are carried in the blood stream to the cells which they act upon by m ...