C H A P T E R T W E N T Y
... 2. Peptide hormones are formed from chains of amino acids; an example is growth hormone. Steroid hormones are a type of lipid derived from cholesterol; an example is testosterone. Biogenic amines are small molecules produced by altering the structure of an amino acid; an example is thyroid hormone. ...
... 2. Peptide hormones are formed from chains of amino acids; an example is growth hormone. Steroid hormones are a type of lipid derived from cholesterol; an example is testosterone. Biogenic amines are small molecules produced by altering the structure of an amino acid; an example is thyroid hormone. ...
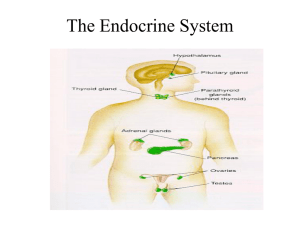
The Endocrine System - St. Ambrose School
... The Endocrine System is made up of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream • Hormones are chemical messengers that target specific cells • The specific cells that are effected by the specific hormones are called target cells • If a cell does not have receptors, or the receptors do not resp ...
... The Endocrine System is made up of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream • Hormones are chemical messengers that target specific cells • The specific cells that are effected by the specific hormones are called target cells • If a cell does not have receptors, or the receptors do not resp ...
chapter twenty
... 2. Peptide hormones are formed from chains of amino acids; an example is growth hormone. Steroid hormones are a type of lipid derived from cholesterol; an example is testosterone. Biogenic amines are small molecules produced by altering the structure of an amino acid; an example is thyroid hormone. ...
... 2. Peptide hormones are formed from chains of amino acids; an example is growth hormone. Steroid hormones are a type of lipid derived from cholesterol; an example is testosterone. Biogenic amines are small molecules produced by altering the structure of an amino acid; an example is thyroid hormone. ...
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 9: THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM I
... Hypothalamus and Pituitary (Fig 6.2 & 6.3) ...
... Hypothalamus and Pituitary (Fig 6.2 & 6.3) ...
Study Guide
... protein) that has been divided into four segments—A, B, C, and D—with an enzyme that cuts up proteins. In the experiment, each segment was physically isolated from the others, and a specific antibody was raised against each segment. The antibodies are identified according to the segment to which eac ...
... protein) that has been divided into four segments—A, B, C, and D—with an enzyme that cuts up proteins. In the experiment, each segment was physically isolated from the others, and a specific antibody was raised against each segment. The antibodies are identified according to the segment to which eac ...
The Endocrine Physiology 2 Inputs that Control
... • Hypothalamus produces Hypophysiotropic hormones that control hormones secreted by anterior pituitary body. 6main hormones secreted by hypothalamus are: o Corticotropin-releasing hormone = CRH stimulates secretion of ACTH o Thyrotropin-releasing hormone = TRH stimulates secretion of Thyroid SH ...
... • Hypothalamus produces Hypophysiotropic hormones that control hormones secreted by anterior pituitary body. 6main hormones secreted by hypothalamus are: o Corticotropin-releasing hormone = CRH stimulates secretion of ACTH o Thyrotropin-releasing hormone = TRH stimulates secretion of Thyroid SH ...
Endocrine system
... • D. The endocrine & nervous systems often work together to maintain homeostasis. • E. The nervous system uses neurotransmitters to act on cells (which is usually short-lived) to maintain homeostasis • F. The endocrine system uses hormones (which effects last longer) to produce homeostasis. ...
... • D. The endocrine & nervous systems often work together to maintain homeostasis. • E. The nervous system uses neurotransmitters to act on cells (which is usually short-lived) to maintain homeostasis • F. The endocrine system uses hormones (which effects last longer) to produce homeostasis. ...
chapter 50 endocrine systems
... Aldosterone and cortisol receptors arose 450 mya by duplication of an ancient cortisol receptor (CR) ...
... Aldosterone and cortisol receptors arose 450 mya by duplication of an ancient cortisol receptor (CR) ...
NVCC Bio 212 - gserianne.com
... Other Endocrine Glands • Adipose Tissue – Leptin • After eating, adipose tissue absorbs glucose and lipids • Peptide hormone, leptin, is released • Binds to receptors in hypothalamus (esp. arcuate and paraventricular nuclei) ...
... Other Endocrine Glands • Adipose Tissue – Leptin • After eating, adipose tissue absorbs glucose and lipids • Peptide hormone, leptin, is released • Binds to receptors in hypothalamus (esp. arcuate and paraventricular nuclei) ...
ANP 201 Dr Smith - University of Agriculture Abeokuta
... cholesterol in the gonads (testes and ovaries) and adrenal cortex of both sexes. They include estrogens, androgens and progesterone. 1. Testosterone (androgen) The androgens of which testosterone is the most prominent are produced mainly by the interstitial cells of the testes. They affect most tiss ...
... cholesterol in the gonads (testes and ovaries) and adrenal cortex of both sexes. They include estrogens, androgens and progesterone. 1. Testosterone (androgen) The androgens of which testosterone is the most prominent are produced mainly by the interstitial cells of the testes. They affect most tiss ...
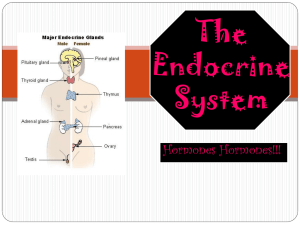
The Endocrine System
... The endocrine system is made up of a network of ductless glands. These glands secrete hormones to regulate many bodily functions, including growth and metabolism. Endocrine diseases are common and usually occur when glands produce an incorrect amount of hormones. Simply put, the endocrine system is ...
... The endocrine system is made up of a network of ductless glands. These glands secrete hormones to regulate many bodily functions, including growth and metabolism. Endocrine diseases are common and usually occur when glands produce an incorrect amount of hormones. Simply put, the endocrine system is ...
Endocrine Physiology
... SS (somatostatin, GH-inhib) CRH (corticotropin-rel) GnRH (gonadotropin-rel) ...
... SS (somatostatin, GH-inhib) CRH (corticotropin-rel) GnRH (gonadotropin-rel) ...
Endocrine_System
... Testosterone • Indirect –Promotes growth hormone responses in the pituitary gland –Causes Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGF) to be released from the liver causing protein synthesis. –Influences the central nervous system by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters and neuromuscular junctions which ...
... Testosterone • Indirect –Promotes growth hormone responses in the pituitary gland –Causes Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGF) to be released from the liver causing protein synthesis. –Influences the central nervous system by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters and neuromuscular junctions which ...
Precocious Puberty in Hydrocephalus
... so called “bone age” on an X ray of the left hand and wrist. Regular growth measurement and physical development should also be documented and compared with normal rates of development. In girls, ultrasound scanning of the ovaries and uterus can also be carried out. When treatment is underway, some ...
... so called “bone age” on an X ray of the left hand and wrist. Regular growth measurement and physical development should also be documented and compared with normal rates of development. In girls, ultrasound scanning of the ovaries and uterus can also be carried out. When treatment is underway, some ...
Lecture 2
... • Glands secrete hormones travel through blood to target cells – Target cells have receptors for binding with specific hormone – Regulates or directs particular function • Two hormone categories based on solubility 1) Hydrophilic • Peptide hormones • Catecholamines (dopamine, epinephrine, norepineph ...
... • Glands secrete hormones travel through blood to target cells – Target cells have receptors for binding with specific hormone – Regulates or directs particular function • Two hormone categories based on solubility 1) Hydrophilic • Peptide hormones • Catecholamines (dopamine, epinephrine, norepineph ...
chapter 39 - section 2
... food. It produces insulin and glucagon. Insulin stimulates cells in the liver and muscles to remove sugar from the blood and store it as glycogen or fat. Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen and release glucose back into the blood. ...
... food. It produces insulin and glucagon. Insulin stimulates cells in the liver and muscles to remove sugar from the blood and store it as glycogen or fat. Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen and release glucose back into the blood. ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... Thyroid Gland (Tetrapods) • Thyroid hormones (TH) – Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) • Increase metabolic rate and body heat production ...
... Thyroid Gland (Tetrapods) • Thyroid hormones (TH) – Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) • Increase metabolic rate and body heat production ...
Saladin, Human Anatomy 3e
... cells and organs. The glands and cells that secrete hormones constitute the endocrine system, and the branch of biology and medicine that deals with them is called endocrinology. 2. The traditional view of an endocrine gland is that it lacks a duct connecting it to an epithelial surface, and secrete ...
... cells and organs. The glands and cells that secrete hormones constitute the endocrine system, and the branch of biology and medicine that deals with them is called endocrinology. 2. The traditional view of an endocrine gland is that it lacks a duct connecting it to an epithelial surface, and secrete ...
Endocrine System Endocrine glands - secrete chemical
... 4. Iodinate tyrosine to make T1 and T2 5. Coupling of T1’s and T2’s to form T3 and T4 6. Pinocytosis and digestion of colloid. Here the colloid is taken back into the follicular cells and digestive enzymes cleave the T3 and T4 from the TGB 7. T3 and T4 are lipid soluble so they diffuse back into the ...
... 4. Iodinate tyrosine to make T1 and T2 5. Coupling of T1’s and T2’s to form T3 and T4 6. Pinocytosis and digestion of colloid. Here the colloid is taken back into the follicular cells and digestive enzymes cleave the T3 and T4 from the TGB 7. T3 and T4 are lipid soluble so they diffuse back into the ...
Dissection of the Brain, Hypothalamus and Pituitary
... Synthesizes and secretes hormones that act on the pituitary (See Hormone Table): Releasing & Inhibiting hormones: small peptides secreted from hypothalamus that control the secretion of protein hormones from the pituitary gland Hormones directly associated with reproduction: GnRH, CRH, PIF, PRF Two ...
... Synthesizes and secretes hormones that act on the pituitary (See Hormone Table): Releasing & Inhibiting hormones: small peptides secreted from hypothalamus that control the secretion of protein hormones from the pituitary gland Hormones directly associated with reproduction: GnRH, CRH, PIF, PRF Two ...
Biology 30 Notes October 3, 2014 Introduction Endocrine System
... Posterior Pituitary – part of the nervous system since it does not produce any of its own hormones. It instead stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. ADH (antidiuretic hormone) and oxytocin. Anterior Pituitary – is a true hormone gland. It produces and releases hGH (human growth ...
... Posterior Pituitary – part of the nervous system since it does not produce any of its own hormones. It instead stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. ADH (antidiuretic hormone) and oxytocin. Anterior Pituitary – is a true hormone gland. It produces and releases hGH (human growth ...
Endocrine System - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... The medical assistant in a local medical office is about to administer an injection of cortisol. The patient asks “Once you inject that steriod in my arm, why won’t it affect my arm and other body parts?” Which of the following would best answer this patient’s question? a. Hormones do not affect any ...
... The medical assistant in a local medical office is about to administer an injection of cortisol. The patient asks “Once you inject that steriod in my arm, why won’t it affect my arm and other body parts?” Which of the following would best answer this patient’s question? a. Hormones do not affect any ...
The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands.
... secretions in the skin or inside the mouth. ...
... secretions in the skin or inside the mouth. ...
Skip to content
... glands that control basic body functions such as metabolism, growth and sexual development. The amount of hormones produced by each gland is carefully balanced. Too much or too little of a certain hormone can have effects throughout the body and cause various endocrine disorders. Many of the hormone ...
... glands that control basic body functions such as metabolism, growth and sexual development. The amount of hormones produced by each gland is carefully balanced. Too much or too little of a certain hormone can have effects throughout the body and cause various endocrine disorders. Many of the hormone ...