“Calm Your Hormones!”
... The Endocrine System A system of “ductless” glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream Chemical “messengers” Distributed throughout body Only affect certain “target” cells If they have the corresponding receptor molecules ...
... The Endocrine System A system of “ductless” glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream Chemical “messengers” Distributed throughout body Only affect certain “target” cells If they have the corresponding receptor molecules ...
Chapter 11 The Endocrine System
... • Examination may reveal low blood pressure (in part because cortisol is needed to permit the full extent of the cardiovascular actions of epinephrine) and low blood sugar, especially after fasting (because of the loss of the normal metabolic actions of cortisol). ...
... • Examination may reveal low blood pressure (in part because cortisol is needed to permit the full extent of the cardiovascular actions of epinephrine) and low blood sugar, especially after fasting (because of the loss of the normal metabolic actions of cortisol). ...
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland
... composed mostly of connective tissue & fat – large in infants & children, size decreases in adulthood – produces: a.) Thymosine b.) Thymopoietin ***Both play a role in the dvlpt & function of the body’s immune system ...
... composed mostly of connective tissue & fat – large in infants & children, size decreases in adulthood – produces: a.) Thymosine b.) Thymopoietin ***Both play a role in the dvlpt & function of the body’s immune system ...
Growth hormone
... biological functions. Prolactin secretion is controlled by an inhibitory dopaminergic path. Hyperprolactinaemia may be caused by drugs (with antidopaminergic actions e.g. metoclopramide), hypothyroidism, or prolactin secreting adenomas. Medical treatment is with bromocriptine, cabergoline, or ...
... biological functions. Prolactin secretion is controlled by an inhibitory dopaminergic path. Hyperprolactinaemia may be caused by drugs (with antidopaminergic actions e.g. metoclopramide), hypothyroidism, or prolactin secreting adenomas. Medical treatment is with bromocriptine, cabergoline, or ...
The Endocrine System
... Ovulation) by bonding to their target cells. Hormones are responsible for long distance communication within the body. ...
... Ovulation) by bonding to their target cells. Hormones are responsible for long distance communication within the body. ...
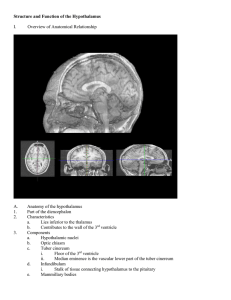
hypothalamus,pituitary
... hormone "to set in motion," Classic definition- hormones are secretory product of the ductless glands, which are released in catalytic amount into blood stream and transported to specific target cells(or organs),where they elicit physiological, morphological and biochemical responses. ...
... hormone "to set in motion," Classic definition- hormones are secretory product of the ductless glands, which are released in catalytic amount into blood stream and transported to specific target cells(or organs),where they elicit physiological, morphological and biochemical responses. ...
Endocrine System - Dr. Diamond`s Website
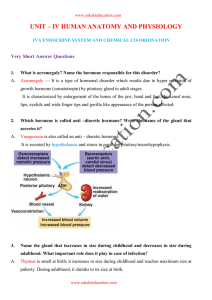
... by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus • Hypothalamus produces two hormones – These hormones are transported to neurosecretory cells of the posterior pituitary • Oxytocin • Antidiuretic hormone (also known as Vasopressin) ...
... by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus • Hypothalamus produces two hormones – These hormones are transported to neurosecretory cells of the posterior pituitary • Oxytocin • Antidiuretic hormone (also known as Vasopressin) ...
DOC
... individual and nutrition, especially early in live, also contribute partially to growth and the individual’s adult size. Gonads The gonads are the sexual glands. The female gonads are the ovaries. The male gonads are the testes. The gonads produce hormones that control sexual development of the indi ...
... individual and nutrition, especially early in live, also contribute partially to growth and the individual’s adult size. Gonads The gonads are the sexual glands. The female gonads are the ovaries. The male gonads are the testes. The gonads produce hormones that control sexual development of the indi ...
Endocrine System: http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/ap1int.htm
... hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products with a release of energy in the process. The thyroid produces two hormones, T3 (called tri-iodothyronine) and T4 (called thyroxine). Thyroid ...
... hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products with a release of energy in the process. The thyroid produces two hormones, T3 (called tri-iodothyronine) and T4 (called thyroxine). Thyroid ...
Endocrine System
... May secrete body chemicals that either stimulate or suppress hormone secretions from the pituitary gland to affect the other glands The primary link between the endocrine and nervous systems. ...
... May secrete body chemicals that either stimulate or suppress hormone secretions from the pituitary gland to affect the other glands The primary link between the endocrine and nervous systems. ...
The Endocrine/Reproductive System
... cross. The pituitary is broken down into two parts, the anterior lobe, which releases hormones when stimulated by the hypothalamus, and the posterior lobe, which stores hormones, produced by the hypothalamus and is released when they are stimulated by the nervous impulses. Hormones controlled by the ...
... cross. The pituitary is broken down into two parts, the anterior lobe, which releases hormones when stimulated by the hypothalamus, and the posterior lobe, which stores hormones, produced by the hypothalamus and is released when they are stimulated by the nervous impulses. Hormones controlled by the ...
Hypothalamus and Visceral Function
... Increases collagen incorporation into extracellular tissue i. Direct effects i. Oppose effects of insulin ii. Increase blood glucose levels Prolactin a. Functions i. Mammary gland growth ii. Lactogenesis b. Elevated during pregnancy and postpartum lactational period i. Estrogen → ↑ PRL release ii. E ...
... Increases collagen incorporation into extracellular tissue i. Direct effects i. Oppose effects of insulin ii. Increase blood glucose levels Prolactin a. Functions i. Mammary gland growth ii. Lactogenesis b. Elevated during pregnancy and postpartum lactational period i. Estrogen → ↑ PRL release ii. E ...
here - Medical Terminology
... 31. Which of the following is the term for a drug that lowers the blood glucose level? A) hypoglycemic B) antihyperglycemic C) hyperglycemic D) hypoglycemic and antihyperglycemic 32. Which of the following hormones affects masculinization? A) oxytocin B) progesterone C) testosterone D) melatonin ...
... 31. Which of the following is the term for a drug that lowers the blood glucose level? A) hypoglycemic B) antihyperglycemic C) hyperglycemic D) hypoglycemic and antihyperglycemic 32. Which of the following hormones affects masculinization? A) oxytocin B) progesterone C) testosterone D) melatonin ...
Endocrine System
... body size, thick tongue and neck – might be a genetic defect of fetal thyroid or a lack of iodine in mother’s diet – Can be prevented by hormone replacement therapy if diagnosed ...
... body size, thick tongue and neck – might be a genetic defect of fetal thyroid or a lack of iodine in mother’s diet – Can be prevented by hormone replacement therapy if diagnosed ...
Specific Endocrine Glands
... same large precursor molecule when stimulated by CRH • b. MSH causes melanocytes to produce more melanin ...
... same large precursor molecule when stimulated by CRH • b. MSH causes melanocytes to produce more melanin ...
presentation source
... • Too much insulin --> hypoglycemia. Since brain can only use glucose for an energy source --> hypoglycemic shock (insulin coma). ...
... • Too much insulin --> hypoglycemia. Since brain can only use glucose for an energy source --> hypoglycemic shock (insulin coma). ...
Physiology is an Integrated Science
... GHRH ; low GH ; exercise inhibited by GHIH = somatostatin PRL prolactin effect: milk production stim PRH ; nursing LH luteinizing hormone effect: ovulation GH ...
... GHRH ; low GH ; exercise inhibited by GHIH = somatostatin PRL prolactin effect: milk production stim PRH ; nursing LH luteinizing hormone effect: ovulation GH ...
Endocrine Review
... c. Stimulates growth of uterine lining for pregnancy 4. Progesterone a. Produced by the ovaries b. Prepares the uterus for embryo implantation c. Helps maintain pregnancy Thymus Gland 1. Located in the chest 2. Large size in children, decreases in size with age 3. Thought to play a role in growth an ...
... c. Stimulates growth of uterine lining for pregnancy 4. Progesterone a. Produced by the ovaries b. Prepares the uterus for embryo implantation c. Helps maintain pregnancy Thymus Gland 1. Located in the chest 2. Large size in children, decreases in size with age 3. Thought to play a role in growth an ...
The Endocrine System
... • Hormones only affect organs and tissues if they have the correct receptor sites. • The receptor will bind with the hormone (like a lock-and-key) • An organ that contains receptors for a particular hormone is called a target organ. ...
... • Hormones only affect organs and tissues if they have the correct receptor sites. • The receptor will bind with the hormone (like a lock-and-key) • An organ that contains receptors for a particular hormone is called a target organ. ...
IVA_ Endocrine_System_Chemical_Co_Ordination
... - Development and maintenance of female reproductive system - Maintenance of menstrual cycle - Development of secondary sexual characters - Estrogen promotes the protein synthesis and calcification and bone growth 2) Progesterone: It is synthesized and secreted by corpus luteum and placenta. Functio ...
... - Development and maintenance of female reproductive system - Maintenance of menstrual cycle - Development of secondary sexual characters - Estrogen promotes the protein synthesis and calcification and bone growth 2) Progesterone: It is synthesized and secreted by corpus luteum and placenta. Functio ...
PowerPoint to accompany
... • usually occurs in late 40s or early 50s • reproductive cycles stop • ovaries no longer produce as much estrogens and progesterone • some female secondary sex characteristics may disappear • may produce hot flashes and fatigue • hormone therapy may prevent effects on bone tissue ...
... • usually occurs in late 40s or early 50s • reproductive cycles stop • ovaries no longer produce as much estrogens and progesterone • some female secondary sex characteristics may disappear • may produce hot flashes and fatigue • hormone therapy may prevent effects on bone tissue ...
Key Endocrine Glands
... Hypersecretion of T3 and T4– causes Grave's disease: thyroid enlargement (goitre), exopthalmos, increased heat production, heat intolerance, increased sweating, and weight loss despite healthy appetite, tremor and ...
... Hypersecretion of T3 and T4– causes Grave's disease: thyroid enlargement (goitre), exopthalmos, increased heat production, heat intolerance, increased sweating, and weight loss despite healthy appetite, tremor and ...
Pituitary Gland Hormones
... it is known as ICSH, interstitial cell stimulating hormone). The interstitial cells that make testosterone are between the seminiferous tubules. Stimulus for release: GnRH from hypothalamus Inhibit: Neg. feedback, hypothalamus dec. release of GnRH as levels of progesterone and testosterone inc. ...
... it is known as ICSH, interstitial cell stimulating hormone). The interstitial cells that make testosterone are between the seminiferous tubules. Stimulus for release: GnRH from hypothalamus Inhibit: Neg. feedback, hypothalamus dec. release of GnRH as levels of progesterone and testosterone inc. ...