atoms - West Ada
... are two isotopes of carbon 12C with a mass of 12.00000 amu(98.892%), and 13C with a mass of 13.00335 amu (1.108%) There are two isotopes of nitrogen , one with an atomic mass of 14.0031 amu and one with a mass of 15.0001 amu. What is the percent abundance of each? ...
... are two isotopes of carbon 12C with a mass of 12.00000 amu(98.892%), and 13C with a mass of 13.00335 amu (1.108%) There are two isotopes of nitrogen , one with an atomic mass of 14.0031 amu and one with a mass of 15.0001 amu. What is the percent abundance of each? ...
Atomic Structure power point
... HAS A VERY LARGE CHARGE IN RELATION TO ITS MASS • IN 1909, ROBERT MILLIKAN, PERFORMED AN INGENIOUS EXPERIMENT TO CALCULATE THE MASS OF AN ELECTRON – HE DISCOVERED THAT THE MASS OF THE ELECTRON IS ABOUT 1/2000TH THE MASS OF THE SIMPLEST ATOM ...
... HAS A VERY LARGE CHARGE IN RELATION TO ITS MASS • IN 1909, ROBERT MILLIKAN, PERFORMED AN INGENIOUS EXPERIMENT TO CALCULATE THE MASS OF AN ELECTRON – HE DISCOVERED THAT THE MASS OF THE ELECTRON IS ABOUT 1/2000TH THE MASS OF THE SIMPLEST ATOM ...
Lesson Objectives Vocabulary Introduction
... smallest atomic radii are found in the upper right; those with the largest atomic radii are found in the lower left. ...
... smallest atomic radii are found in the upper right; those with the largest atomic radii are found in the lower left. ...
Midterm Review Teacher Answer Key December 21, 2011 `see
... Polonium-210 can be created in the laboratory by bombarding bismuth-209 with neutrons to create bismuth210. The bismuth-210 undergoes beta decay to produce polonium-210. Polonium-210 has a halflife of 138 days and undergoes alpha decay. Complete the nuclear equation on the answer sheet or on a separ ...
... Polonium-210 can be created in the laboratory by bombarding bismuth-209 with neutrons to create bismuth210. The bismuth-210 undergoes beta decay to produce polonium-210. Polonium-210 has a halflife of 138 days and undergoes alpha decay. Complete the nuclear equation on the answer sheet or on a separ ...
File
... - affect charge and properties (other than mass) of element - can be gained or lost to form a charged particle (aka an ion) The actual mass of a proton or neutron is on the order of 10-24 g and an electron is about 10-28 g. Relative masses are used to get simpler, more manageable (practical) numbers ...
... - affect charge and properties (other than mass) of element - can be gained or lost to form a charged particle (aka an ion) The actual mass of a proton or neutron is on the order of 10-24 g and an electron is about 10-28 g. Relative masses are used to get simpler, more manageable (practical) numbers ...
Atomic Theory - Portland Public Schools
... An atomic mass unit is sometimes called a Dalton (D). 1.00 g = 6.02214 x 1023 amu. This number is also known as Avogadro’s Number and it defines the size of a quantity we call a mole. ...
... An atomic mass unit is sometimes called a Dalton (D). 1.00 g = 6.02214 x 1023 amu. This number is also known as Avogadro’s Number and it defines the size of a quantity we call a mole. ...
bonding, structure, properties and energy changes
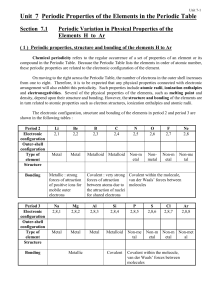
... Important groups of the periodic table These groups and their names are: • Group 1: the alkali metals – the most reactive metals • Group 2: the alkaline earth metals – moderately reactive metals • Group 17: the halogens – the most reactive nonmetals • Group 18: the noble gases – these elements a ...
... Important groups of the periodic table These groups and their names are: • Group 1: the alkali metals – the most reactive metals • Group 2: the alkaline earth metals – moderately reactive metals • Group 17: the halogens – the most reactive nonmetals • Group 18: the noble gases – these elements a ...
Unit 2: Structure of Matter Content Outline: History of the Atomic
... 1. Some of the symbols use the Latin term, instead of the English word like Iron, its symbol is Fe for “Ferrum”. a. Latin is used because it is a “dead” language (will not change over time) and was the original language of science. E. The Periodic Table was created based upon increasing Atomic Numbe ...
... 1. Some of the symbols use the Latin term, instead of the English word like Iron, its symbol is Fe for “Ferrum”. a. Latin is used because it is a “dead” language (will not change over time) and was the original language of science. E. The Periodic Table was created based upon increasing Atomic Numbe ...
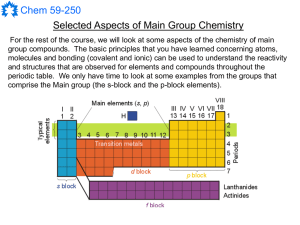
Main Group Notes 1
... up to six bonds. This provides for common oxidation state from -2 to +6 electrons (with a complete octet) around the group 16 atom so such compounds are also “electron-rich” but the high electronegativities of O and S make them good oxidizing agents. ...
... up to six bonds. This provides for common oxidation state from -2 to +6 electrons (with a complete octet) around the group 16 atom so such compounds are also “electron-rich” but the high electronegativities of O and S make them good oxidizing agents. ...
Section 4 bonding packet answers
... Name _____Date _____ Period ____ Ionic Bonding Worksheet For each pair of elements below draw an atomic diagram showing. Bonding Basics - Covalent Bonds Answer Key/Teacher Notes Complete the chart for each element. Follow your teacher’s directions to complete each covalent. All about chemical bondin ...
... Name _____Date _____ Period ____ Ionic Bonding Worksheet For each pair of elements below draw an atomic diagram showing. Bonding Basics - Covalent Bonds Answer Key/Teacher Notes Complete the chart for each element. Follow your teacher’s directions to complete each covalent. All about chemical bondin ...
Unit 05 - Periodicity - Lincoln Park High School
... The relative size of an atom or ion can be determined based on its location in the periodic table. The radius of an atom is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms. Therefore, radius is directly proportional to size. Atomic size generally increases as you move down a group of the peri ...
... The relative size of an atom or ion can be determined based on its location in the periodic table. The radius of an atom is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms. Therefore, radius is directly proportional to size. Atomic size generally increases as you move down a group of the peri ...
Document
... 1. What is the smallest particle something can be divided into? 2. How is an element different from a compound? 3. What does the Atomic Number tell you? 4. What does the Atomic Mass tell you? 5. What are the 3 parts of an atom? ...
... 1. What is the smallest particle something can be divided into? 2. How is an element different from a compound? 3. What does the Atomic Number tell you? 4. What does the Atomic Mass tell you? 5. What are the 3 parts of an atom? ...
CCH 3 Mole Notes
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in number of neutrons and atomic mass KNOW-(Hydrogen has 3 isotopes, protium 11H (1 proton and 0 neutrons), deuterium 21H (1 proton and 1 neutron), tritium 31H (1 proton and 2 neutrons) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed (Not true tod ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in number of neutrons and atomic mass KNOW-(Hydrogen has 3 isotopes, protium 11H (1 proton and 0 neutrons), deuterium 21H (1 proton and 1 neutron), tritium 31H (1 proton and 2 neutrons) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed (Not true tod ...
Atomic Number, Atomic Mass
... The number of protons is the Atomic Number (Z) and defines the element. The Mass Number (A) is the total mass of the atom, i.e. number of protons (Z) + number of neutrons (N) ...
... The number of protons is the Atomic Number (Z) and defines the element. The Mass Number (A) is the total mass of the atom, i.e. number of protons (Z) + number of neutrons (N) ...
Lectures 8-9 - U of L Class Index
... Assigning Electrons to Atomic Orbitals In 1925, Wolfgang Pauli stated the Pauli exclusion principle: Because electrons in the same atomic orbital have the same values for n, l, and ml and because there are only two possible values for ms (____ and ____), each atomic orbital can contain a maximum of ...
... Assigning Electrons to Atomic Orbitals In 1925, Wolfgang Pauli stated the Pauli exclusion principle: Because electrons in the same atomic orbital have the same values for n, l, and ml and because there are only two possible values for ms (____ and ____), each atomic orbital can contain a maximum of ...
Lectures 8-9 - U of L Class Index
... Assigning Electrons to Atomic Orbitals In 1925, Wolfgang Pauli stated the Pauli exclusion principle: Because electrons in the same atomic orbital have the same values for n, l, and ml and because there are only two possible values for ms (____ and ____), each atomic orbital can contain a maximum of ...
... Assigning Electrons to Atomic Orbitals In 1925, Wolfgang Pauli stated the Pauli exclusion principle: Because electrons in the same atomic orbital have the same values for n, l, and ml and because there are only two possible values for ms (____ and ____), each atomic orbital can contain a maximum of ...
Summer Resources - mvhs
... e¯ behave as waves, showing particle-wave nature. EMR which are waves, behave as particles as well as showing dual. 3. How is the location of an electron described? Using quantum numbers. 4. Define atomic orbital according to the quantum mechanical model. >90% probability of finding an e¯ at any tim ...
... e¯ behave as waves, showing particle-wave nature. EMR which are waves, behave as particles as well as showing dual. 3. How is the location of an electron described? Using quantum numbers. 4. Define atomic orbital according to the quantum mechanical model. >90% probability of finding an e¯ at any tim ...
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements - Mifflin County School District
... • isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons • isotopes are identified by their mass numbers protons + neutrons ...
... • isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons • isotopes are identified by their mass numbers protons + neutrons ...
Document
... across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a period, and decreases as you move down a group. ...
... across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a period, and decreases as you move down a group. ...