File - Science With BLT
... d. Metal electrons give off light when excited to a higher energy level. 2. A wooden splint soaked with potassium chloride solution produces a purple color when placed in the flame of a Bunsen burner. The Bunsen burner provides the: a. energy to move electrons in the metal ion to a higher energy lev ...
... d. Metal electrons give off light when excited to a higher energy level. 2. A wooden splint soaked with potassium chloride solution produces a purple color when placed in the flame of a Bunsen burner. The Bunsen burner provides the: a. energy to move electrons in the metal ion to a higher energy lev ...
File - Get Involved!
... Quantum Mechanical Model of Atoms • Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle-Unable to calculate both the momentum and location of an electron in an atom simultaneously • Electrons travel in diffuse clouds or orbitals around the nucleus described by probability distributions • Quantum Numbers are used to d ...
... Quantum Mechanical Model of Atoms • Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle-Unable to calculate both the momentum and location of an electron in an atom simultaneously • Electrons travel in diffuse clouds or orbitals around the nucleus described by probability distributions • Quantum Numbers are used to d ...
chapter-5-periodic-classification-of-elements
... discovered at that time. Mendeléev named them by prefixing a Sanskrit numeral, Eka (one) to the name of preceding element in the same group. It was correct and useful as scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respective ...
... discovered at that time. Mendeléev named them by prefixing a Sanskrit numeral, Eka (one) to the name of preceding element in the same group. It was correct and useful as scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respective ...
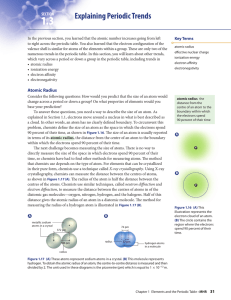
1.3 Explaining Periodic Trends
... To answer these questions, you need a way to describe the size of an atom. As explained in Section 1.1, electrons move around a nucleus in what is best described as a cloud. In other words, an atom has no clearly defined boundary. To circumvent this problem, chemists define the size of an atom as th ...
... To answer these questions, you need a way to describe the size of an atom. As explained in Section 1.1, electrons move around a nucleus in what is best described as a cloud. In other words, an atom has no clearly defined boundary. To circumvent this problem, chemists define the size of an atom as th ...
Section 1 - TeacherWeb
... FIGURE 10Isotopes Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain 6 protons and 6 electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon-12 is the most common isotope. An isotope is identified by its mass number, which is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The most commo ...
... FIGURE 10Isotopes Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain 6 protons and 6 electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon-12 is the most common isotope. An isotope is identified by its mass number, which is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The most commo ...
valence electrons
... (protons and neutrons and electrons) (change of element). • Chemical Reactions involve electrons (bonding) (no change of element). • The opening of the nucleus releases a tremendous amount of energy. • Chemical reactions involve releases of smaller amounts of energy. ...
... (protons and neutrons and electrons) (change of element). • Chemical Reactions involve electrons (bonding) (no change of element). • The opening of the nucleus releases a tremendous amount of energy. • Chemical reactions involve releases of smaller amounts of energy. ...
CHAPTER-3 CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND
... element are called atomic properties. The properties such as atomic radius, ionic radius, ionisation energy, electro-negativity, electron affinity and valence etc., called atomic properties. ATOMIC RADIUS- The distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell of the electrons in the ato ...
... element are called atomic properties. The properties such as atomic radius, ionic radius, ionisation energy, electro-negativity, electron affinity and valence etc., called atomic properties. ATOMIC RADIUS- The distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell of the electrons in the ato ...
Honors Chemistry
... indivisible, spherical particles made up all of matter. He also argued that these particles were rearranged during a chemical reaction. ...
... indivisible, spherical particles made up all of matter. He also argued that these particles were rearranged during a chemical reaction. ...
Honors Chemistry
... indivisible, spherical particles made up all of matter. He also argued that these particles were rearranged during a chemical reaction. ...
... indivisible, spherical particles made up all of matter. He also argued that these particles were rearranged during a chemical reaction. ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide
... a. metalloids c. metals b. liquids d. nonmetals ____ 101. Which subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of an element? a. proton c. neutron b. electron d. none of the above ____ 102. Which of the following elements is a transition metal? a. cesium c. tellurium b. cop ...
... a. metalloids c. metals b. liquids d. nonmetals ____ 101. Which subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of an element? a. proton c. neutron b. electron d. none of the above ____ 102. Which of the following elements is a transition metal? a. cesium c. tellurium b. cop ...
Unit 1 Review, pages 138–145
... As a result, electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus, decreasing atomic radius. Having electrons closer to the nucleus increases the amount of energy needed to remove an electron, the attraction of the atom for additional electrons, and the attraction for bonded electrons. Therefore, ionization e ...
... As a result, electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus, decreasing atomic radius. Having electrons closer to the nucleus increases the amount of energy needed to remove an electron, the attraction of the atom for additional electrons, and the attraction for bonded electrons. Therefore, ionization e ...
MENDELEEV`S PERIODIC TABLE
... table are arranged according to atomic number (the number of protons in an element). This fixed Mendeleev’s problem with some elements not fitting the pattern when arranged by atomic mass. Summary Mendeleev transformed an earlier understanding about the classification of elements into a grand plan ...
... table are arranged according to atomic number (the number of protons in an element). This fixed Mendeleev’s problem with some elements not fitting the pattern when arranged by atomic mass. Summary Mendeleev transformed an earlier understanding about the classification of elements into a grand plan ...
Simple View of Atomic Structure - Chemwiki
... The atomic number is the number of protons (9); the mass number counts protons + neutrons (19). If there are 9 protons, there must be 10 neutrons adding up to a total of 19 nucleons in the atom. The atomic number is tied to the position of the element in the periodic table; the number of protons the ...
... The atomic number is the number of protons (9); the mass number counts protons + neutrons (19). If there are 9 protons, there must be 10 neutrons adding up to a total of 19 nucleons in the atom. The atomic number is tied to the position of the element in the periodic table; the number of protons the ...
mendeleev*s periodic table
... table are arranged according to atomic number (the number of protons in an element). This fixed Mendeleev’s problem with some elements not fitting the pattern when arranged by atomic mass. Summary Mendeleev transformed an earlier understanding about the classification of elements into a grand plan ...
... table are arranged according to atomic number (the number of protons in an element). This fixed Mendeleev’s problem with some elements not fitting the pattern when arranged by atomic mass. Summary Mendeleev transformed an earlier understanding about the classification of elements into a grand plan ...
Study Guide: Elements, Compounds, Mixtures Physical Properties
... Physical Properties: Can be observed or measured without chemically changing a substance. Can be used to identify an unknown substance (some are more useful for this purpose than others, such as: specific heat, density (mass/volume), melting point, boiling point) Are: malleability, solubility, densi ...
... Physical Properties: Can be observed or measured without chemically changing a substance. Can be used to identify an unknown substance (some are more useful for this purpose than others, such as: specific heat, density (mass/volume), melting point, boiling point) Are: malleability, solubility, densi ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
... Law of Multiple Proportions: If two elements (A and B) form more than one compound (AB, AB2, AB3 …) then the ratios of the masses of the second element which combine with a fixed mass of the first element will be the ratio of small whole number - Show how chemical formulas are put together ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions: If two elements (A and B) form more than one compound (AB, AB2, AB3 …) then the ratios of the masses of the second element which combine with a fixed mass of the first element will be the ratio of small whole number - Show how chemical formulas are put together ...
alkali metal
... Atoms of I are larger than those of S M has an atomic number one less than that of A The atomic radius of K is the largest of the group ...
... Atoms of I are larger than those of S M has an atomic number one less than that of A The atomic radius of K is the largest of the group ...
File
... These particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged subatomic particles. Protons cluster with uncharged subatomic particles called neutrons. Protons and neutrons form the central positively charged core, or nucleus, of an atom. Fast-moving, negatively charged electro ...
... These particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged subatomic particles. Protons cluster with uncharged subatomic particles called neutrons. Protons and neutrons form the central positively charged core, or nucleus, of an atom. Fast-moving, negatively charged electro ...
Slajd 1
... Atoms for Democritus had two properties: size and shape. 1. Atoms connect each other in different orders (stoichometry and structural formula?) and create different substances. 2. Atoms are in permanent motion and collide each other (like in Boltzmann’s perfect gas model?), their motion decides abou ...
... Atoms for Democritus had two properties: size and shape. 1. Atoms connect each other in different orders (stoichometry and structural formula?) and create different substances. 2. Atoms are in permanent motion and collide each other (like in Boltzmann’s perfect gas model?), their motion decides abou ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... compact disc players. In a sample of gallium, there is 60.10% of 69Ga (atomic mass 68.926) atoms and 39.90% of 71Ga (atomic mass 70.925) ...
... compact disc players. In a sample of gallium, there is 60.10% of 69Ga (atomic mass 68.926) atoms and 39.90% of 71Ga (atomic mass 70.925) ...
"Part 1" Resource
... (a natural conclusion for him, as he worked to correct the relationships between world globes and maps) allowed the known elements to be placed in unbroken order of increasing weight of their atoms - the periodicity concept - which was then used by Mark Leach's model of the telluric screw Newlands a ...
... (a natural conclusion for him, as he worked to correct the relationships between world globes and maps) allowed the known elements to be placed in unbroken order of increasing weight of their atoms - the periodicity concept - which was then used by Mark Leach's model of the telluric screw Newlands a ...
Chapter 4
... of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. 5) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged. ...
... of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. 5) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged. ...