presentation1-elements-atoms-and-isotopes
... The isotopes of an element are virtually identical in their chemical reactions. This is because they have the same number of protons and the same number of electrons. The uncharged neutrons make little difference to chemical properties but do affect physical properties such as melting point and dens ...
... The isotopes of an element are virtually identical in their chemical reactions. This is because they have the same number of protons and the same number of electrons. The uncharged neutrons make little difference to chemical properties but do affect physical properties such as melting point and dens ...
d) Ramsay. The idea of arranging the elements in the periodic table
... c) test for radioactivity. ...
... c) test for radioactivity. ...
Chapter 8. The Periodic Table
... the periodic recurring resemblances along the horizontal original line of increasing atomic mass. A modern periodic table is given inside the front cover of this book. Unlike Mendeleev’s original table, which had only a few small gaps for undiscovered elements, the modern form has large gaps, which ...
... the periodic recurring resemblances along the horizontal original line of increasing atomic mass. A modern periodic table is given inside the front cover of this book. Unlike Mendeleev’s original table, which had only a few small gaps for undiscovered elements, the modern form has large gaps, which ...
The Atom
... a new unit was developed to mass atoms . C-12 was chosen as the reference standard. An atom of C-12 was arbitrarily assigned a mass of 12 atomic mass units. The masses of all other atoms are compared with the mass of this type of carbon atom. According to this definition, an atomic mass unit is defi ...
... a new unit was developed to mass atoms . C-12 was chosen as the reference standard. An atom of C-12 was arbitrarily assigned a mass of 12 atomic mass units. The masses of all other atoms are compared with the mass of this type of carbon atom. According to this definition, an atomic mass unit is defi ...
Chapter 1 - Atomic Structure
... We have already learned that atoms are composed of three particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. The central nucleus of the atom contains the neutrons and positively charged protons. The nucleus is surrounded by as many orbital electrons (each with a charge of –1) as there are protons (each with ...
... We have already learned that atoms are composed of three particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. The central nucleus of the atom contains the neutrons and positively charged protons. The nucleus is surrounded by as many orbital electrons (each with a charge of –1) as there are protons (each with ...
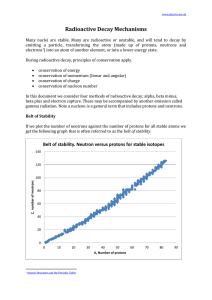
Radioactive Decay Mechanisms
... 2. for smaller atoms the ratio neutrons:protons is 1:1 3. for larger atoms the ratio of neutrons:protons approaches about 1.5:1 Since the strong nuclear force weakens significantly with distance, as the atom gets bigger. If the number protons to neutrons remained in the ratio of 1:1 for larger atoms ...
... 2. for smaller atoms the ratio neutrons:protons is 1:1 3. for larger atoms the ratio of neutrons:protons approaches about 1.5:1 Since the strong nuclear force weakens significantly with distance, as the atom gets bigger. If the number protons to neutrons remained in the ratio of 1:1 for larger atoms ...
Unit C3, C3.1
... The periodic table on the Data Sheet may help you to answer some of these questions. (a) ...
... The periodic table on the Data Sheet may help you to answer some of these questions. (a) ...
Periodic Table and Electrons
... Periodicity is regularly repeating patterns or trends in the chemical and physical properties of the elements arranged in the periodic table. Atomic radius is the measure of the distance between radii of two identical atoms of an element. Atomic radius decreases from left to right and increases from ...
... Periodicity is regularly repeating patterns or trends in the chemical and physical properties of the elements arranged in the periodic table. Atomic radius is the measure of the distance between radii of two identical atoms of an element. Atomic radius decreases from left to right and increases from ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... A. The History of the Periodic Table *1. In 1828, Dobereiner made one of the earliest attempts to “list” the ELEMENTS; proposed the Law of Triads stated there were groups of “3” ELEMENTS where the middle ELEMENT’S atomic MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.0 ...
... A. The History of the Periodic Table *1. In 1828, Dobereiner made one of the earliest attempts to “list” the ELEMENTS; proposed the Law of Triads stated there were groups of “3” ELEMENTS where the middle ELEMENT’S atomic MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.0 ...
Atomic Structure notes
... Atoms of one element can neither be subdivided nor changed into atoms of any other element. ...
... Atoms of one element can neither be subdivided nor changed into atoms of any other element. ...
4.1 PPT- Atomic Theory and Bonding
... • Electrons appear in shells in a very predictable manner. • The period number = the number of shells in the atom. • Except for the transition elements (family 3-12), the last digit of the group number = the number of electrons in the valence shell. ...
... • Electrons appear in shells in a very predictable manner. • The period number = the number of shells in the atom. • Except for the transition elements (family 3-12), the last digit of the group number = the number of electrons in the valence shell. ...
Unit 3: Light and Electrons
... electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.” In other words, no atomic orbital can contain more than two electrons. 2. Hund’s Rule – The most stable arrangement of electrons around an atom is one with the maximum number of unpaired electrons. This minimizes electron-electron ...
... electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.” In other words, no atomic orbital can contain more than two electrons. 2. Hund’s Rule – The most stable arrangement of electrons around an atom is one with the maximum number of unpaired electrons. This minimizes electron-electron ...
Atom Anatomy, Bohr Models and Ions
... Until now, all atoms have been electrically neutral with equal numbers of negatively charged electrons and positively charged protons. However, atoms of an element often have different amounts of electrons. However, they can NOT have different numbers of protons. Protons are unique to a specific ato ...
... Until now, all atoms have been electrically neutral with equal numbers of negatively charged electrons and positively charged protons. However, atoms of an element often have different amounts of electrons. However, they can NOT have different numbers of protons. Protons are unique to a specific ato ...
Unit 3: Light and Electrons
... electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.” In other words, no atomic orbital can contain more than two electrons. 2. Hund’s Rule – The most stable arrangement of electrons around an atom is one with the maximum number of unpaired electrons. This minimizes electron-electron ...
... electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.” In other words, no atomic orbital can contain more than two electrons. 2. Hund’s Rule – The most stable arrangement of electrons around an atom is one with the maximum number of unpaired electrons. This minimizes electron-electron ...
Chapter 2 Worksheet: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... dioxide is always CO2). c. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 4 postulates: all matter is made of atoms (once thought to be indivisible); all atoms of a given elements are identical (atoms of different elements are different); atoms are not created or destroyed in a reaction; atoms combine in small, whole-numbe ...
... dioxide is always CO2). c. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 4 postulates: all matter is made of atoms (once thought to be indivisible); all atoms of a given elements are identical (atoms of different elements are different); atoms are not created or destroyed in a reaction; atoms combine in small, whole-numbe ...
lanthanides - schultz915
... Group 18 is also known as a. Noble gases b. Alkali metals c. Inner-transition metals d. Alkaline earths ...
... Group 18 is also known as a. Noble gases b. Alkali metals c. Inner-transition metals d. Alkaline earths ...
Atoms - Willmar Public Schools
... Like earlier model’s, Bohr’s model was improved as scientists made further discoveries. Bohr was incorrect in assuming that electrons traveled in fixed orbits. Today, scientists know that electrons move in a less predicted way. An electron cloud is a visual model of the most likely locations for ele ...
... Like earlier model’s, Bohr’s model was improved as scientists made further discoveries. Bohr was incorrect in assuming that electrons traveled in fixed orbits. Today, scientists know that electrons move in a less predicted way. An electron cloud is a visual model of the most likely locations for ele ...
Unit 6 – The Atom Vocabulary
... ii) Listed on the periodic table for each element on the bottom left corner. iii) Listed in order of energy levels (1) Example: ...
... ii) Listed on the periodic table for each element on the bottom left corner. iii) Listed in order of energy levels (1) Example: ...
Summer - Honors Chemistry
... In a NEUTRAL ATOM, protons and electrons must be present in equal numbers. However, CHARGED IONS can be formed by losing or gaining electrons. Note that the number of protons never changes when forming ions. If an atom gains electrons, it becomes negative and is called an anion. Nonmetals form anion ...
... In a NEUTRAL ATOM, protons and electrons must be present in equal numbers. However, CHARGED IONS can be formed by losing or gaining electrons. Note that the number of protons never changes when forming ions. If an atom gains electrons, it becomes negative and is called an anion. Nonmetals form anion ...
Medical Chemistry Lecture By : Asst. Lect. Tariq-H-Almgheer
... The number of protons in the nucleus is an important property of an atom. This number determines not only the number of electrons outside the nucleus, but also the atomic number. ...
... The number of protons in the nucleus is an important property of an atom. This number determines not only the number of electrons outside the nucleus, but also the atomic number. ...
Problem Solving Drill - Rapid Learning Center
... needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 2. Electronegativity is one of the most important concepts in chemistry, specifically in the description of bonding. It is defined as the tendency of an atom to attract (or pull) electrons to itself. The higher the ...
... needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 2. Electronegativity is one of the most important concepts in chemistry, specifically in the description of bonding. It is defined as the tendency of an atom to attract (or pull) electrons to itself. The higher the ...
Atoms and electrons
... postulated that the single valence electron of a hydrogen atom revolves around the nuclear proton in only certain allowed circular orbits, and that radiation emitted by the electron, if it moves from one orbit to another, has a frequency proportional to the energy difference of the two orbits. For m ...
... postulated that the single valence electron of a hydrogen atom revolves around the nuclear proton in only certain allowed circular orbits, and that radiation emitted by the electron, if it moves from one orbit to another, has a frequency proportional to the energy difference of the two orbits. For m ...