chapter 2 - atoms and elements
... interest in quantitative experiments. Among them was Robert Boyle, whose quantitative experiments led to the Boyle’s law for ideal gas. Boyle also introduced the concept of elements that is different from the one proposed by the Greek. He defined that a substance may be classified as element if it c ...
... interest in quantitative experiments. Among them was Robert Boyle, whose quantitative experiments led to the Boyle’s law for ideal gas. Boyle also introduced the concept of elements that is different from the one proposed by the Greek. He defined that a substance may be classified as element if it c ...
atomic history 2 - reich
... After having received the doctorate in 1869, Roentgen got a series of charges as teacher in various German universities and in collaboration with Kundt it performed careful studies on the behavior of the subject; for example it was the first one to show, with a thermometer done in house, that is eas ...
... After having received the doctorate in 1869, Roentgen got a series of charges as teacher in various German universities and in collaboration with Kundt it performed careful studies on the behavior of the subject; for example it was the first one to show, with a thermometer done in house, that is eas ...
23.32 KB - KFUPM Resources v3
... B) The size of the hydrogen 1s orbital is defined as the surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability. C) The square of the wave function represents the probability distribution of the elctron in the orbital. D) In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is viewed as a standing wav ...
... B) The size of the hydrogen 1s orbital is defined as the surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability. C) The square of the wave function represents the probability distribution of the elctron in the orbital. D) In the quantum mechanical model, the electron is viewed as a standing wav ...
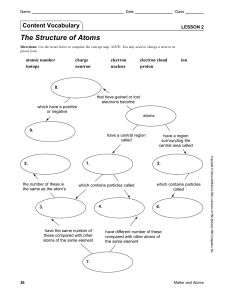
Lesson 2 | The Structure of Atoms
... 4. A negatively charged particle that occupies the space in an atom outside the nucleus is called a(n) electron. a. Electrons are much smaller in size than protons and neutrons, and they move very quickly. b. The region surrounding an atom’s nucleus, where one or more electrons are most likely to be ...
... 4. A negatively charged particle that occupies the space in an atom outside the nucleus is called a(n) electron. a. Electrons are much smaller in size than protons and neutrons, and they move very quickly. b. The region surrounding an atom’s nucleus, where one or more electrons are most likely to be ...
Atomic Structure - Kania´s Science Page
... either gain 4 or lose 4, so it can have a charge of + or – 4 depending on whatever it needs to do. ...
... either gain 4 or lose 4, so it can have a charge of + or – 4 depending on whatever it needs to do. ...
Ionic bonding
... from one atom to another. Usually observed when a metal bonds to a nonmetal. Metals have low ionization energy, making it relatively easy to remove electrons from them Nonmetals have high electron affinities, making it advantageous to add electrons to these atoms The oppositely charged ions are then ...
... from one atom to another. Usually observed when a metal bonds to a nonmetal. Metals have low ionization energy, making it relatively easy to remove electrons from them Nonmetals have high electron affinities, making it advantageous to add electrons to these atoms The oppositely charged ions are then ...
Periodicity of Elements and Periodic Table CHAPTER – 4
... 1. They are mono atomic. 2. They exist in gaseous state. 3. Outer most shell of these elements is either complete or contains eight electrons. 4. These elements are mostly chemically non-reactive. 5. These elements have no tendency to form compounds (only a few of these compounds are known). Atomic ...
... 1. They are mono atomic. 2. They exist in gaseous state. 3. Outer most shell of these elements is either complete or contains eight electrons. 4. These elements are mostly chemically non-reactive. 5. These elements have no tendency to form compounds (only a few of these compounds are known). Atomic ...
Slide 1
... • __________: atoms of the same element that have _______________ due to different numbers of __________. • _____________: the total number of _______ and _________ that make up the nucleus of an isotope ~ Isotopes are written with the _____________ written after the element name or symbol with a __ ...
... • __________: atoms of the same element that have _______________ due to different numbers of __________. • _____________: the total number of _______ and _________ that make up the nucleus of an isotope ~ Isotopes are written with the _____________ written after the element name or symbol with a __ ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... Lithium-6 and lithium-7 are the only two stable isotopes of lithium. [4 marks] Predict the likely modes of decay for isotopes of lithium that are heavier than the stable isotopes. Briefly explain your reasoning. β– decay [2 marks] Heavier isotopes of an element have more neutrons than the stable iso ...
... Lithium-6 and lithium-7 are the only two stable isotopes of lithium. [4 marks] Predict the likely modes of decay for isotopes of lithium that are heavier than the stable isotopes. Briefly explain your reasoning. β– decay [2 marks] Heavier isotopes of an element have more neutrons than the stable iso ...
Chapter 2
... physicists were using an atomic mass unit defined as equal to one sixteenth of the mass of the oxygen-16 atom (the isotope of oxygen containing 8 protons and 8 neutrons). Thus the two amu scales were inconsistent: for chemists, 1 u was one-sixteenth of the average mass of the oxygen atoms in the che ...
... physicists were using an atomic mass unit defined as equal to one sixteenth of the mass of the oxygen-16 atom (the isotope of oxygen containing 8 protons and 8 neutrons). Thus the two amu scales were inconsistent: for chemists, 1 u was one-sixteenth of the average mass of the oxygen atoms in the che ...
Chapter 03 - La Salle University
... orbital, and 6 in three 2p orbitals. ► The third shell can hold 18 electrons, 2 in a 3s orbital, 6 in three 3p orbitals, and 10 in five 3d orbitals, and so on. Prentice Hall © 2007 ...
... orbital, and 6 in three 2p orbitals. ► The third shell can hold 18 electrons, 2 in a 3s orbital, 6 in three 3p orbitals, and 10 in five 3d orbitals, and so on. Prentice Hall © 2007 ...
7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... A billiard ball is an imperfect model for an atom. The ball has a definite “hard” boundary, while an atom has no definite edge and can be reshaped by interactions with other atoms. That said, the billiard ball is a more appropriate analogy for the nonbonding radius of a fluorine atom. The ball’s rad ...
... A billiard ball is an imperfect model for an atom. The ball has a definite “hard” boundary, while an atom has no definite edge and can be reshaped by interactions with other atoms. That said, the billiard ball is a more appropriate analogy for the nonbonding radius of a fluorine atom. The ball’s rad ...
1.1 - cloudfront.net
... If we were to place a sample of carbon into a mass spectrometer and analyze its mass, we would find that some of the carbon atoms have a relative mass of 12, while other atoms have a relative mass of 13, and still others have a relative mass of 14. The mass spectrometer measures the percent abundanc ...
... If we were to place a sample of carbon into a mass spectrometer and analyze its mass, we would find that some of the carbon atoms have a relative mass of 12, while other atoms have a relative mass of 13, and still others have a relative mass of 14. The mass spectrometer measures the percent abundanc ...
Atomic
... in order of atomic (proton) number and so that elements with similar properties are in columns, known as groups. The table is called a periodic table because similar properties occur at regular intervals. Elements in the same group in the periodic table have the same number of electrons in their out ...
... in order of atomic (proton) number and so that elements with similar properties are in columns, known as groups. The table is called a periodic table because similar properties occur at regular intervals. Elements in the same group in the periodic table have the same number of electrons in their out ...
Chapter 5
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
10/2/2013 1 5 Early Atomic Theory and Structure Chapter Outline
... Dalton’s theory of atoms, proposed in the early 1800s, states: 1. Elements are composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in mass and size. 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or ...
... Dalton’s theory of atoms, proposed in the early 1800s, states: 1. Elements are composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in mass and size. 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or ...
Atomic Structure - Renton School District
... until you reach a particle that can not be divided any further and still retains the properties of gold– the atom! ...
... until you reach a particle that can not be divided any further and still retains the properties of gold– the atom! ...
Practice Packet Level 3: Atomics - Mr. Palermo`s Flipped Chemistry
... field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in which ...
... field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in which ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions - Moodle @ FCT-UNL
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Instructor`s Guide
... • All living things contain the radioactive isotope carbon-14 — and even human beings undergo radioactive decay! • Over 99.9% of an atom’s mass is concentrated in its nucleus. • Over 50 trillion neutrinos, created by nuclear reactions in the sun, pass harmlessly through our bodies every second. ...
... • All living things contain the radioactive isotope carbon-14 — and even human beings undergo radioactive decay! • Over 99.9% of an atom’s mass is concentrated in its nucleus. • Over 50 trillion neutrinos, created by nuclear reactions in the sun, pass harmlessly through our bodies every second. ...
History of the Atom Reading
... slightly deflected. But to their amazement, some of the alpha particles were greatly deflected, and some even bounced back, as shown in Figure 1-2B. From this experiment, Rutherford concluded that atoms have a dense central core, called a nucleus, while the remainder of the atom is essentially empty ...
... slightly deflected. But to their amazement, some of the alpha particles were greatly deflected, and some even bounced back, as shown in Figure 1-2B. From this experiment, Rutherford concluded that atoms have a dense central core, called a nucleus, while the remainder of the atom is essentially empty ...
Bonding Web Practice Trupia - Trupia
... (2) Chlorine molecules have strong covalent ____25. When phosphorus and chlorine atoms bonds. combine to form a molecule of PCl3, 6 electrons (3) Chlorine molecules have weak will form intermolecular forces of attraction. (1) nonpolar covalent bonds ...
... (2) Chlorine molecules have strong covalent ____25. When phosphorus and chlorine atoms bonds. combine to form a molecule of PCl3, 6 electrons (3) Chlorine molecules have weak will form intermolecular forces of attraction. (1) nonpolar covalent bonds ...