Problems - El Camino College
... c) The mass or an electron 1s about the same as the mass ofa proton. d) There are subatom ic particles in addition to the electron, proton. and neutron. e) The mass of an atom i~ uniformly distributed throughout the atom. f) Most of the particles fucd i11to the gold foi l in the Rutherford experimen ...
... c) The mass or an electron 1s about the same as the mass ofa proton. d) There are subatom ic particles in addition to the electron, proton. and neutron. e) The mass of an atom i~ uniformly distributed throughout the atom. f) Most of the particles fucd i11to the gold foi l in the Rutherford experimen ...
History of the Atom Reading
... slightly deflected. But to their amazement, some of the alpha particles were greatly deflected, and some even bounced back, as shown in Figure 1-2B. From this experiment, Rutherford concluded that atoms have a dense central core, called a nucleus, while the remainder of the atom is essentially empty ...
... slightly deflected. But to their amazement, some of the alpha particles were greatly deflected, and some even bounced back, as shown in Figure 1-2B. From this experiment, Rutherford concluded that atoms have a dense central core, called a nucleus, while the remainder of the atom is essentially empty ...
NYS Regents Chemistry
... a) Make observations. An observation can lead to a question. b) Hypothesis – An educated guess based on observed facts. A hypothesis can be revised based upon experimental data. c) Controlled Experiments – All factors or variables are held constant while only one variable is changed at a time in ord ...
... a) Make observations. An observation can lead to a question. b) Hypothesis – An educated guess based on observed facts. A hypothesis can be revised based upon experimental data. c) Controlled Experiments – All factors or variables are held constant while only one variable is changed at a time in ord ...
Chapter 4 Review Answers
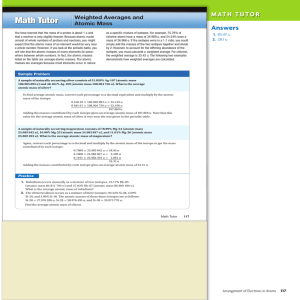
... A sample of naturally occurring silver consists of 51.839% Ag-107 (atomic mass 106.905 093 u) and 48.161% Ag-109 (atomic mass 108.904 756 u). What is the average atomic mass of silver? To find average atomic mass, convert each percentage to a decimal equivalent and multiply by the atomic mass of the ...
... A sample of naturally occurring silver consists of 51.839% Ag-107 (atomic mass 106.905 093 u) and 48.161% Ag-109 (atomic mass 108.904 756 u). What is the average atomic mass of silver? To find average atomic mass, convert each percentage to a decimal equivalent and multiply by the atomic mass of the ...
Chapter 3
... Using Aufbau principle or periodic table a. Potassium: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s1 b. Phosphorus: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p3 Problem: Examine the electron configurations below, and name the element. 1s2 2s2 1s2 2s2 2p3 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 Answer: Going through the periodic table. 1s2 2s2 (He) 1s2 2s2 ...
... Using Aufbau principle or periodic table a. Potassium: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s1 b. Phosphorus: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p3 Problem: Examine the electron configurations below, and name the element. 1s2 2s2 1s2 2s2 2p3 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 Answer: Going through the periodic table. 1s2 2s2 (He) 1s2 2s2 ...
unit 3 ppt
... halogens is based on the presence of seven electrons in their outer energy levels—one electron short of the stable noble-gas configuration. (8 valence e- is called an “octet”) ...
... halogens is based on the presence of seven electrons in their outer energy levels—one electron short of the stable noble-gas configuration. (8 valence e- is called an “octet”) ...
atom
... • A substance that is mixed together without chemically bonding is called a mixture. – Example: Air (a mixture of several gases) © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • A substance that is mixed together without chemically bonding is called a mixture. – Example: Air (a mixture of several gases) © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Notes
... Draw a nucleus with the element symbol inside. Carbon is in the 2nd period, so it has two energy levels, or shells. ...
... Draw a nucleus with the element symbol inside. Carbon is in the 2nd period, so it has two energy levels, or shells. ...
Biol 1020 Ch. 2 Chemistry
... there are 92 naturally occurring elements, from hydrogen up to uranium http://serc.carleton.edu/images/usingdata/nasaimages/periodic-table.gif ...
... there are 92 naturally occurring elements, from hydrogen up to uranium http://serc.carleton.edu/images/usingdata/nasaimages/periodic-table.gif ...
CH 2 development of atomic theory
... Describe Thomson’s e/m experiment, Millikan’s oil drop experiment, and Rutherford’s gold foil experiment. Explain the significance of each experiment. Thomson made a cathode ray tube with a fluorescent screen so that he could observe the ray. In the experiment, he adjusted the magnetic and electric ...
... Describe Thomson’s e/m experiment, Millikan’s oil drop experiment, and Rutherford’s gold foil experiment. Explain the significance of each experiment. Thomson made a cathode ray tube with a fluorescent screen so that he could observe the ray. In the experiment, he adjusted the magnetic and electric ...
Activity 4 Are Atoms Indivisible?
... particles as they passed through sheets of gold foil, Rutherford and his student Hans Geiger noticed that some particles were scattered through larger angles than predicted by the existing theory of atomic structure. Fascinated, Rutherford asked Geiger’s research student Ernest Marsden to search for ...
... particles as they passed through sheets of gold foil, Rutherford and his student Hans Geiger noticed that some particles were scattered through larger angles than predicted by the existing theory of atomic structure. Fascinated, Rutherford asked Geiger’s research student Ernest Marsden to search for ...
Atomic Structure - The Student Room
... increases across a period. Electron Shielding – more inner electron shells shield the nuclear charge from the outer electron, so the electron is easier to remove. Shielding increases down a group. Atomic Radius – in larger atoms, the outer electrons are further from the nucleus due to the number of ...
... increases across a period. Electron Shielding – more inner electron shells shield the nuclear charge from the outer electron, so the electron is easier to remove. Shielding increases down a group. Atomic Radius – in larger atoms, the outer electrons are further from the nucleus due to the number of ...
Atom Models - Learn District 196
... by talking about the constant division of an object until the object could no longer be divided. The idea of the Atom had to wait for 2200 years to be proven. ...
... by talking about the constant division of an object until the object could no longer be divided. The idea of the Atom had to wait for 2200 years to be proven. ...
of atoms. - Digital Chalkboard
... 2. Make models of other atoms. You will need more than two shells for larger atoms. 3. Use other materials to make models of atoms. 4. Study the periodic tabie. Look at how the number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom deter mines what family it is in. ...
... 2. Make models of other atoms. You will need more than two shells for larger atoms. 3. Use other materials to make models of atoms. 4. Study the periodic tabie. Look at how the number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom deter mines what family it is in. ...
Chem BIG REVIEW - Jones-wiki
... 4. Which best describes the relationship between subatomic particles in any neutral atom? A. The number of protons equals the number of electrons. B. The number of protons equals the number of neutrons. C. The number of neutrons equals the number of electrons. D. The number of neutrons is greater th ...
... 4. Which best describes the relationship between subatomic particles in any neutral atom? A. The number of protons equals the number of electrons. B. The number of protons equals the number of neutrons. C. The number of neutrons equals the number of electrons. D. The number of neutrons is greater th ...
Unit 1 Safety and Science
... So how many neutrons does Krypton have? Simply round up the mass to the nearest whole number and subtract the atomic number. In effect, (total mass) – (number of protons) = (number of neutrons) So Krypton has 84 – 36 = 48 neutrons. What is an isotope? All atoms of the same element have equal number ...
... So how many neutrons does Krypton have? Simply round up the mass to the nearest whole number and subtract the atomic number. In effect, (total mass) – (number of protons) = (number of neutrons) So Krypton has 84 – 36 = 48 neutrons. What is an isotope? All atoms of the same element have equal number ...
Document
... Any given element can have more than one isotope. To distinguish between the different isotopes of an atom, the element is named with its mass number, for example, lithium-7. Remember that the mass number is the number of protons and neutrons added together. When symbols are used to represent an iso ...
... Any given element can have more than one isotope. To distinguish between the different isotopes of an atom, the element is named with its mass number, for example, lithium-7. Remember that the mass number is the number of protons and neutrons added together. When symbols are used to represent an iso ...
Name: _ Date: Period: ______ Page: ______ Atomic Structure and
... heavy central core called the nucleus, and very far away from the nucleus were the rapidly swirling electrons. The atom was largely empty space, which explained how the alpha particles were able to get through the gold foil. The small, heavy nucleus with a positive charge caused the deflection of so ...
... heavy central core called the nucleus, and very far away from the nucleus were the rapidly swirling electrons. The atom was largely empty space, which explained how the alpha particles were able to get through the gold foil. The small, heavy nucleus with a positive charge caused the deflection of so ...
topic 3: periodicity
... dip from N to O: oxygen fourth 2p electron goes into the first 2p orbital on which there is already an electron with opposite spin; the resulting repulsion between these two electrons - which is minimised because of their opposite spin - makes it easier to remove that electron. ...
... dip from N to O: oxygen fourth 2p electron goes into the first 2p orbital on which there is already an electron with opposite spin; the resulting repulsion between these two electrons - which is minimised because of their opposite spin - makes it easier to remove that electron. ...
Chapter 7 The Development of the Periodic Table
... based on similar chemical properties. – The term period suggests that the elements show regular patterns in their chemical properties ...
... based on similar chemical properties. – The term period suggests that the elements show regular patterns in their chemical properties ...